Curve interpolation methods and options – Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 147
3 Controller Features
3.6.7.5. Curve Interpolation Methods and Options
The RMC supports several interpolation methods and options to satisfy a wide range of curve
applications.
Interpolation Methods
The interpolation method is specified in the Properties pane in the Curve tool, or in the
Curve Add (82) command. Choose from one of the methods below. The Cubic (2)
method is the most common method and creates the smoothest motion.
•
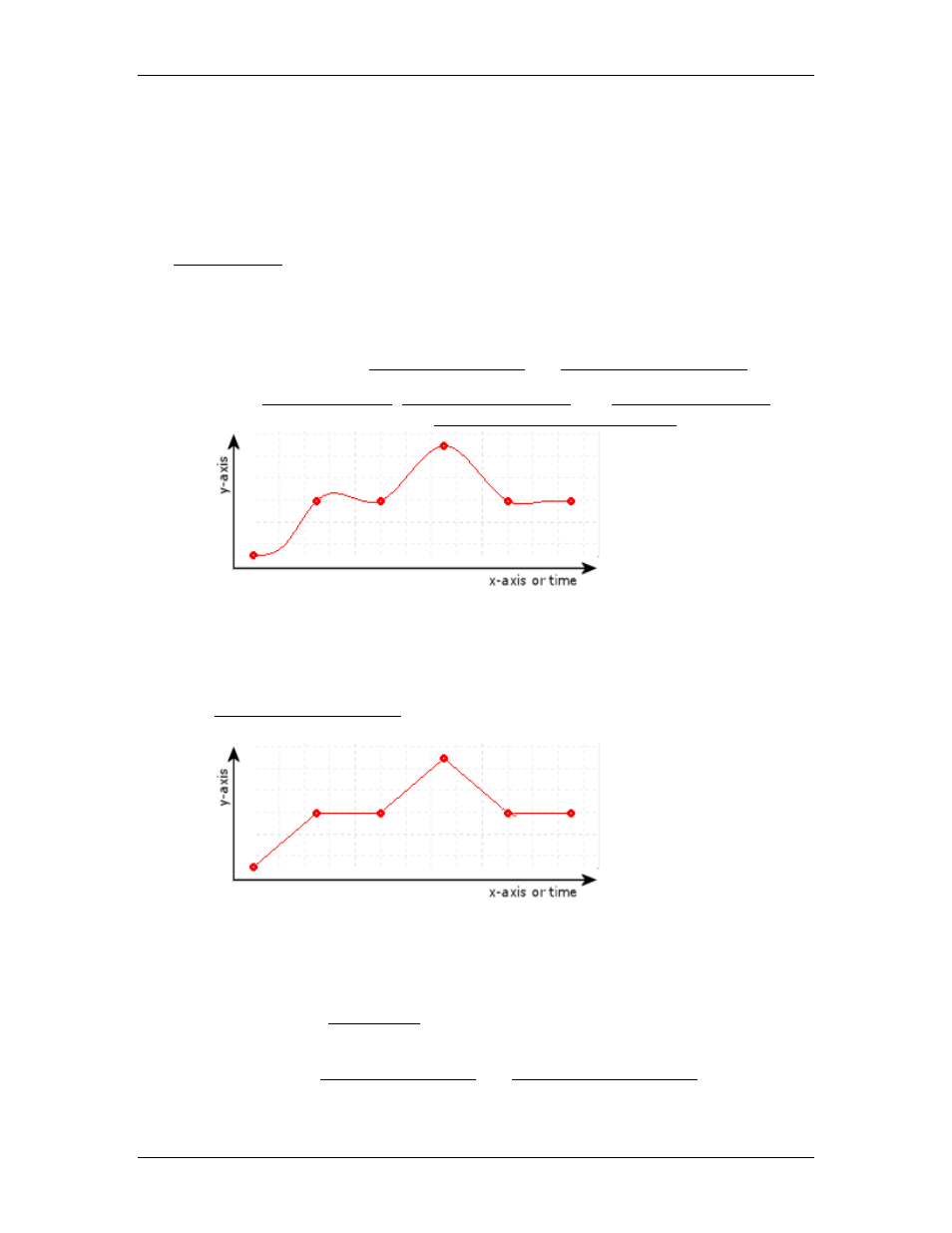
Cubic (2)
The curve will smoothly go through all points. This is the most common
interpolation method. This method will create smooth motion.
On position axes, the Velocity Feed Forward and Acceleration Feed Forward will
apply to cubic interpolated curves, but higher order gains should not be used, such
as the Jerk Feed Forward, Double Differential Gain, and Triple Differential Gain.
On pressure or force axes, the Pressure/Force Rate Feed Forward will apply.
•
Linear (1)
The curve will consist of straight-line segments between each point. Because the
velocity is not continuous, a position axis will tend to overshoot at each point. This
type of curve is typically more suitable for pressure or force axes.
On position axes, the Target Acceleration will always be zero. Therefore, the
Acceleration Feed Forward will have no effect for linear interpolated curves.
•
Constant (0)
The curve will consist of step jumps to each point. The curve will not be continuous.
This method is seldom used, but may be useful in applications where step jumps
are desired, such as some blow-molding systems. This method requires that the
axis not be tuned very tightly, or the axis may oscillate and Output Saturated errors
may occur. The Position I-PD control algorithm is recommended for following
constant interpolated curves.
On position axes, the Target Velocity and Target Acceleration will always be zero.
Therefore, the Velocity Feed Forward and Acceleration Feed Forward will have no
effect for constant interpolated curves.
deltamotion.com
127
