Configuring the egress queues, Egress queues and qos markers, Egress queue commands hierarchy – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 993
Quality of Service (QoS) Introduction
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
C613-50046-01 REV A
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
38.21
Configuring the Egress Queues
Previous sections have explained the ingress functions. These include how the incoming
data can be classified and marked according to its priority and allocated to an egress
queue, then finally how metering and remarking is applied. At this point the data then
flows across the switch to its destination egress port where its transit to the egress queues
is controlled.
The means by which data is applied to the egress queues is dependent on three functions:
■
Egress queue and QoS markers that are set within each data packet
■
Egress controls that are applied to the whole switch
■
Egress controls that are applied to each individual switch port
Egress Queues and QoS markers
Once the data packets have been appropriately filtered, classified, policed, and remarked,
they travel across the switch’s internal paths carrying their assigned QoS tag markers such
as their priority, class and destination queues. For more details on ingress data marking,
refer to the earlier sections of this chapter. At the egress port these markers are read and
used to determine which queues each data packet will be forwarded to, and the priorities
that will be applied.
There are eight egress queues allocated to each egress port. The egress queue that a
particular packet passes through is determined by either the configuration of the switch,
or by the markers contained within the packet itself.
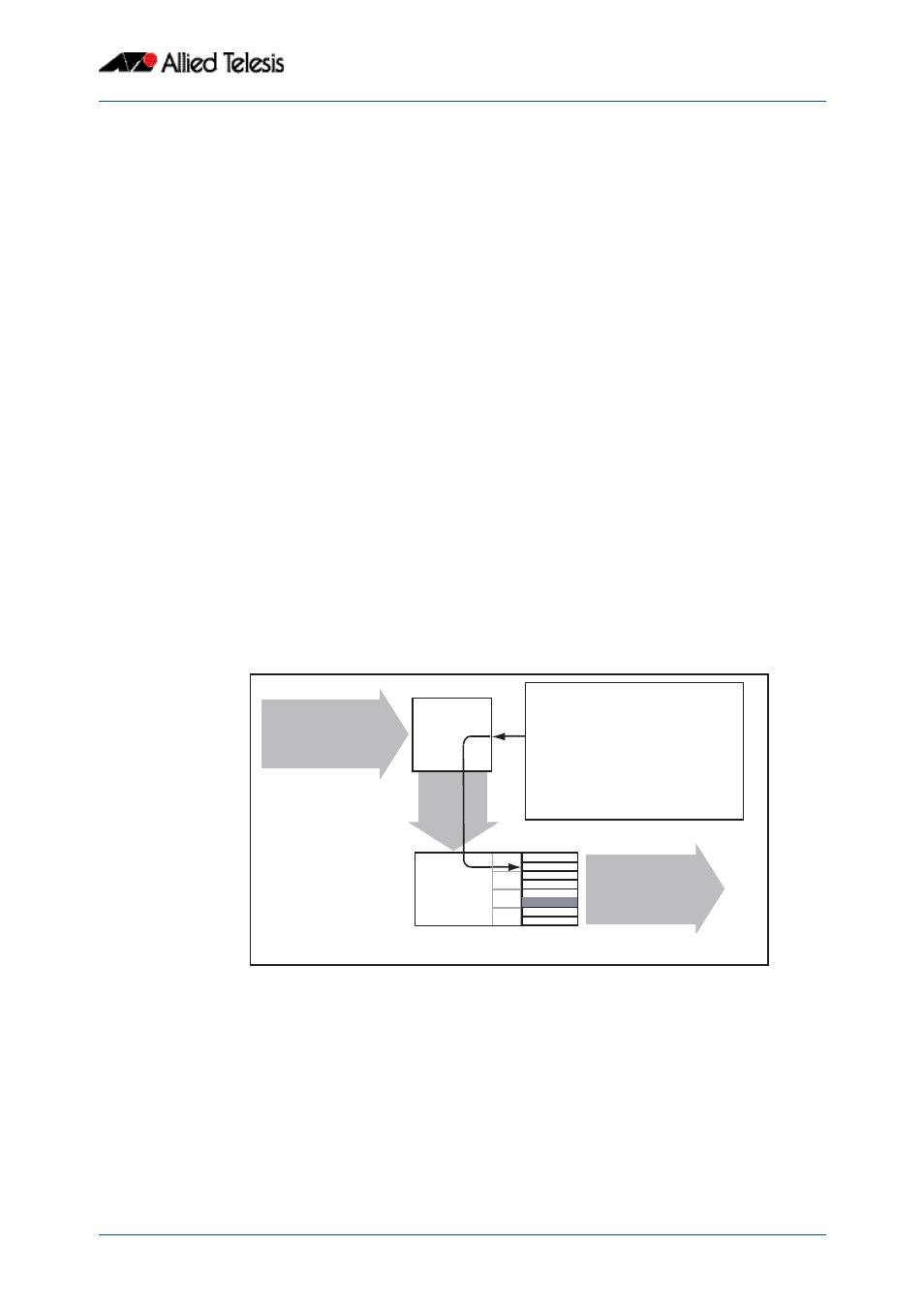
Figure 38-9: Default Egress Queue
Egress Queue Commands Hierarchy
The destination queue that any one packet will take depends on the markers within the
packet, and the way the queueing commands have been set. Also, some queueing
commands will override others. Here is how the switch prioritizes its queueing commands.
Imagine a packet entering an ingress port then traveling through the switch fabric to
reach its appropriate egress port. In this situation the following hierarchy will apply:
QoS_EgressDefaultQueue
Incoming Data
mls qos queue <0-7>
This command is applied to an ingress port
and - in the absence of other tagging - will
apply the egress queue tag selected by this
command. This example shows the
mls qos queue command set to 6.
If this command is not set, then unmarked
packets arriving at an egress port will be
sent to queue 2.
Ingress
port
Egress Queues
fabric queues
default queue
Outgoing Data
Egress
port
Q6
