2 mdt, Mdt overview, Mdt -20 – Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 564: Mdt overview -20, 1 mdt overview
RMC100 and RMCWin User Manual
6-20
Controlling Speed from a Tachometer Feedback
Transitioning from Position to Auxiliary Pressure/Force Control
6.2 MDT
6.2.1 MDT Overview
Magnetostrictive displacement transducers are designed for use in rugged industrial
environments. They are non-contact, wear-free, highly reliable, and offer accurate and repeatable
linear position measurement. In the motion control industry magnetostrictive displacement
transducers are typically inserted into hydraulic cylinders for measurement of the cylinders’
extension/retraction position.
Each RMC100 MDT interface module has circuitry for multiple magnetostrictive transducers.
Each axis can be configured for a Start/Stop transducer or a Pulse Width Modulated transducer.
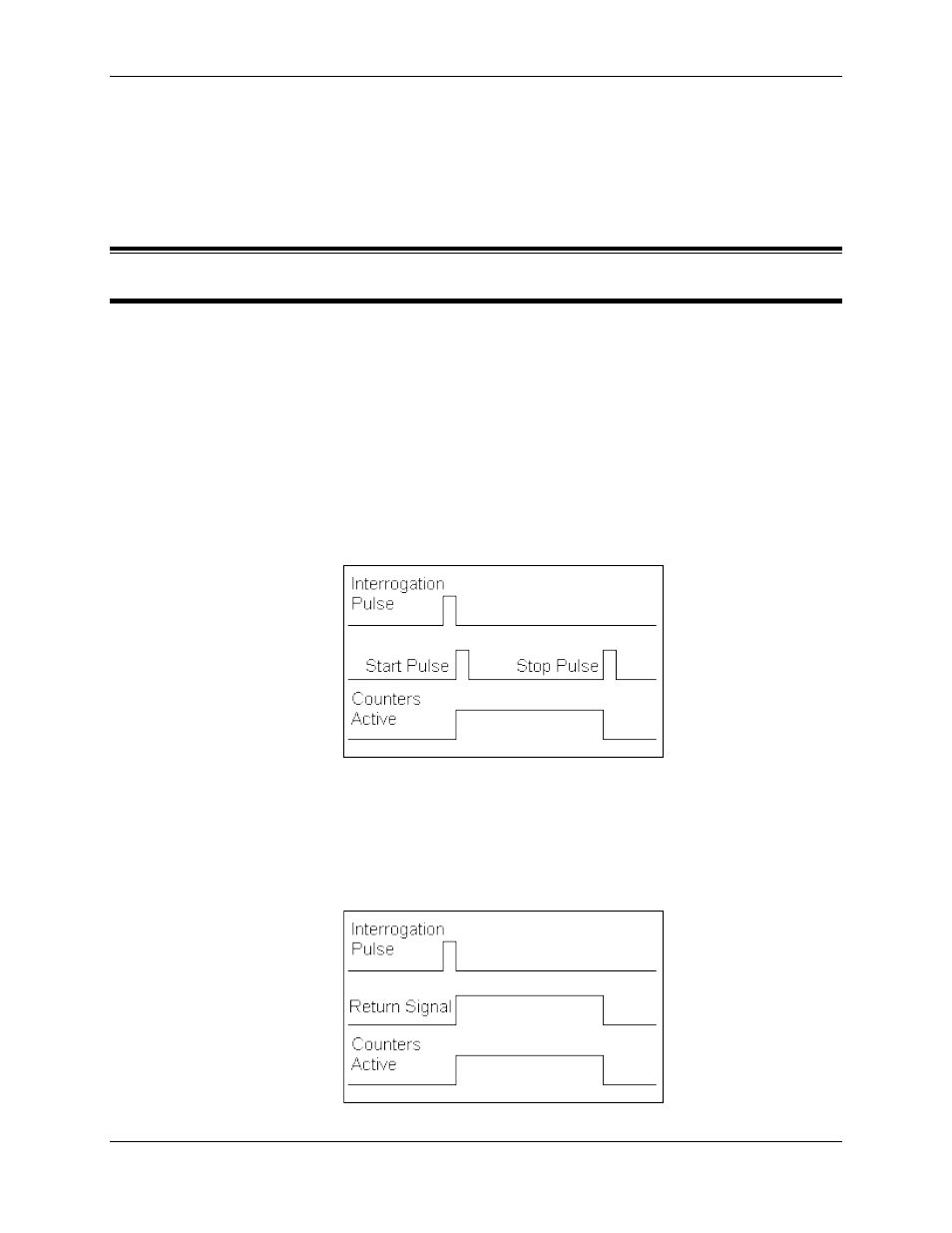
To make a measurement with a Start/Stop transducer, the RMC sends an interrogation pulse to
the transducer. The transducer responds by returning 2 pulses—a Start pulse and a Stop pulse.
The RMC’s internal counters begin to count when the first pulse, Start, is received and stop
counting when the second pulse, Stop, is received. The time between the start pulse and the stop
pulse is proportional to the transducer position.
Start/Stop Pulse Transducer
To make a measurement with a Pulse Width Modulated transducer, the RMC sends an
interrogation pulse to the transducer. The transducer responds with a return signal. The return
signal is high while the transducer is determining its’ position. The counters on the RMC100 MDT
interface module are counting during the time that the return signal is high. The time that the
return signal is high is proportional to the transducer position.
