Gain scheduling, Valve linearization, E valve linearization – Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 107: E gain scheduling
3 Controller Features
3.5.8. Gain Scheduling
Gain scheduling is the process of dynamically changing the gains of an axis based on some
scheduling variable. The scheduling variable may be any measurable quantity in any RMC
register, such as axis position, pressure, temperature, etc.
For example, an axis may require different gains based on its position. In this case, the axis'
position is the scheduling variable. By defining the gains as a function of the axis's position,
the gain scheduling results in optimum control.
Gain Scheduling Using Curves
Gain scheduling can be implemented in the RMC by using curves and the curve
interpolation functions. Gain scheduling involves these steps:
1. Determine the gain values at several points
Tune the axis for several different values of the scheduling variable. For example, if
the scheduling variable is the axis position, you should tune the axis at the ends, and
perhaps one or more positions in the middle. Record the gains for each position.
2. Define the gain curve for each gain
Using the Curve Tool and the gain values you recorded, create a curve for each gain.
The scheduling variable will be the x values of the curve, and the gain values will be
the y values. The curve interpolates between the points you entered, providing a
smooth gain scheduling function. Cubic curves will provide the smoothest transition
between gains, although linear curves will work as well. If you choose a cubic curve,
choose the Natural Velocity Endpoint Behavior. Constant curves are not recommended,
as they will cause undesirable discontinuities in the gain terms, especially the Feed
Forwards.
3. Continually apply the gain to the axis
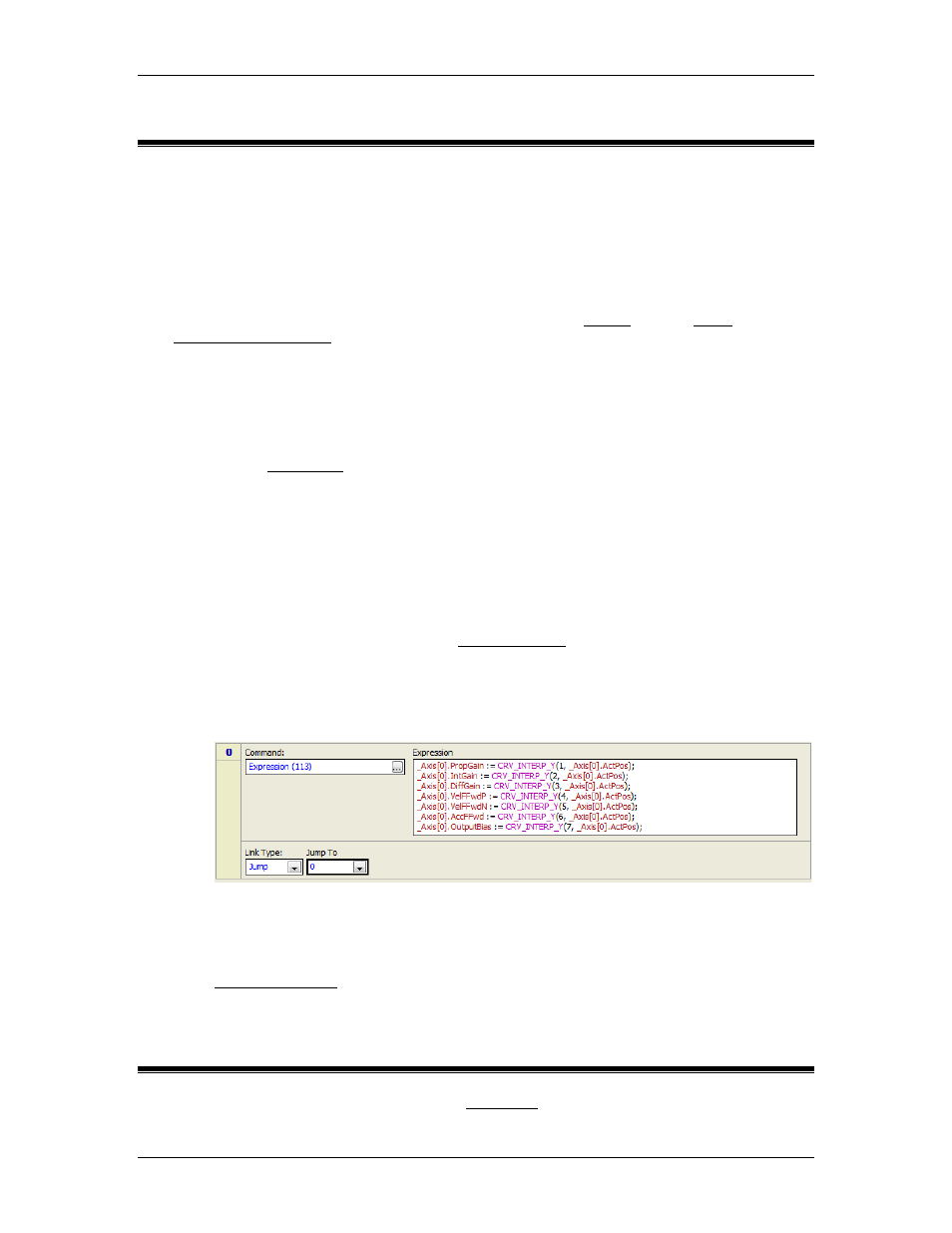
Create a user program that uses the CRV_INTERP_Y function to get the curve values
for the current scheduling variable value, and apply the values to the gains. The user
program must run continuously.
For example, the user program below will apply the gains and the output bias based
on the axis position. The expression can easily be expanded to handle multiple
axes.
To successfully use this program, make sure the RMC is in RUN mode. This can be
done by setting the RMC to start up in RUN mode in the Programming Properties,
on the RUN/PROGRAM page. Also, in the Programming Properties, on the Halts
tab, make sure the task this program is running on is set to halt. To start this user
program when the RMC starts up in RUN mode, use the _FirstScan tag on the
3.5.9. Valve Linearization
Valve linearization refers to compensating for non-linear hydraulic valves.
deltamotion.com
87
