Figure 21.16 sample scif initialization flowchart – Renesas SH7781 User Manual
Page 1117
21. Serial Communication Interface with FIFO (SCIF)
Rev.1.00 Jan. 10, 2008 Page 1087 of 1658
REJ09B0261-0100
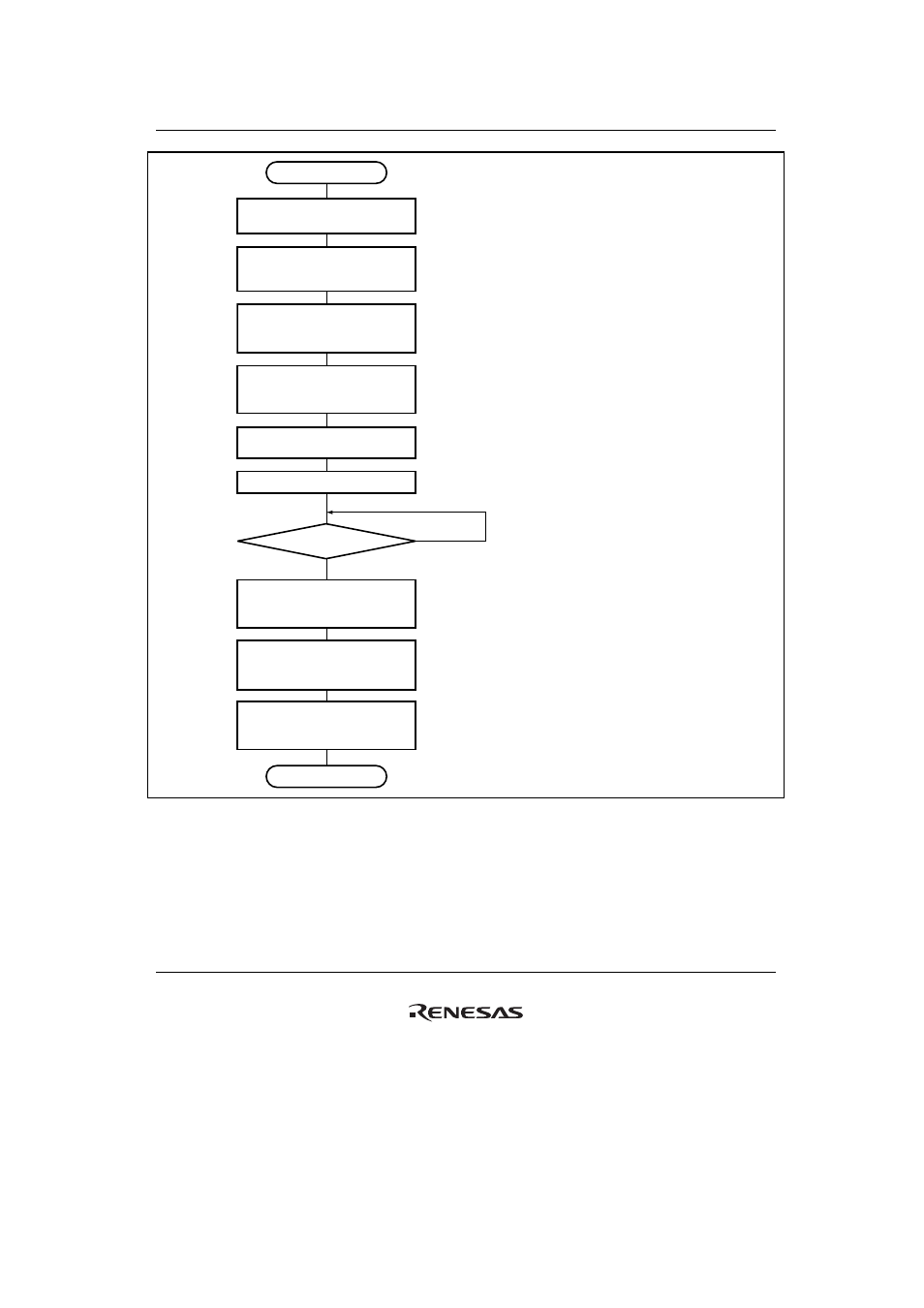
Start of initialization
Clear TE and RE bits
in SCSCR to 0
Set TFCL and RFCL bits
in SCFCR to 1 to clear
the FIFO buffer
After reading BRK, DR,
and ER flags in SCFSR,
write 0 to clear them
Set CKE1 and CKE0 bits
in SCSCR (leaving TE, RE, TIE,
and RIE bits cleared to 0)
Set data transfer format
in SCSMR
Set value in SCBRR
1-bit interval elapsed?
Set RTRG1 and RTRG0 and
TTRG1 and TTRG0 bits in SCFCR,
and clear TFCL and RFCL bits to 0
Set TE and RE bits in SCSCR
to 1, and set TIE, RIE,
and REIE bits
Set external pins to be used
(SCIF_CLK, SCIF_TXD,
and SCIF_RXD)
End of initialization
Wait
No
Yes
Leave the TE and RE bits cleared
to 0 until the initialization almost
ends. Be sure to clear the TIE,
RIE, TE, and RE bits to 0.
Set the CKE1 and CKE0 bits.
Set the data transfer format in
SCSMR.
Write a value corresponding to
the bit rate into SCBRR. This
is not necessary if an external
clock is used. Wait at least one
bit interval after this write before
moving to the next step.
Set the external pins to be used.
Set SCIF_RXD input for reception and
SCIF_TXD output for transmission.
The input/output of the SCIF_CLK pin
must match the setting of the CKE1
and CKE0 bits.
Set the TE or RE bit in SCSCR
to 1. Also set the TIE, RIE, and
REIE bits to enable the SCIF_TXD,
SCIF_RXD, and SCIF_CLK pins to
be used. When transmitting, the
SCIF_TXD pin goes to the mark
state. When receiving in clocked
synchronous mode with the
synchronization clock output (clock
master) selected, a clock starts to
be output from the SCIF_CLK pin
at this point.
[1]
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
Figure 21.16 Sample SCIF Initialization Flowchart
