Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 508
RMC100 and RMCWin User Manual
5-258
RMC should have returned its response as shown above. The checksum in the response can
then be checked using the CCD function again.
The Mitsubishi-RMC Protocol defines the following three request/response packets. Each is
composed of 16-bit fields, with each being sent low-byte first by the Mitsubishi. Send buffer
locations will be referred to as Dxx00 to Dxx99, where xx are two digits, and receive buffer
locations will be referred to as Dyy00 to Dyy99, where yy are two digits.
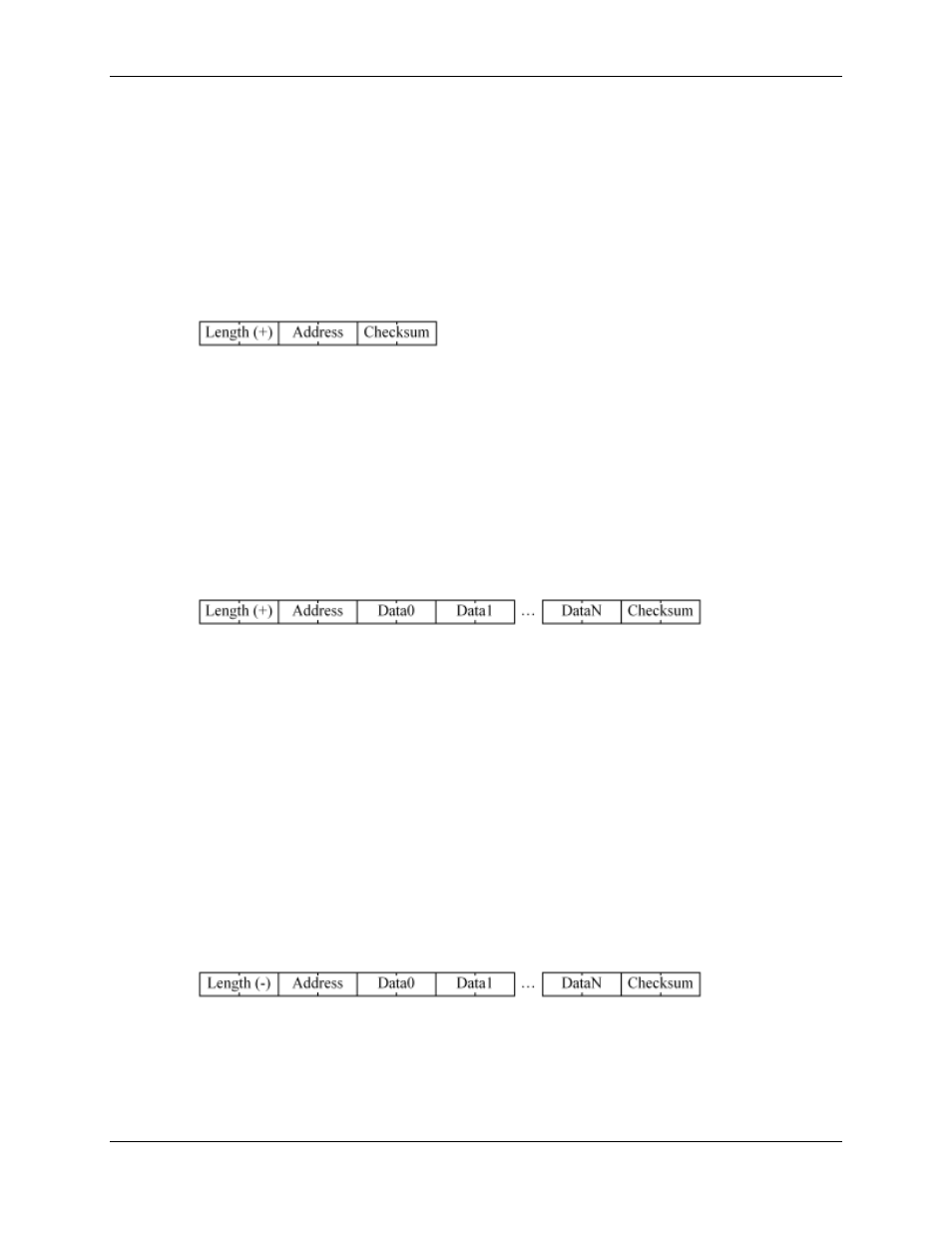
Read Data from the RMC
Request (to RMC):
Dxx00 Length. Gives the number of 16-bit registers to read from the RMC. This number will
be positive, as differentiated from the Write Data request, which uses the
negative of the length.
Dxx01 Address. Gives the address of the first register to read from the RMC. See RMC
Register Map (PROFIBUS-DP) for the addresses of all RMC registers.
Dxx02 Checksum. The checksum is calculated using the PLC's CCD function. The length,
address, and any data is included in the checksum. The CCD function calculates
both a checksum and a parity check; only the checksum is used. Notice that the
CCD function will also modify Dxx03.
Response (from RMC):
Dyy00 Length. Will match the request's length.
Dyy01 Address. Will match the request's address.
Dyy02 Data. First data word read.
Dyy03 Data. Second data word read.
…
Dyy01+N Data. Last data word read.
Dyy02+N Checksum. Validate with the CCD instruction.
Write Data to the RMC
Request (to RMC):
Dxx00 Length. Negative of the number of 16-bit registers to write to the RMC. This number is
negative to differentiate it from the Read Data request, which uses the positive of
the length.
Dxx01 Address. Gives the address of the first register to write in the RMC. See RMC Register
Map (PROFIBUS-DP) for the addresses of all RMC registers.
