Arrays, N array, E arrays – Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 348
RMC70/150 and RMCTools User Manual
Array values can be initialized as shown in the example above. The number of initialized
values must equal the number of items in the array.
Parentheses can be used as a repetition factor, where the number preceding the
parentheses specifies the number of repetitions.
Examples:
[8,2,3(0),10] is the same as [8,2,0,0,0,10]
[10(0)] initializes an array of length 10 to all zeros.
Size Limits
The maximum length of a local array is 32. A single user program step can have up to
128 items declared, including variables and individual array items.
5.13.6. Arrays
An array is a numerically indexed sequence of elements of the same data type. The elements
of an array are specified by the index. In the RMC, an array index starts at 0 and extends to
the number of elements minus 1. The RMC supports only one-dimensional arrays. For an
example on using arrays, see Example: Using Arrays.
This topic treats arrays in the Variable Table. For information on local arrays in user program
steps, see Local Variables in Expressions. For information on arrays in User Functions, see the
User Functions and Declaring Variables in User Functions topics.
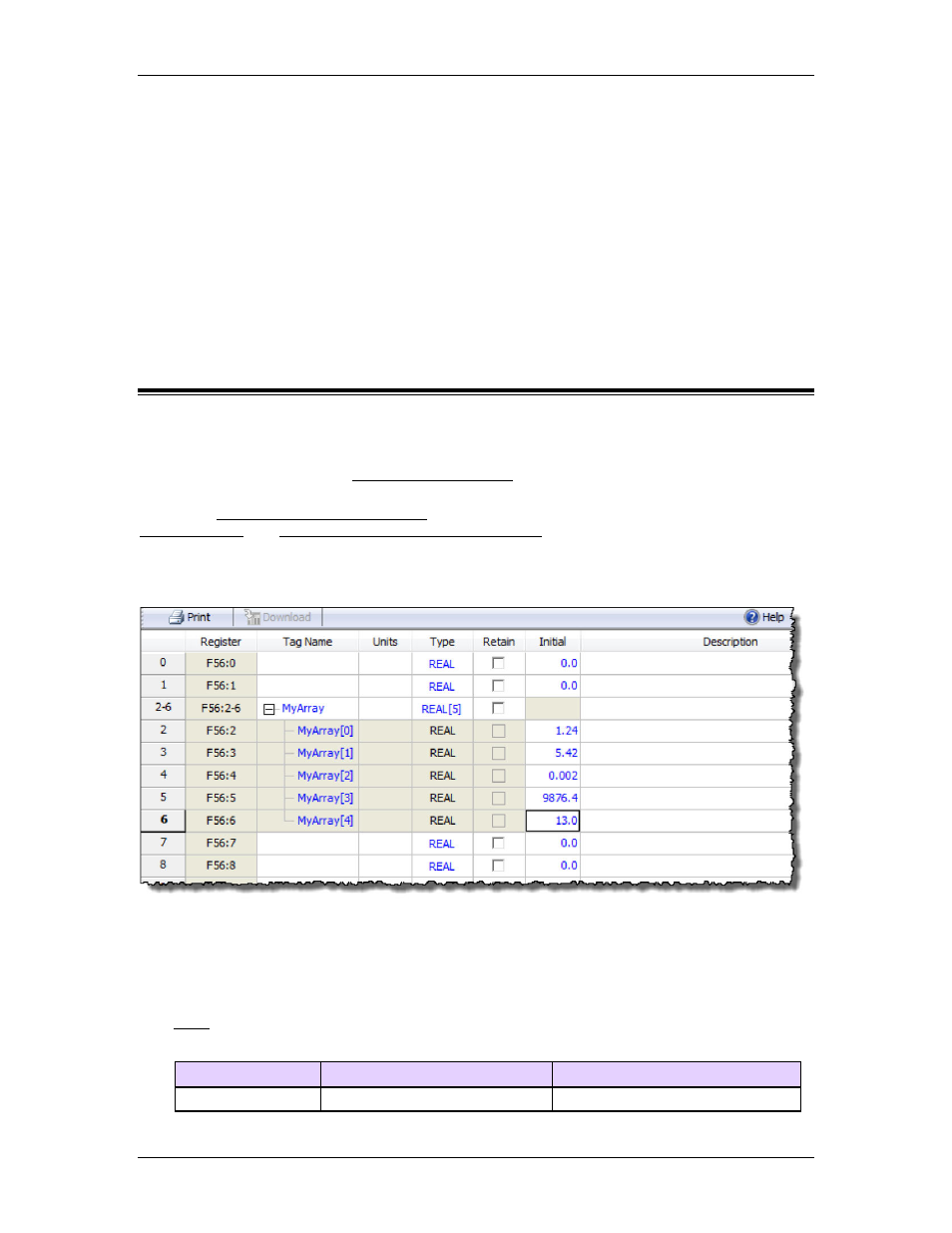
Array Declaration Example
This is an example of declaring an array of 5 REALs starting at variable 2:
Array indexing can only be used within the RMC expressions. When accessing RMC arrays from
a host controller, you must use the register addresses for the protocol you are using.
Indexing Array Elements
To specify an element of an array, insert the index in brackets after the tag name in the
format 'array_name[index]'. The index can be an expression and must evaluate to a
DINT data type.
Examples
Definitions
Indexing Examples
Description
MyArray as
MyArray[4]
Specifies the element of the
328
Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
