Rmc ethernet protocols, Rmc ethernet protocols -61, 2 rmc ethernet protocols – Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 311
Ethernet 5.2
Communications
5-61
must go through an IP router. An IP router is a device that sends packets it receives from one
network that are intended for devices on another network to the other network. Here is the
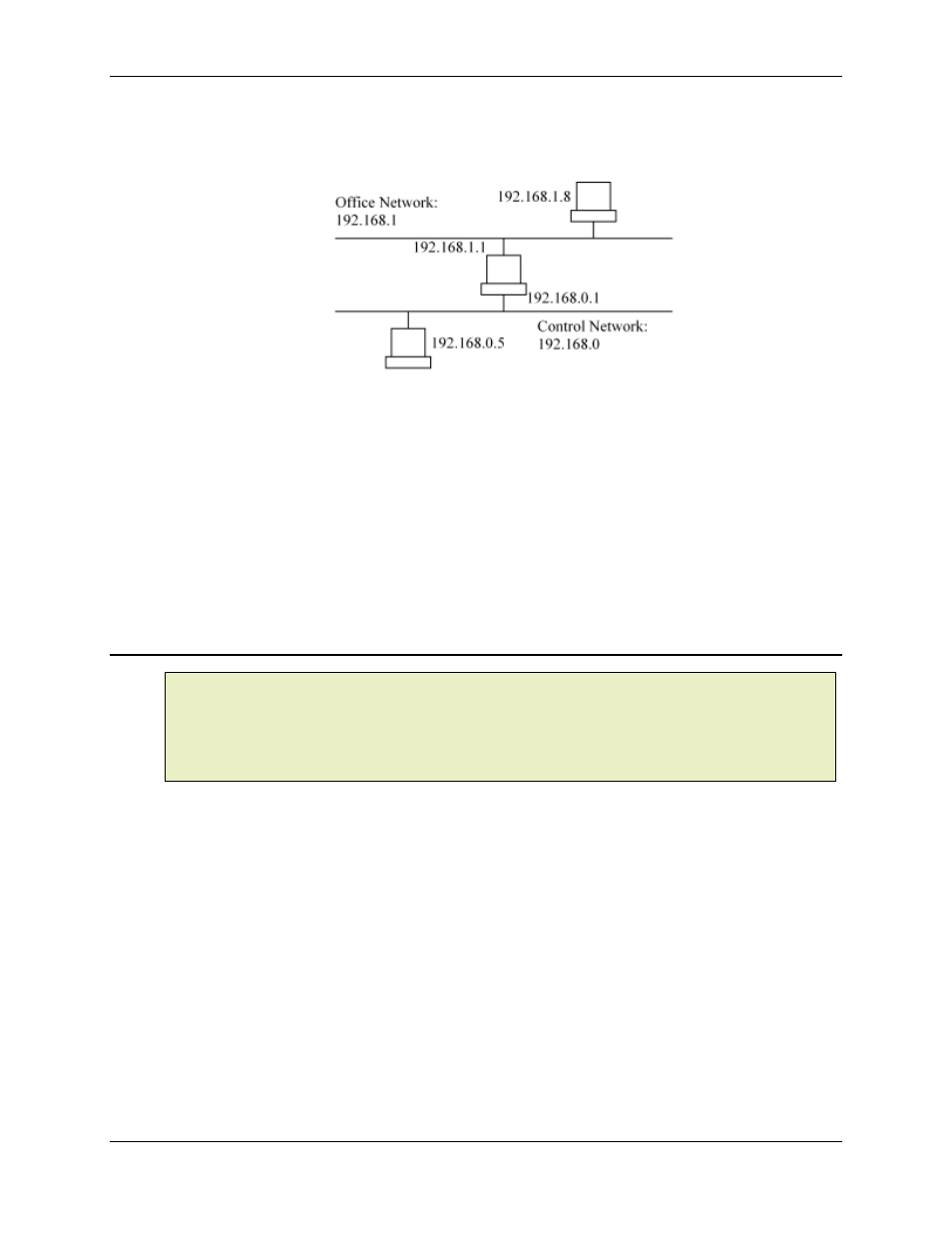
example intranet:
How does 192.168.0.5 send a message to 192.168.1.8? The answer is that it must use a third
parameter called the default gateway. This parameter is the IP address of the router who will take
care of getting the packet to its destination. The rule for most devices is to send packets to
devices with the same network address directly over its network, but to send packets to devices
with a different network address to the default gateway. In the above network, the device at
192.168.0.5 would have a default gateway of 192.168.0.1, and the device at 192.168.1.8 would
have a default gateway of 192.168.1.1.
The default gateway parameter is optional if the device will be on a network that is not connected
to any other networks, or if you have an intranet but do not want to allow the device to
communicate with devices on networks other than its own.
5.2.5.2 RMC Ethernet Protocols
Note:
This section is provided for information only and is not required to be understood for using
the RMC Ethernet module successfully. It is not intended to be a complete authority on
networking. For that, we recommend Internetworking with TCP/IP, Volume I: Principles,
Protocols, and Architecture by Douglas E. Comer (Prentice Hall, 1995). It is intended to be a
brief summary of the architecture and a complete list of low-level protocols supported on the
RMC for use by network administrators.
Networking is often viewed conceptually as layers of protocols. Each layer contains a header,
used to fulfill the purpose of that layer, and data. These layers are set up such that each layer
contains the header and data from the next higher layer within its data area, as shown in the
following diagram:
