Appendix f. lpfc driver blockguard functionality, Overview, Figure f-1 – Dell Emulex Family of Adapters User Manual
Page 978
Emulex Drivers Version 10.2 for Linux User Manual
P010081-01A Rev. A
Appendix F. lpfc Driver BlockGuard Functionality
Overview
978
Appendix F. lpfc Driver BlockGuard
Functionality
Overview
Emulex BlockGuard™ provides a way to check the integrity of data read and written
from the host to the disk and back through the SAN. This check is implemented
through the Data Integrity Field (DIF) defined in the ANSI T10 standard.
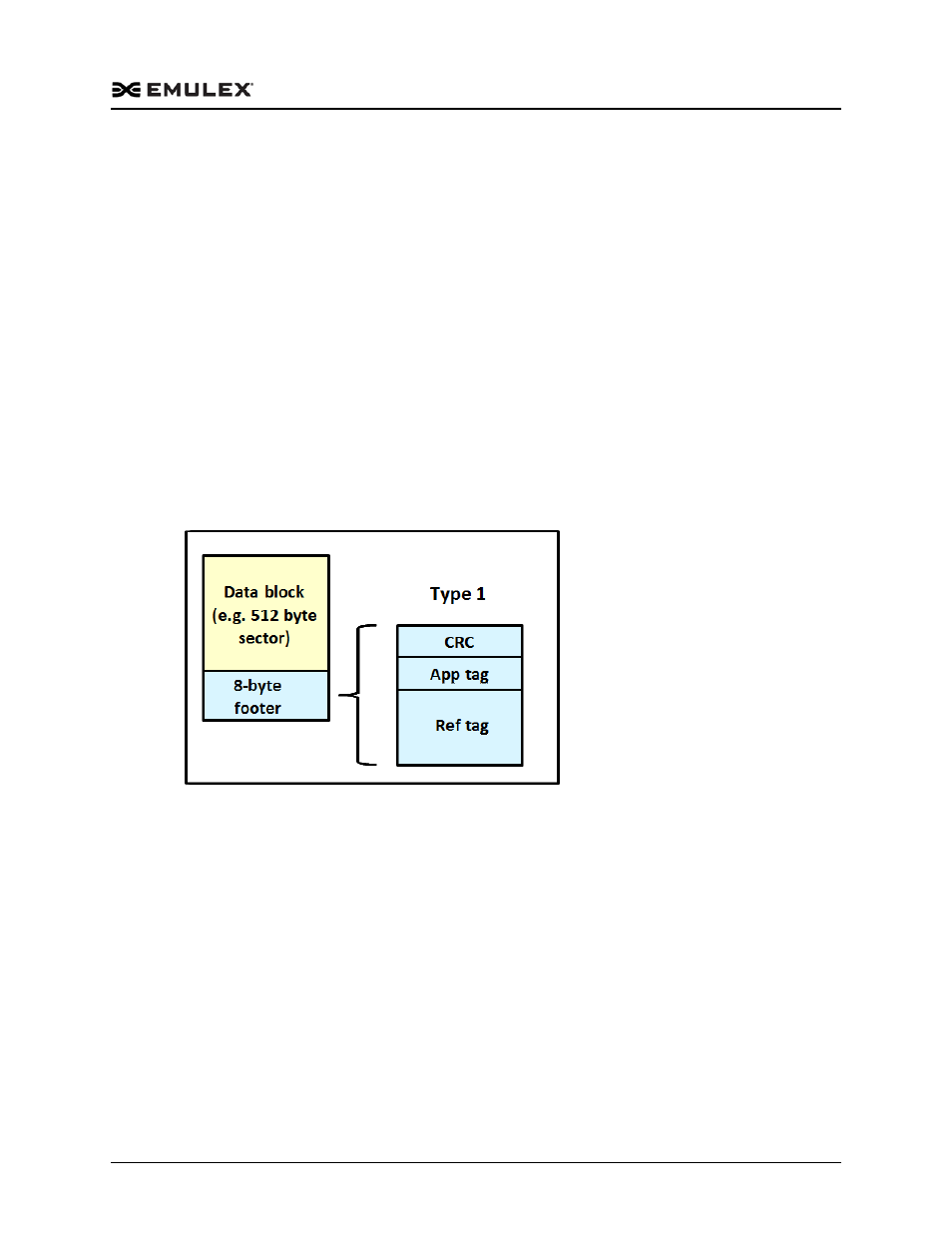
The Emulex lpfc driver supports T10 DIF Type 1. In the Type 1 implementation, the
8-byte DIF consists of a Ref Tag (or LBA), an App Tag, and a Guard Tag (or CRC). A
Type 1 DIF is defined as a having a 2-byte Guard Tag, a 2-byte App tag, and a 4-byte
Ref tag, which consists of the lower 32 bits of the logical block address.
Figure F-1 shows a data block (with a 512 byte sector) with the 8-byte footer attached to
the end. The contents of the 8-byte footer are shown with the fields which make up the
Type 1 DIF; the Guard Tag, the App Tag, and the Ref Tag. The App Tag is not used by
the lpfc driver.
Figure F-1 Data Block showing Type 1 DIF
When data is written, the DIF is generated by the Host, or by the HBA, based on the
block data and the logical block address. The DIF field is added to the end of each data
block, and the data is sent through the SAN to the storage target. The storage target
validates the CRC and Ref tag and, if correct, stores both the data block and DIF on the
physical media. If the CRC does not match the data, then the data was corrupted
during the write. A Check Condition is returned back to the host with the appropriate
error code. The host records the error and retransmits the data to the target. In this way,
data corruption is detected immediately on a write and never committed to the
physical media. On a read, the DIF is returned along with the data block to the host,
which validates the CRC and Ref tags. Since this validation is done by the hardware, it
adds a very small amount of latency to the I/O.
The format of the Guard Tag can optionally be an IP Checksum instead of the CRC
mandated by T10 DIF. This can be beneficial because the Initiator Host uses less CPU
overhead to generate an IP Checksum than it does with a CRC. The IP Checksum is
