Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 556
RMC70/150 and RMCTools User Manual
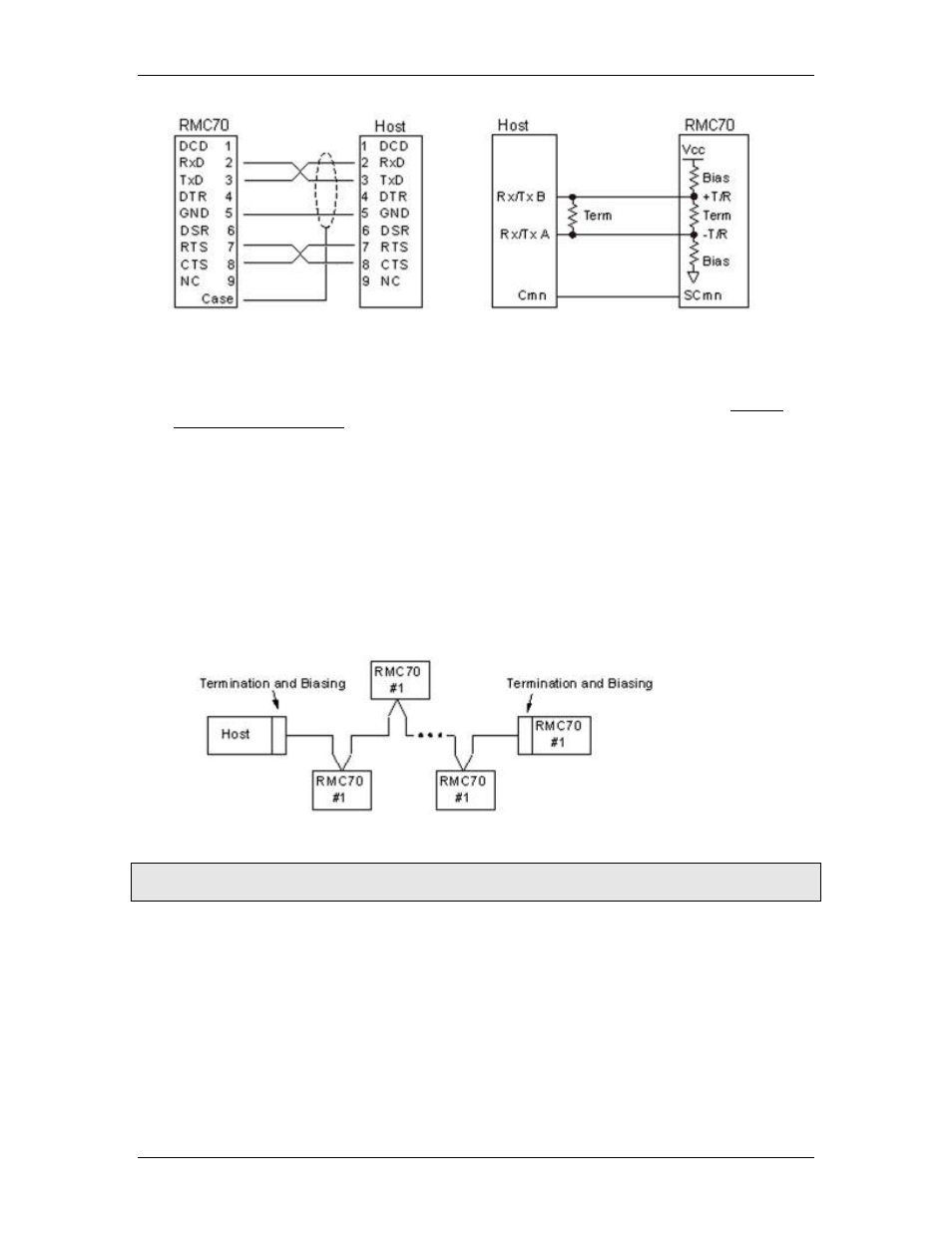
Fig. 1: Point-to-Point RS-232
Network
Fig. 2: Point-to-Point RS-485 Network
Figure 2 shows biasing and termination. Termination and biasing can be left out of
networks at the expense of maximum cable distance and noise immunity. See RS-485
Termination and Biasing for details.
Multi-Drop
Only RS-485 supports multi-drop. Multi-drop is the connecting of multiple slaves with a
single master. Slaves should be chained together. Neither a star topology nor a chain with
long stubs (wires from the main chain to the device) should be used. These topologies will
cause excessive ringing on the network and unreliable data transmission.
The number of devices that can be connected to the network is dictated by the number of
unit loads that each represents. According to the TIA/EIA-485-A specification, there can
be a maximum of 32 unit loads connected to a single network. Each RMC represents unit
load for a total of 124 RMCs on the network, assuming the host is a unit load.
Figure 3 shows a typical multi-drop chain:
Fig. 3: Daisy-Chained RS-485 Network
Note:
Termination should only be located at the extreme ends of the network:
Figure 4 shows one host with two RMC controllers in a daisy-chained two-wire RS-485
configuration:
536
Delta Computer Systems, Inc.
