Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 390
RMC70/150 and RMCTools User Manual
RMC
Module
Details
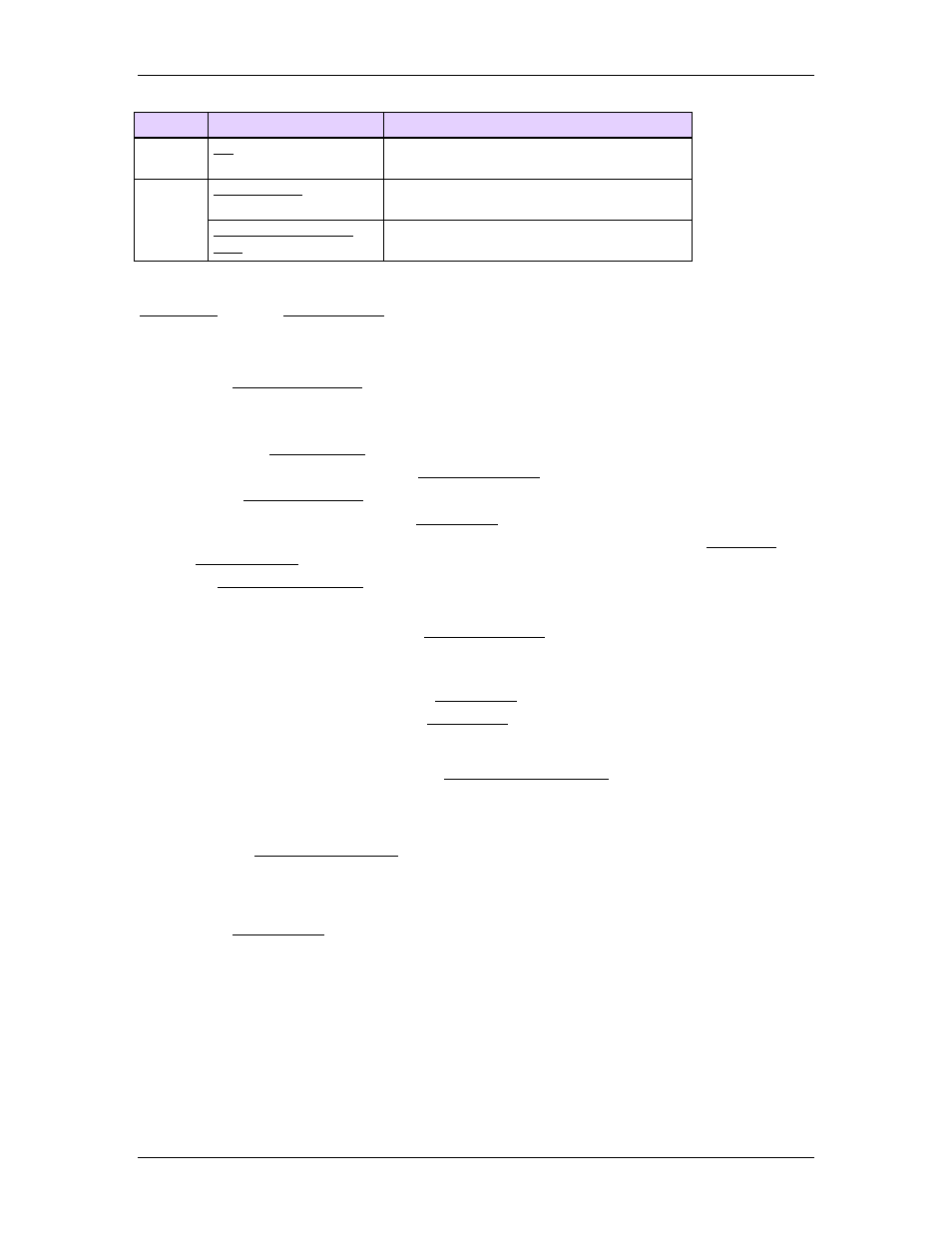
RMC70 D8 Expansion module 8 DI/O points, individually programmable
as inputs or outputs.
RMC150 DI/O Module
8 outputs, 18 inputs. Fits in slots 0, 2, 3,
4, and 5.
2 outputs, 2 inputs
In addition to the discrete I/O described in this topic, each RMC70 axis module also has one
Fault Input and one Enable Output per axis. The RMC70 QA and RMC150 Quad modules also
have discrete inputs for homing and registration.
Using General Discrete I/O
See the Using Discrete I/O topic for details on implementing the uses of discrete I/O
listed below. Tag names can be assigned to general discrete I/O.
Discrete inputs can be used for the following:
•
To start a User Program.
•
As part of the condition for the Conditional Jump link type in User Programs.
•
In the Expression (113) command in a User Program.
•
Inputs can be forced using the I/O Monitor in RMCTools.
•
If configured to do so, one input can control whether the controller is in Run Mode or
•
Discrete outputs can be used for the following:
•
The outputs can be set with the Expression (113) command in a User Program.
•
The outputs can be set by writing to the address of the output in the RMC via a PLC,
HMI, etc.
•
Outputs can be toggled using the I/O Monitor in RMCTools.
•
Outputs can be forced using the I/O Monitor in RMCTools.
Configuring the Discrete I/O
To configure the discrete I/O, use the Configuring Discrete IO topic.
Viewing the Discrete I/O
There are two ways to view the state of the discrete I/O:
•
Use the Discrete I/O Monitor in RMCTools.
•
Look at the LEDS on the module, if the module has LEDs.
Addressing Discrete I/O
See the Register Map for details on the addresses of the discrete I/O registers.
Discrete I/O points are represented as bits in the RMC. To address a bit, you must specify
the bit in the register that contains it. Not all host controllers allow this, depending on the
protocol. For example, addressing a bit in an F file using an Allen-Bradley protocol is not
supported in many HMIs. Typically, specifying bits in any word is possible with most
controllers using Modbus/RTU or Modbus/TCP. Notice that you may need to address the
upper 16-bit portion of the 32-bit register in order to pick out the bits higher than 15.
In RMCTools, the discrete I/O addresses are shown in the IEC 61131-3 format:
370
Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
