Diagnosing a slow-draining f_port – Brocade Network Advisor SAN + IP User Manual v12.3.0 User Manual
Page 1870
1798
Brocade Network Advisor SAN + IP User Manual
53-1003155-01
Flow Mirror
44
2. Enter a name (flow_protocol) for the flow definition in the Name field.
The name cannot be over 20 characters and can only include alphanumeric characters or
underscores.
NOTE
For a physical switch, the name must be unique. However, for logical switches, the name does
not have to be unique.
3. Clear the Monitor check box.
4. Select the Mirror check box.
5. Select the CPU Mirroring or Local Flow Mirror option.
By default, CPU Mirroring is enabled.
6. Select the Persist over switch reboots check box to persist this flow definition over reboots.
7. Select the Activate all selected features check box to immediately activate the flow after
creation.
8. Enter an asterisk (*) in the Destination field.
9. Enter the frame type (abts) in the Frame Type field.
To select a frame type from a list, click the ellipsis button. Refer to
“Flow frame type
parameters”
on page 1729" for a list of the supported frame type parameters.
10. Click OK to save the flow definition.
When the flow definition activates, the Flow Vision dialog box displays with the new flow
selected (highlighted) in the Flow Definitions table. To review the sub-flow data for the selected
flow, refer to
“Monitoring a Flow Mirror flow”
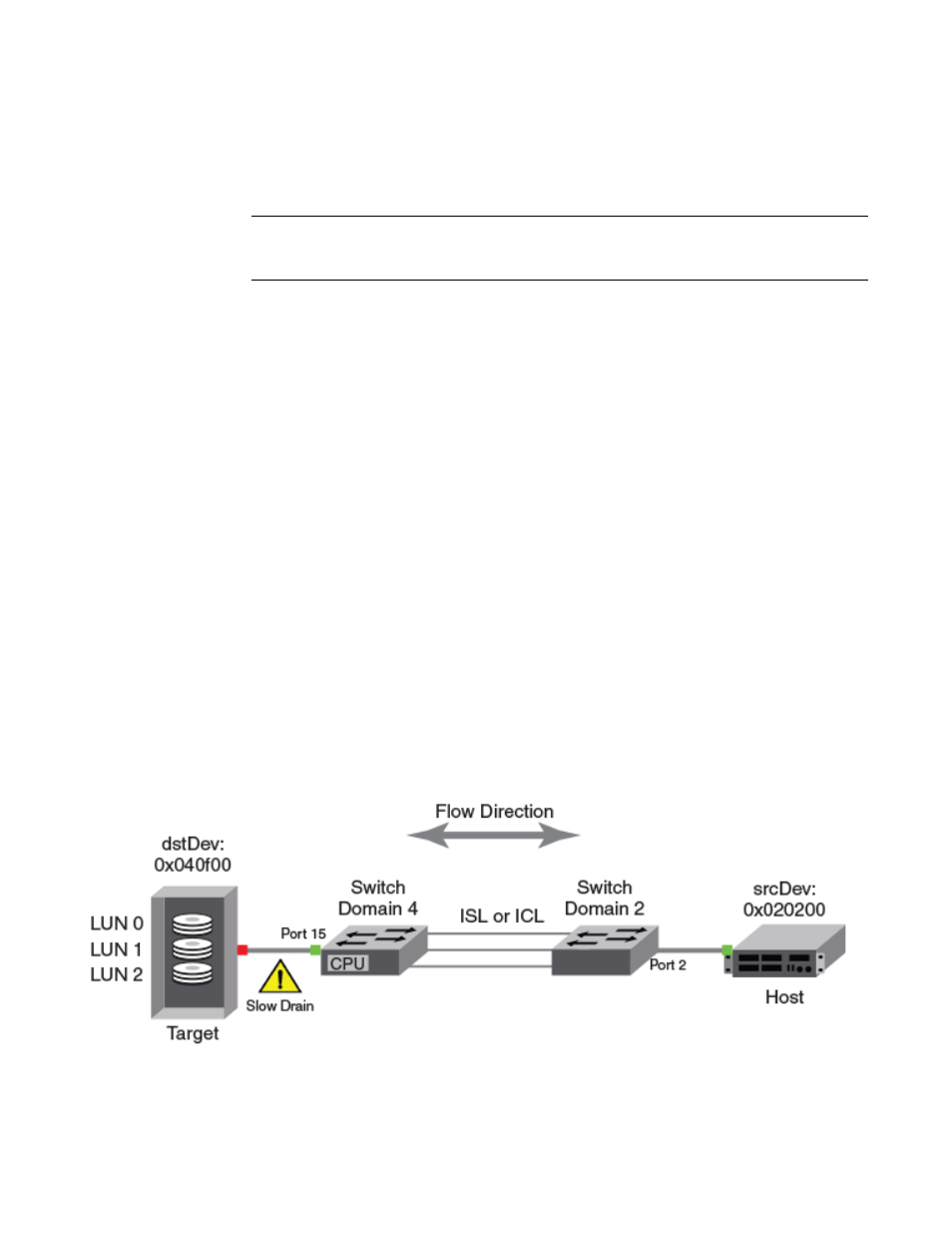
Diagnosing a slow-draining F_Port
The following example creates a flow to mirror traffic passing in both directions from device
0x010200 to F_Port 15 on device 0x040500. The collected frame data may help you diagnose the
slow-draining device.
provides a diagram of what is happening in this example.
FIGURE 806
Flow Mirror revealing a slow drain
