Configuring a virtual link – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 1553
AMF Introduction and Configuration
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
C613-50046-01 REV A
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
59.9
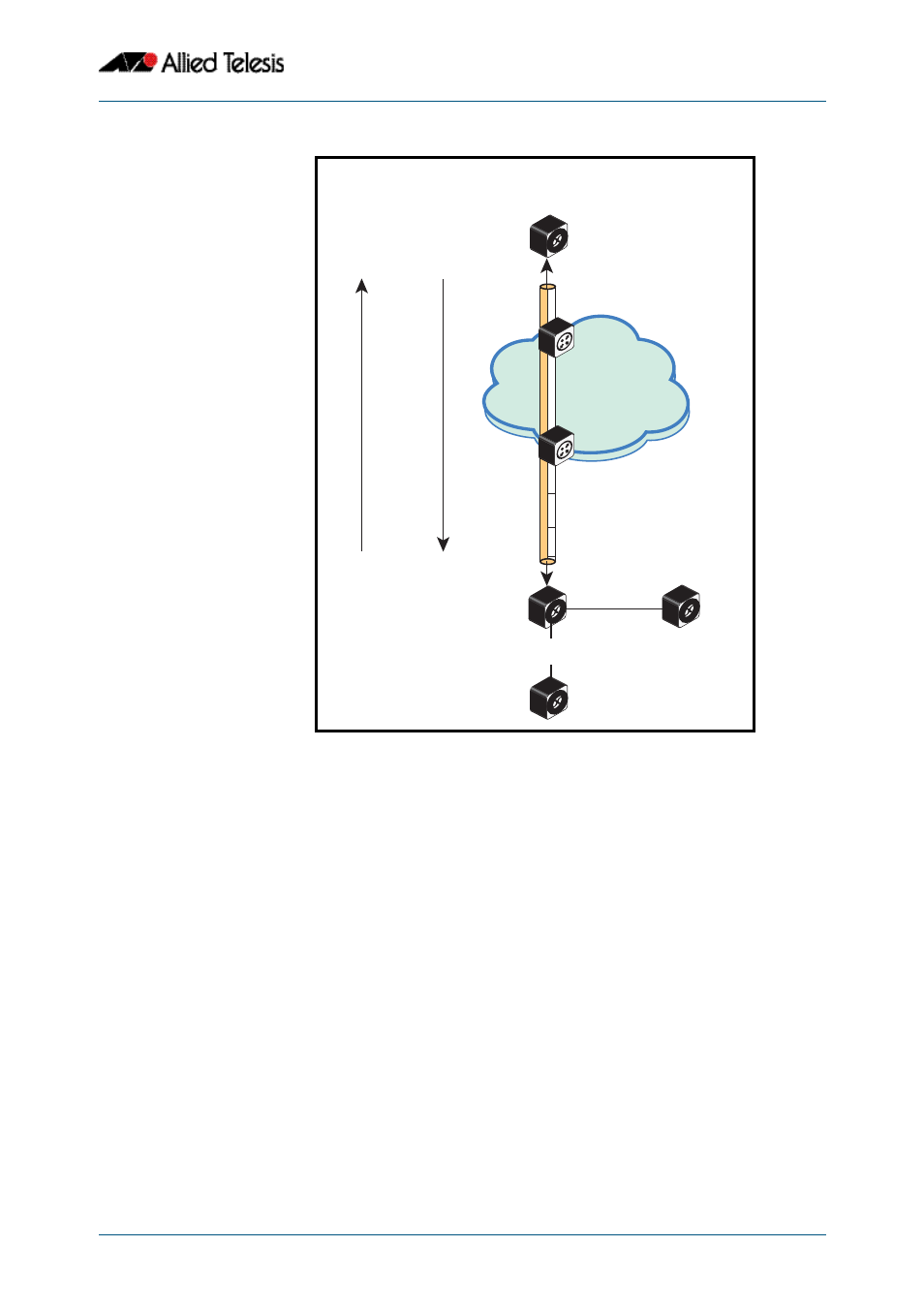
Figure 59-4: AMF Virtual Link
Configuring a Virtual Link
The Layer two tunnel that this command creates enables a local AMF session to appear to
pass transparently across a Wide Area Network (WAN) such as the Internet. The addresses
configured as the local and remote tunnel IP addresses must have IP connectivity to each
other. If the tunnel is configured to connect a head office and branch office over the
Internet, typically this would involve using some type of managed WAN service such as a
site-to-site VPN. Tunnels are only supported using IPv4.
Configuration involves creating the following:
■
local tunnel ID
■
local IP address
■
remote tunnel ID
■
remote IP address
A reciprocal configuration is also required on the corresponding remote device. The local
tunnel ID must be unique to the device on which it is configured.
The tunneled link may operate via external (non AlliedWare Plus) routers in order to
provide wide area network connectivity. However in this configuration, these devices
perform a conventional router to router connection. The protocol tunneling function is
accomplished by the AMF nodes.
UDP Header
IP Header
IP
Network
AMF Local Site (subnet 192.168.1.0)
AMF Local Site (subnet 192.168.2.0)
ATMF virtual-link ID and IP (Example1B).eps
amf virtual-link id ip remote-id remote-ip (Example)
Switch 1
AMF Node 10
Router 1
Router 2
192.168.1.1
Tunnel ID = 1
Tunnel remote ID = 2
192.168.2.1
Tunnel ID = 2
Tunnel remote ID = 1
Switch 2
AMF Node 20
192.168.1.1
Tu
nneled P
acket - AMF Up/Do
wn Link
AMF Up/Downlink
(Layer 2 connectivity)
AMF Crosslink
(Layer 2 connectivity)
192.168.2.1
192.168.2.1
192.168.1.1
