Differentiated services architecture – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 976
Quality of Service (QoS) Introduction
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
38.4
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
C613-50046-01 REV A
Differentiated Services Architecture
Whilst a full description of the differential services model is outside the scope of this
software reference, a brief introduction is provided. For further information, RFC 2475
provides an in depth definition of the architecture.
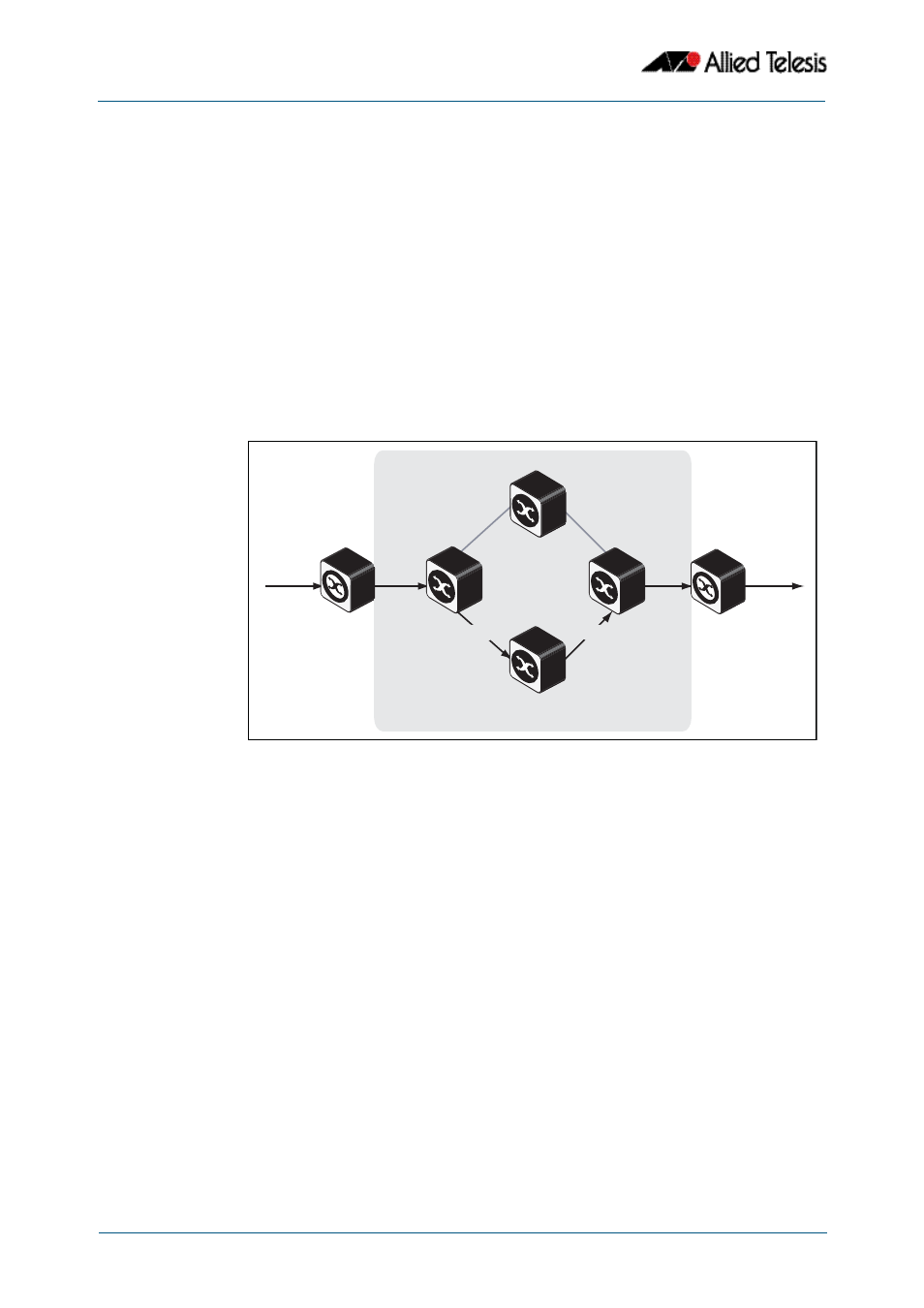
The basic differential services model envisages a multi router network within which
common service qualities are applied. At the network boundary, QoS Edge Routers inspect
the traffic and classify it into common service quality groups called Per Hop Behaviors
(PHBs). A specific marker value called a Differential Services Code Point (DSCP) is added to
the IP header of each packet, which allocates it to a PHB. QoS Core Routers within the
network can then use the DSCP to decide on an appropriate service quality level to apply.
When a network contains a consistently applied differential services code points DSCP it is
referred as a Differential Services Domain (often shortened to DiffServe Domain).
shows a simple Differential Services Domain.
Figure 38-2: Differentiated Services Domain
DiffServe-Domain
QoS
Boundary
Switch
Unmarked
Packets
QoS
Boundary
Switch
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
QoS
Core
Switches
QoS
Core
Switches
Differential Services
Domain
Classify by source IP
address
Mark with DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
Remark to a new DSCP value
Classify by DSCP=40
Limit bandwidth
