Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 1161
10 Wiring and Installation
I/O 5
Input or Output
I/O 6
Input or Output
I/O 7
Input or Output
Input Cmn Common to one side of all inputs
Discrete Outputs
Each discrete output is a solid state relay (SSR). When it is "OFF", it has high impedance,
and when "ON" it has low impedance (50 Ω maximum, 25 Ω typical). Because the output
is isolated, the user must power it externally. The maximum current and voltage for the
output is 75 mA (50 mA for Class I, Div 2) and 30 V.
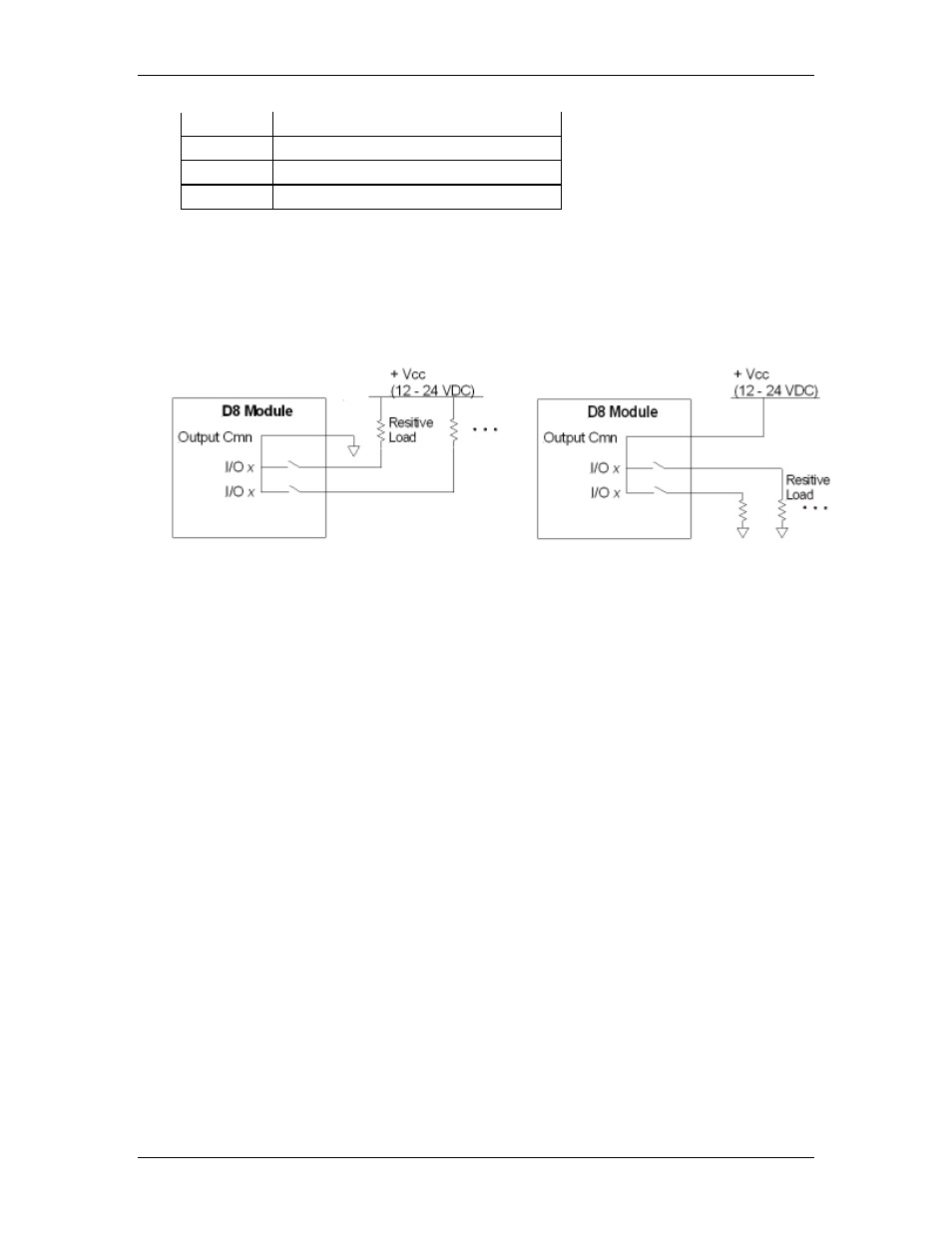
Using Outputs with Resistive Loads
Figure 2: SSR switching resistive load: low-side
configuration.
Figure 3: SSR switching resistive load:
high-side configuration.
Example: Calculating maximum current for resitive load.
To calculate the maximum current through the SSR in the above diagram, we assume
zero SSR resistance:
Max. current = 24V / 480Ω = 50mA
Max. current = 12V / 480Ω = 25mA
In the 24V case, the maximum current is right at the maximum allowed by the SSRs. The
outputs may be overpowered if the resistance is reduced further. To calculate the typical
current through the SSR, we use the typical SSR resistance of 25W:
Typical current = 24V / (480Ω + 25Ω) = 47.5mA
Typical current = 12V / (480Ω + 25Ω) = 23.8mA
Using Outputs with Inductive Loads
External fuses should be used to protect the SSRs if there is a possibility of over-
current. When switching inductive loads, it is important to place a diode or tranzorb
across the load to protect the switch when transitioning from an ”ON” to an ”OFF” state.
Otherwise, the collapsing magnetic field can cause a reverse voltage spike in excess of
the 30 V rating of the SSR. See figures below for details.
deltamotion.com
1141
