Common and internal spanning tree (cist), Common and internal spanning tree – Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus Operating System Version 5.4.4C (x310-26FT,x310-26FP,x310-50FT,x310-50FP) User Manual
Page 483
Spanning Tree Introduction: STP, RSTP, and MSTP
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches
C613-50046-01 REV A
AlliedWare Plus
TM
Operating System - Version 5.4.4C
18.15
Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST)
The CIST is the default spanning tree instance of MSTP, i.e. all VLANs that are not members
of particular MSTIs are members of the CIST. Also, an individual MST region can be
regarded as a single virtual bridge by other MST regions. The spanning tree that runs
between regions is the CIST. The CIST is also the spanning tree that runs between MST
regions and Single Spanning Tree (SST) entities. So, in
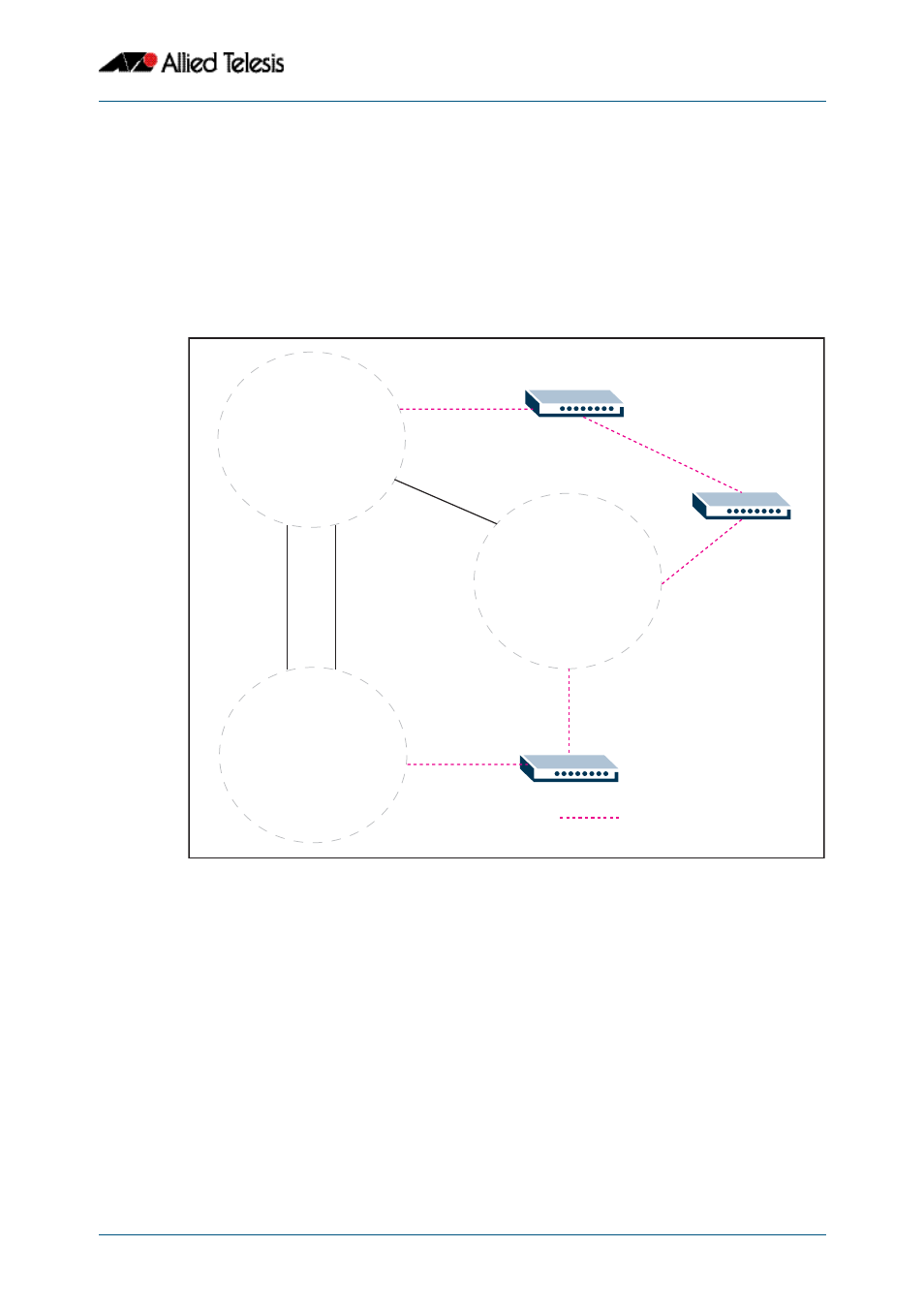
, the STP that is running
between the regions, and to the SST bridges, is the CIST.
Figure 18-3: The CIST operates on links between regions and to SST devices
Compatibility with
Previous Spanning
Tree Protocols
MSTP provides for compatibility with older spanning tree protocols in several ways. In
addition to the MST region described in the previous section, the protocol provides for
single spanning tree systems by employing a Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST).
The CIST applies a common and internal spanning tree protocol to the whole of the
bridged network and is a direct equivalent to the internal spanning tree (IST) protocol of
earlier versions.
In common with legacy spanning tree systems, the CIST protocol first determines its root
bridge from all the bridges on the network. This is the bridge that contains the lowest
bridge identifier. The protocol then selects a regional root bridge for each MSTR. This is the
bridge that provides the best path to the CIST root. After the MSTR root bridges have been
chosen, they then act on the region’s behalf in such a way that the region appears to the
Common Spanning Tree (CST) as a virtual bridge. So in addition to having multiple MSTIs,
each region operates as a bridge in a CST.
RSTP operates on these links
MSTP
Region 1
MSTP
Region 2
MSTP
Region 3
The three switches shown
are non-MSTP capable
MSTP_vs_RSTP
