Velocity pid, Velocity pid, o – Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 103
3 Controller Features
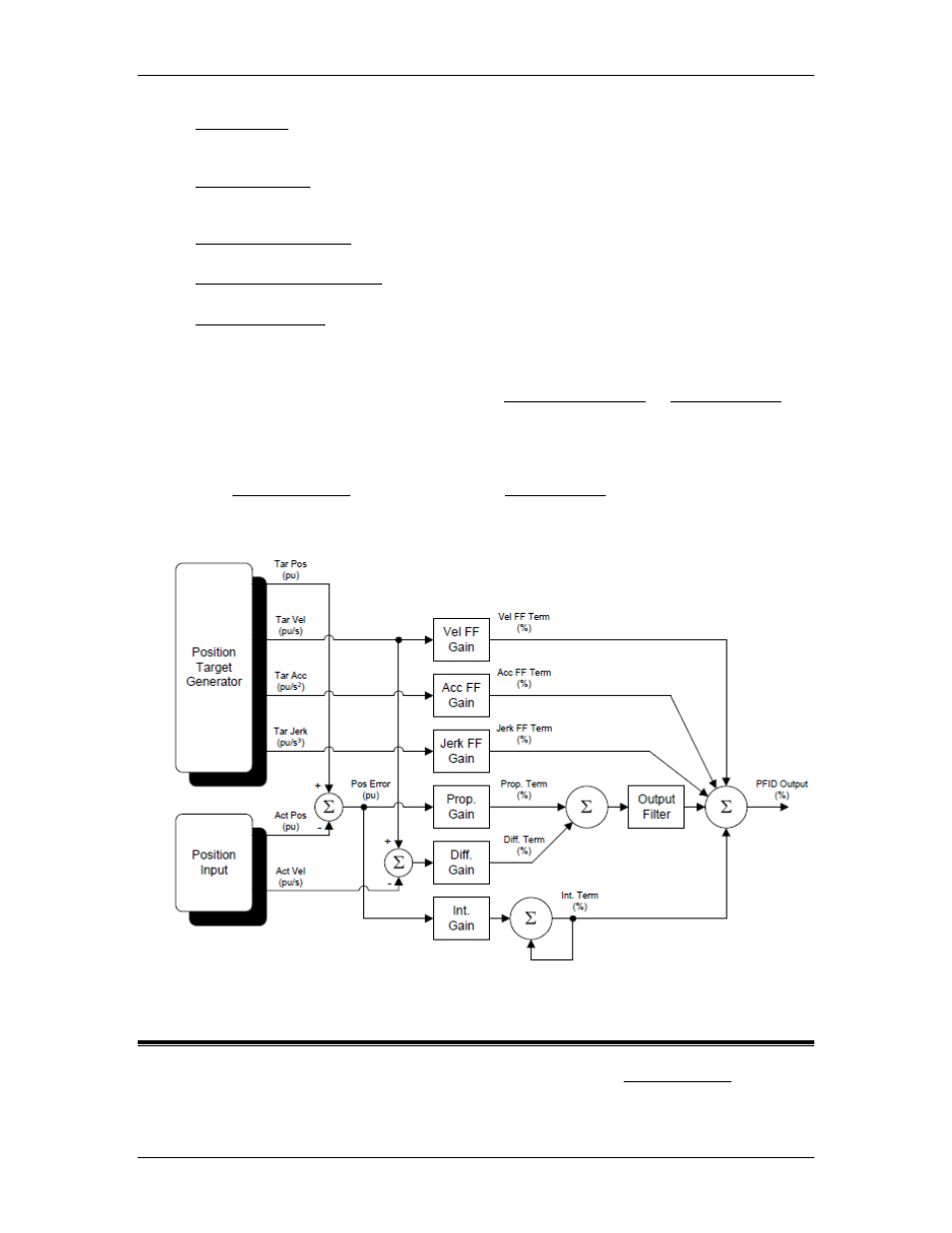
•
The Integral Gain is multiplied by the accumulated Position Error. This helps the axis
get into position over time.
•
The Differential Gain is multiplied by the difference between the Target and Actual
Velocities. This helps the axis keep up with quick changes in velocity.
•
The Velocity Feed Forward is multiplied by the Target Velocity.
•
The Acceleration Feed Forward is multiplied by the Target Acceleration.
•
The Jerk Feed Forward is multiplied by the Target Jerk. The Jerk Feed Forward is not
necessary for most applications.
In addition, higher-order gains may be used if Acceleration Control or Active Damping are
selected.
Tuning Position PID
See the Tuning Overview topic for details. The Tuning Wizard can be used to tune position
PID control.
Diagram
3.5.5. Velocity PID
Velocity PID is the algorithm typically used to perform closed-loop velocity control on a
position or velocity axis. PID stands for the central gains used in this mode: Proportional,
Integral, and Differential. The Velocity PID provides very good control and is suitable for
deltamotion.com
83
