Active damping, As active damping, R active damping – Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 114
RMC70/150 and RMCTools User Manual
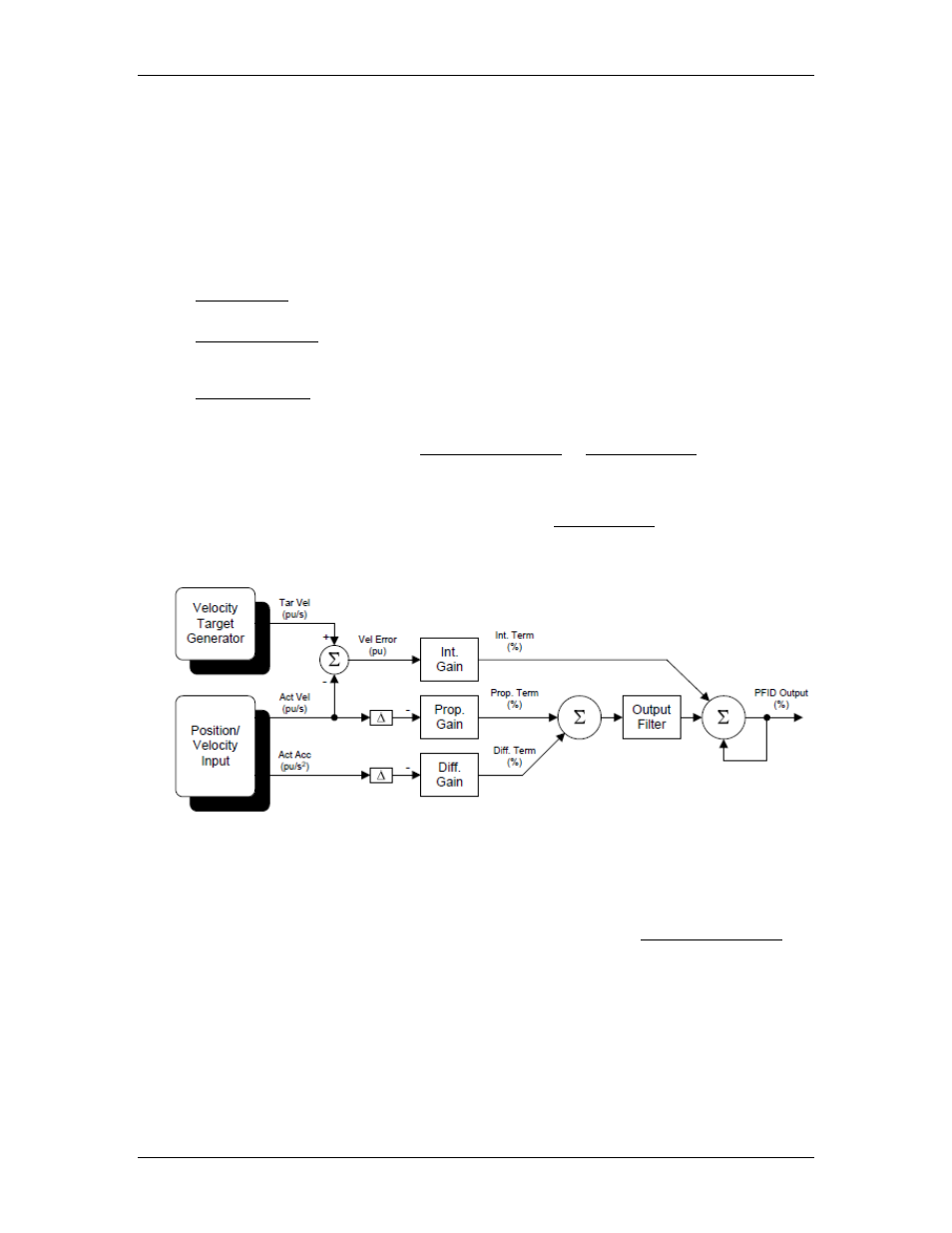
Each closed loop motion command issued to the RMC specifies a target profile, which
defines where the axis should be at any given moment. For each loop time when the axis
is in closed loop control, the Velocity I-PD algorithm calculates the values from each gain,
as described below. Then, the terms from the Proportional and Differential gains are
subtracted from the Integral Gain term. The resulting value (in percent) is multiplied by
the maximum output (typically 10V), to come up with the Control Output voltage for that
loop time.
Gains and Feed Forwards
The Velocity I-PD uses the gains listed below. It does not use any Feed Forwards.
•
The Integral Gain is multiplied by the accumulated Velocity Error.
•
In this control mode, the Proportional Gain multiplied by the change in the Actual
Velocity is subtracted from the Control Output each control loop.
•
In this control mode, the Differential Gain multiplied by the change in the Actual
Acceleration is subtracted from the Control Output each control loop.
Higher-order gains may be used if Acceleration Control or Active Damping are selected. In
addition, in Active Damping control, the Velocity I-PD does not use the Differential gain.
Tuning Velocity I-PD
The velocity I-PD gains must be tuned manually. The Tuning Wizard cannot be used to
tune velocity I-PD control.
Diagram
3.5.12.3. Active Damping
Active Damping is an algorithm that reduces oscillation in a motion control system. It can
help control systems prone to oscillation or with low damping, such as pneumatic cylinders.
Active damping requires information on the accelerations or forces acting on the system. The
active damping algorithm uses this information to affect the Control Output so that the
accelerations or forces do not cause oscillations.
Active damping gives best results when a secondary input is used. although in some cases,
active damping can be achieved using only the primary position or velocity feedback.
Active Damping is especially useful for controlling fluid power systems with significant
compression in the fluid. This includes:
94
Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
