Configure dhcpv6 relay / client, Stateful_client configuration – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 1750
DHCP for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Introduction and Configuration
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
65.14
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
C613-50046-01 REV A
Configure DHCPv6 Relay / Client
In this example, a stateful client device (via IANA) obtains its interface address from a
DHCPv6 Server pool. In this example, the DHCPv6 Client resides in a network that is
remote from the DHCPv6 Server and communicates via an intermediate DHCPv6 Relay.
Diagnostics command output is shown following the configuration output.
The DHCPv6 Server needs a route to the remote LAN, where the client request originates
from via the appropriate next-hop. In this example, the next-hop address is the link-local
address of the DHCPv6 Relay. The route could be statically configured as in this example,
or dynamically learned via an IPv6 routing protocol.
Link addresses are configured in DHCPv6 Server address pools when there are remote
clients that communicate via intermediate relay(s).
When a DHCPv6 Relay receives a request from the DHCPv6 Client, it sends a relay-forward
message toward the DHCPv6 Server. The DHCPv6 Relay message includes an address from
the client-facing interface in the link-address field of the relay-forward message. The
address of the server-facing interface is used as the IPv6 source of the relay message, and
the server will send any reply to that address.
The DHCPv6 Relay automatically adds a route for the delegated prefix into its routing
table for the duration of the valid lease, via the interface where the PD client device
resides.
When an address on the incoming interface of the DHCPv6 Server or a link address set in
the incoming delegation request packet matches the link-address prefix configured in the
delegation pool, the server is able to match and use the appropriate delegation pool for
relayed delegation request messages.
Active bindings are stored in non-volatile memory, and are retained over a device reboot.
For more command information, see the
command on the
DHCPv6 Relay, and the
command on the Stateful Client.
Note bold configuration command entries show hostnames and interfaces.
Also note the default VLAN interface vlan1 is applied to all ports on a device.
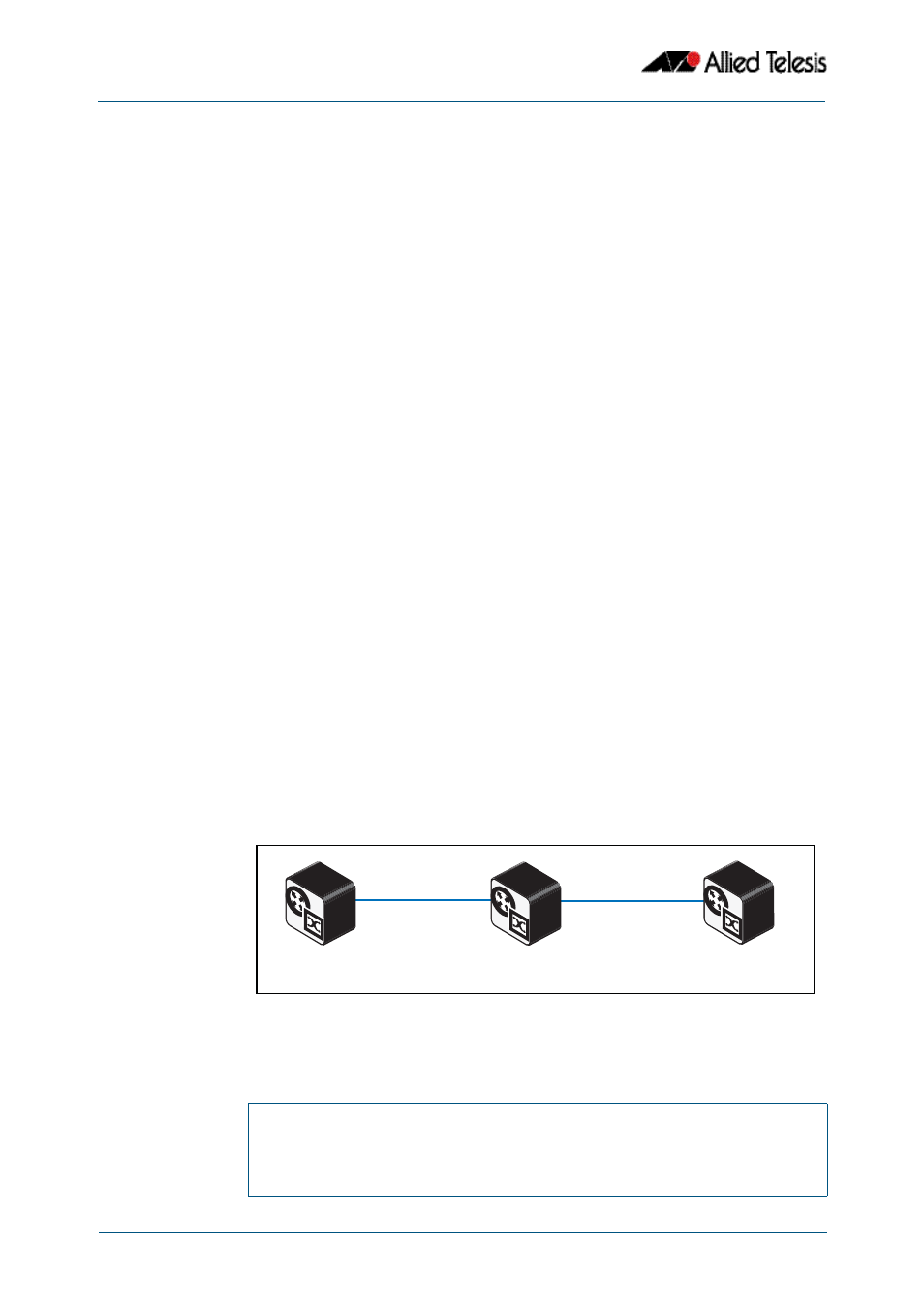
Figure 65-6: DHCPv6 Relay / Stateful Client configuration topology:
Stateful_Client Configuration
See the below configuration for a device with the hostname Stateful_Client:
hostname Stateful_Client
!
interface vlan1
ipv6 address dhcp
dhcpv6_relay_server_client1
Stateful_Client
DHCPv6_Relay
DHCPv6_Server
vlan1
vlan1
vlan2
port1.0.2
