Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 509
6 Communication
•
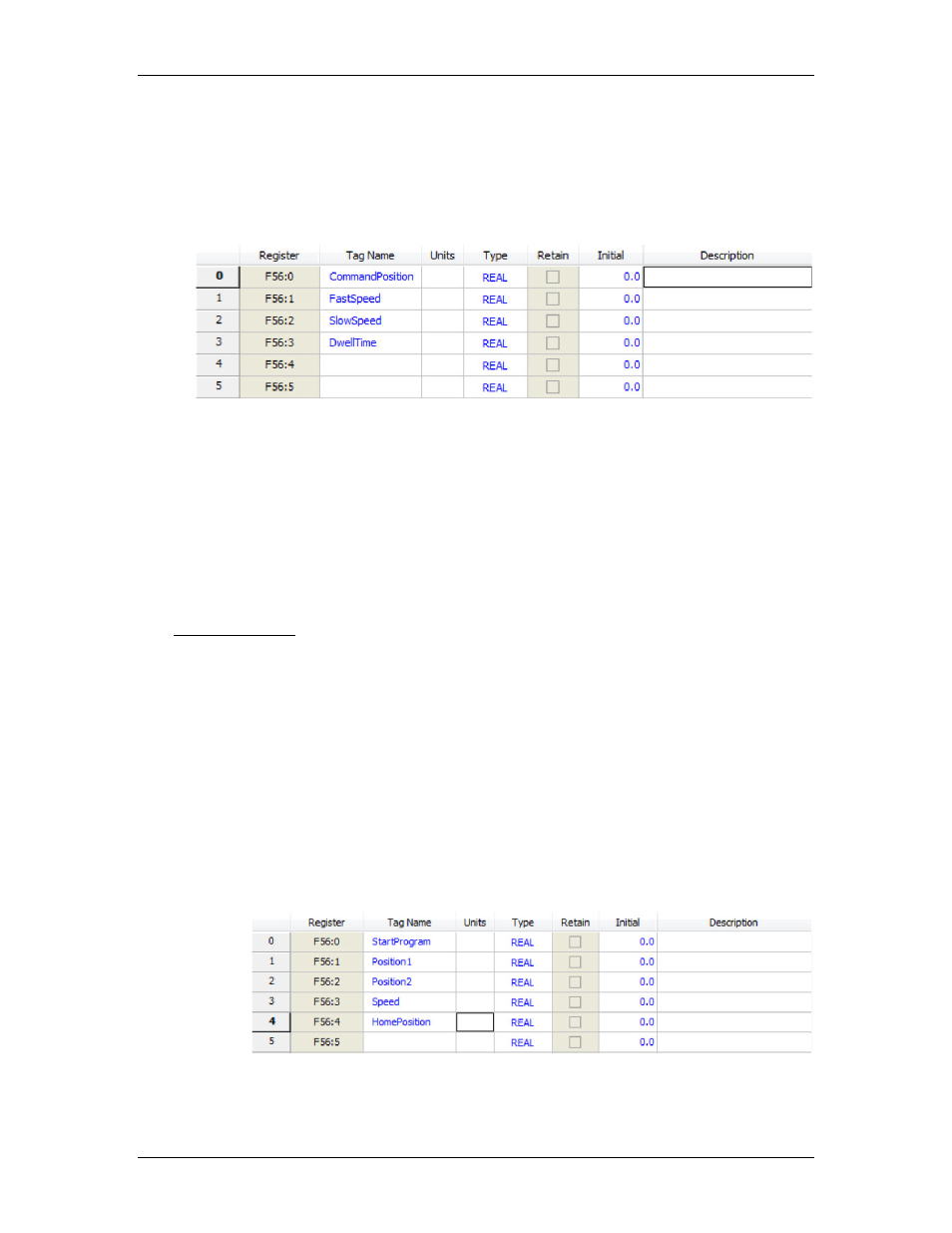
Command Position (REAL Data Type)
•
FastSpeed (REAL Data Type)
•
SlowSpeed (REAL Data Type)
•
DwellTime (REAL Data Type)
Therefore, the user sets the tag names and Data Types of the first four items in the
Variable Table like this:
4. Perform Communications
After configuring the PROFIBUS and setting up the Indirect Data Map and Variable Table,
start the PROFIBUS communications. Once the PROFIBUS connection is established, the
RMC's Indirect Data Map registers will continuously be sent to the PLC's Input Data, and
the PLCs' Output Data will continuously be sent to the RMC's Variable Table. The RMC's
variables can be used for anything that they normally are used for. However, trying to
change the PROFIBUS variables from user programs is not very useful, because the
variables will be overwritten by the PROFIBUS.
Issuing Commands via I/O Mode
To issue commands, or write to RMC registers (other than the I/O Mode variables), or do
anything else via the I/O modes, you must create a user program. You can then use the
Program Triggers to start a user program when an I/O Mode variable becomes a certain
value.
To program the RMC to do this, you must:
1. Create user programs to do the desired actions.
2. Define a variable for starting the programs.
3. Edit the Program Triggers to start the user programs based on the value of the
variable.
Example
Bruce is using I/O Mode (8 regs). He wants to run two different user programs on the
machine. The first program will move back and forth once, and the second will move
to a home position. The PLC will send the two cycle positions, the speed, and the
home position to the RMC.
1. Bruce defines variable zero as StartProgram, and defines 4 more variables
for his cycle positions, speed, and home position.
2. Bruce creates the user programs and calls them Cycle and MoveHome:
deltamotion.com
489
