1 unified tlb (utlb) configuration – Renesas SH7781 User Manual
Page 194
7. Memory Management Unit (MMU)
Rev.1.00 Jan. 10, 2008 Page 164 of 1658
REJ09B0261-0100
7.3
TLB Functions (TLB Compatible Mode; MMUCR.ME = 0)
7.3.1
Unified TLB (UTLB) Configuration
The UTLB is used for the following two purposes:
1. To translate a virtual address to a physical address in a data access
2. As a table of address translation information to be recorded in the ITLB in the event of an
ITLB miss
The UTLB is so called because of its use for the above two purposes. Information in the address
translation table located in external memory is cached into the UTLB. The address translation
table contains virtual page numbers and address space identifiers, and corresponding physical page
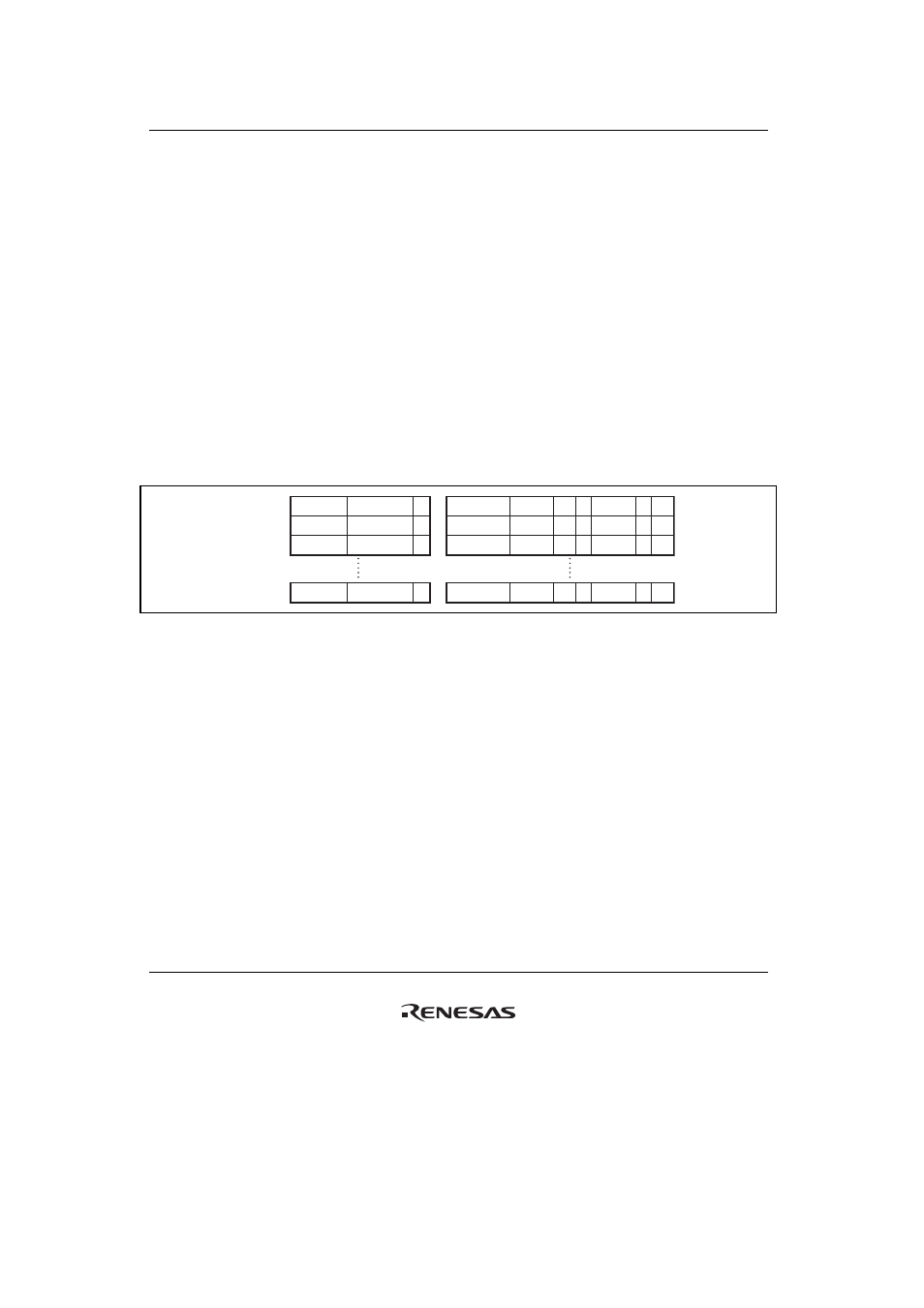
numbers and page management information. Figure 7.6 shows the UTLB configuration. The
UTLB consists of 64 fully-associative type entries. Figure 7.7 shows the relationship between the
page size and address format.
PPN[28:10]
PPN[28:10]
PPN[28:10]
SZ[1:0]
SZ[1:0]
SZ[1:0]
SH
SH
SH
C
C
C
PR[1:0]
PR[1:0]
PR [1:0]
ASID[7:0]
ASID[7:0]
ASID[7:0]
VPN[31:10]
VPN[31:10]
VPN[31:10]
V
V
V
Entry 0
Entry 1
Entry 2
D
D
D
WT
WT
WT
PPN[28:10] SZ[1:0] SH C PR[1:0]
ASID[7:0]
VPN[31:10] V
Entry 63
D WT
Figure 7.6 UTLB Configuration (TLB Compatible Mode)
Legend:
• VPN: Virtual page number
For 1-Kbyte page: Upper 22 bits of virtual address
For 4-Kbyte page: Upper 20 bits of virtual address
For 64-Kbyte page: Upper 16 bits of virtual address
For 1-Mbyte page: Upper 12 bits of virtual address
• ASID: Address space identifier
Indicates the process that can access a virtual page.
In single virtual memory mode and user mode, or in multiple virtual memory mode, if the SH
bit is 0, this identifier is compared with the ASID in PTEH when address comparison is
performed.
