Delta RMC151 User Manual
Page 209
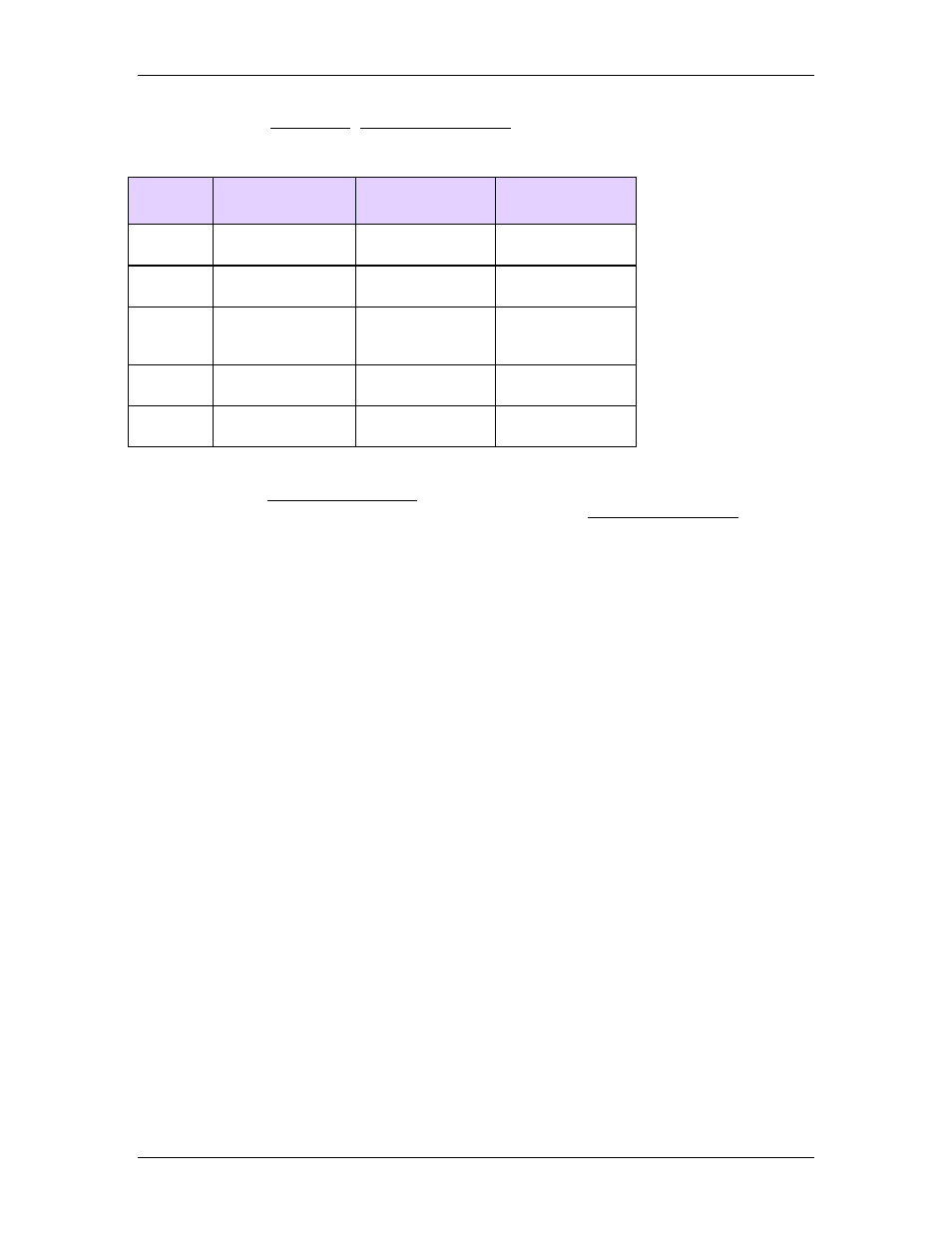
3 Controller Features
RMC150: SSI Module, Universal I/O module
The RMCs provide the following SSI options:
SSI
Options
RMC70
MA Module
RMC150
SSI Module
RMC150
UI/O Module
Data
Bits
8 to 32
8 to 31
8 to 32
SSI
Format
Binary or Gray
Code
Binary or Gray
Code
Binary or Gray
Code
SSI
Errors
None, all zeros,
all ones, or bit
21
None, all zeros,
all ones, or bit
21
None, all zeros,
all ones, or bit
21
Clock
Rates
150, 250, and
375 kHz
230 or 921kHz
250kHz, 500kHz
or 971kHz
Wire
Delay
n/a
n/a
available
Universal I/O Module SSI Options
The RMC150 Universal I/O module supports additional SSI features, such as monitor
mode and inter-RMC communications. For details, see the Universal I/O module topic
Synchronized SSI for Linear Magnetostrictive Transducers
When using magnetostrictive SSI transducers, it is highly recommended that a
synchronized SSI transducer be selected. This ensures that the time between position
samples matches the control loop time of the RMC controller. If the transducer is not
synchronized, the sample time may not match and will adversely affect control. When the
sample time does not match the loop time it introduces jitter to the position
measurement which gets worse as the axis speed increases. Make sure to specify that the
transducer be of the synchronized type.
Synchronized SSI is not an issue for rotary encoders.
SSI Advantages
SSI transducers and absolute encoders offer the following advantages:
•
High resolution. Down to 1 μm (approx. 0.00004") for linear SSI transducers.
•
Noise immunity
•
Cost effective data transfer (only one 5-wire cable with shield is needed)
•
Transmission rate independent of data length and resolution
•
Transmission over long distances
•
Direct connection to the RMCs SSI axis module
Data Format
To read an SSI position, the RMC sends clock pulses to the transducer and the SSI device
returns the data as follows:
1. The SSI channel sends the first clock pulse by setting the Clock signal low, then high.
2. On the first rising edge of the Clock signal, the SSI transducer returns the most-
significant bit of the data on the Data line.
3. The SSI channel sends the second clock pulse by setting the Clock signal low, then
high. When the Clock signal goes high, the SSI channel samples the bit on the Data
line. When the SSI device sees the clock signal go high, it places the second bit of
data on the Data line.
4. This continues until all bits have been clocked and sampled.
deltamotion.com
189
