Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 617
6 Communication
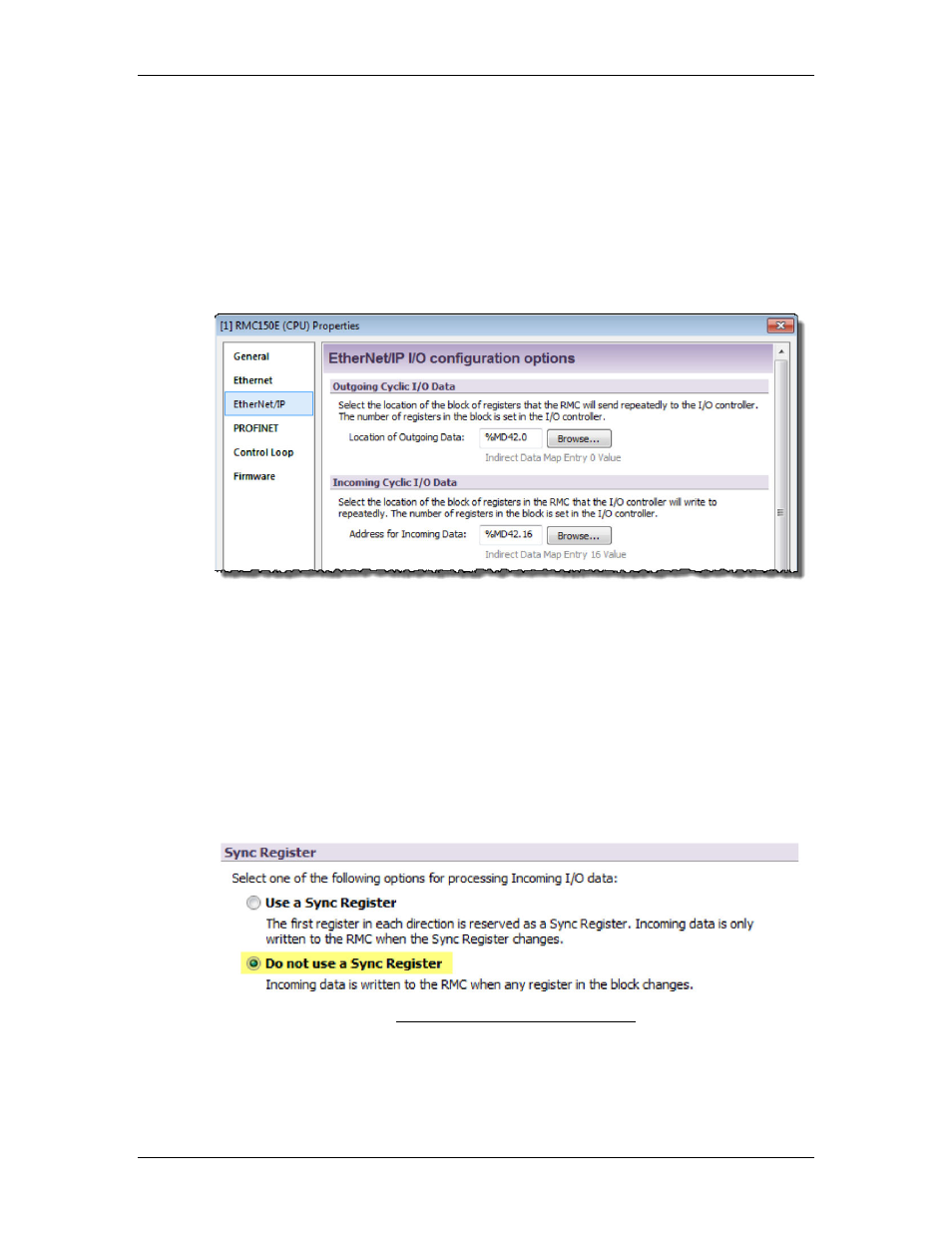
In the Outgoing Cyclic I/O Data section, enter the starting location for the
Outgoing Cyclic I/O Data. In our example, verify that the location is the Indirect
Data Map Entry 0 Value.
In the Incoming Cyclic I/O Data section, enter the starting address for the
Incoming Cyclic I/O Data. Click the Browse button and browse to the desired RMC
location for the outgoing data. This should be a location in the Indirect Data Map,
the Variable Table, or Command Area as discussed in the Determine I/O Data
Locations in the RMC section above.
For example, the PROFINET Settings Page below shows an RMC150 with the
Outgoing Data coming from the Indirect Data map starting at item 0 and the
Incoming Data going to the Indirect Data starting at item 16.
5. Choose Whether to Use a Sync Register
The Sync Register provides a method for the PLC to synchronize the Input Data and
Output Data. With a Sync Register, the Incoming Data is not written to the RMC
until the Sync Register changes. If you prefer to have the Incoming Data be written
whenever any value in the Incoming Data changes, choose the option to not use a
Sync Register.
Because the S7 PLCs use the DPRD_DAT (SFC14) and DPWR_DAT (SFC15) system
functions to control when the data is copied into and out of the S7’s DBs, the Sync
Register generally does not need to be used with the S7.
To select whether or not to use the Sync Register, in the Project pane, expand the
Modules folder, double-click the CPU module, and choose PROFINET. Then select
the desired option under Sync Register:
For more details, see the Using a PROFINET I/O Connection topic.
6. Configure Custom Data Records
While Custom Data Records can be set up at this time, they are not required to
establish the PROFINET connection, and are generally better to set up later in the
deltamotion.com
597
