Radius security, Shared secret, Radius packet – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 1255
RADIUS Introduction and Configuration
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
C613-50046-01 REV A
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
46.5
packet, so the RADIUS Server may use it to choose access type. For 802.1X sessions,
the NAS-Port-Type sent by the NAS is Ethernet (15).
■
802.1X VLAN assignment uses:
Tunnel-Type(64), Tunnel-Medium-Type(65), Tunnel-Private-Group-ID(81),
Egress-VLANID(56), and Egress-VLAN-Name(58) attributes (specified in RFC4675 used
to specify 802.1Q tagged and untagged VLAN assignments with LLDP-MED/Voice-
VLAN).
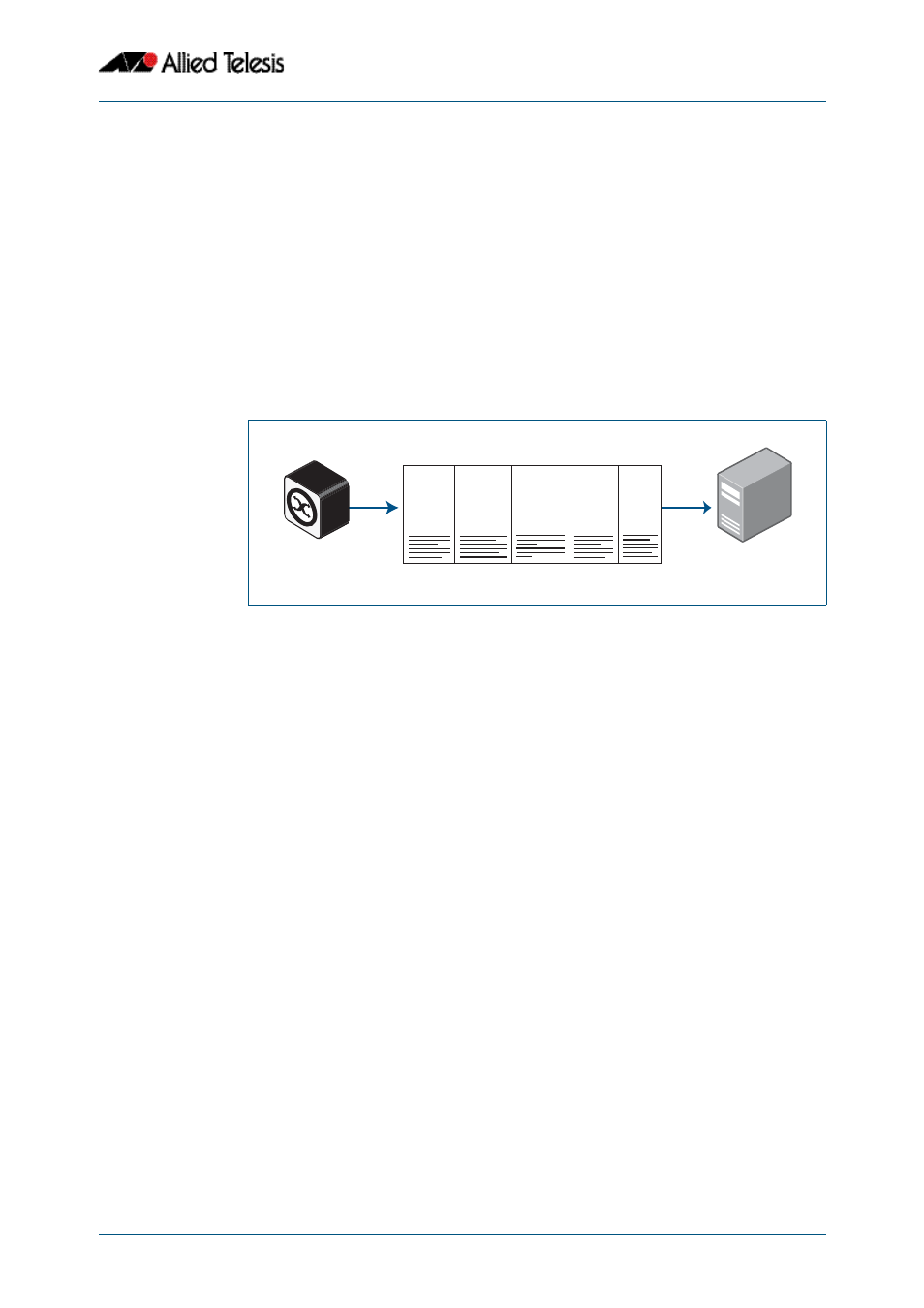
Attributes are carried within RADIUS packets in the form of TLVs (Type Length Values).
Every attribute has an attribute ID number in the Type field of the TLV. The Length field
holds a one-byte number that represents then length of the TLV. The Value field holds the
value of the attribute.
Figure 46-3: Example showing TLVs in a RADIUS Packet from a NAS to a RADIUS
Server
RADIUS Security
RADIUS is used for network security and carries user authentication information, so can be
a target for security attacks. To counter threats there are three elements to RADIUS
security:
■
Shared secret
■
Authenticator
■
Password Encryption
Shared Secret
Every NAS and server are configured with a pre-shared key, called the “shared secret”,
which is a key string, with no particular format of at least 16 characters.
The protocol has no method for choosing and sharing the secret between the NAS and
the server. The secret must be manually generated and separately configured on the NAS
and on the server.
The shared secret itself never appears in any RADIUS packets. It is used as an input to the
algorithms used for creating encrypted values that are carried in the packets.
RADIUS server
NAS
Header
Username
TLV
Other
TLV
Password
TLV
RADIUS Packet
