3 operation in clocked synchronous mode – Renesas SH7781 User Manual
Page 1115
21. Serial Communication Interface with FIFO (SCIF)
Rev.1.00 Jan. 10, 2008 Page 1085 of 1658
REJ09B0261-0100
21.4.3
Operation in Clocked Synchronous Mode
Clocked synchronous mode, in which data is transmitted or received in synchronization with clock
pulses, is suitable for fast serial communication.
Since the transmitter and receiver are independent units in the SCIF, full-duplex communication
can be performed by sharing the clock. Both the transmitter and receiver have a 64-stage FIFO
buffer structure, so that data can be read or written during transmission or reception, enabling
continuous data transmission or reception.
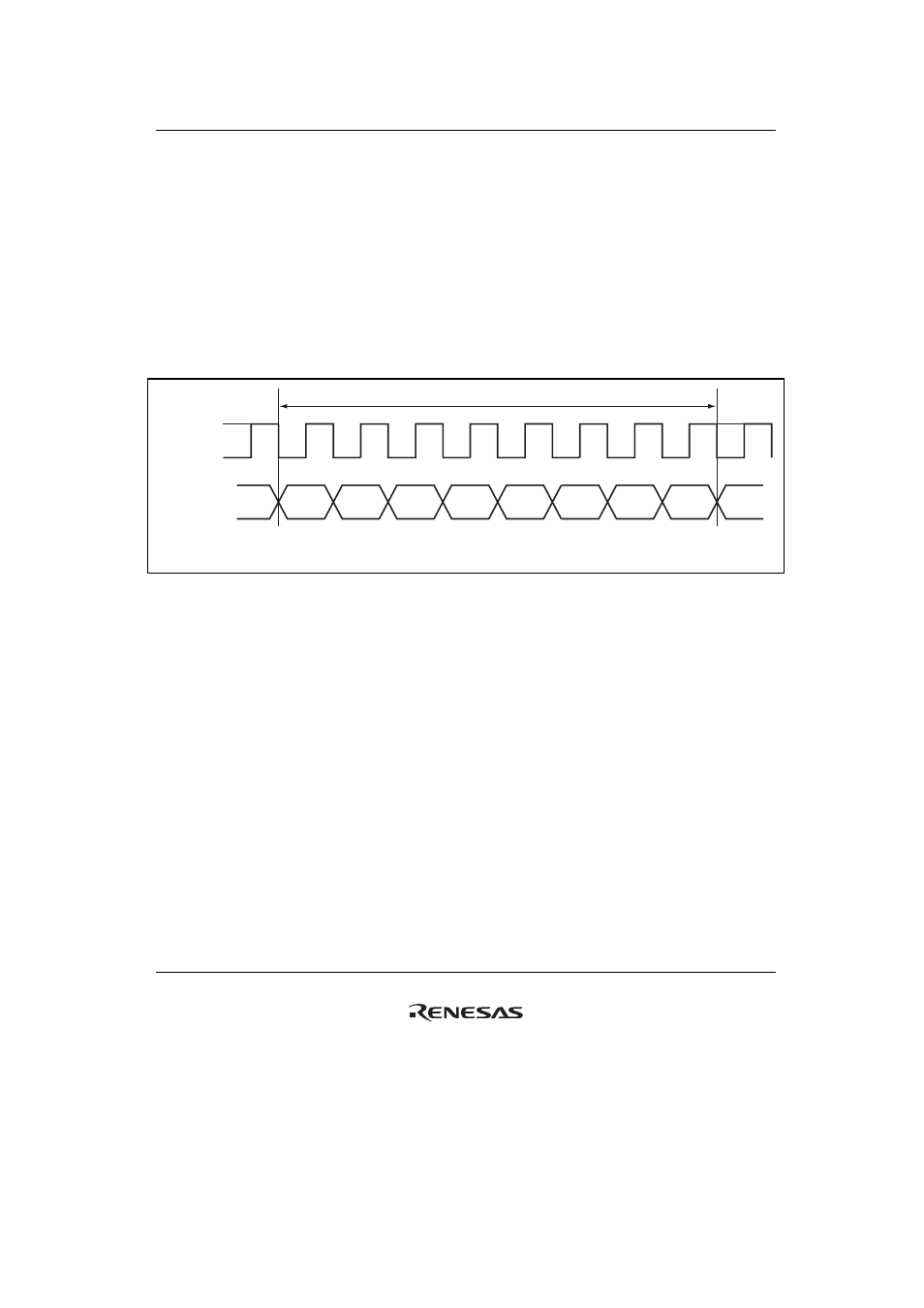
Figure 21.15 shows the general format for clocked synchronous communication.
One unit of transfer data (character or frame)
*
*
Bit 0
Bit 1
Bit 2
Bit 3
Bit 4
Bit 5
Bit 6
Bit 7
Don't care
Don't care
LSB
MSB
Synchronization
clock
Serial data
Note: * High except in continuous transfer
Figure 21.15 Data Format in Clocked Synchronous Communication
In clocked synchronous serial communication, data on the communication line is output from one
fall of the synchronization clock to the next fall. Data is guaranteed to be accurate at the start of
the synchronization clock.
In serial communication, each character is output starting with the LSB and ending with the MSB.
After the MSB is output, the communication line remains in the state of the last data.
In clocked synchronous mode, the SCIF receives data in synchronization with the rise of the
synchronization clock.
