Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 351
Ethernet 5.2
Communications
5-101
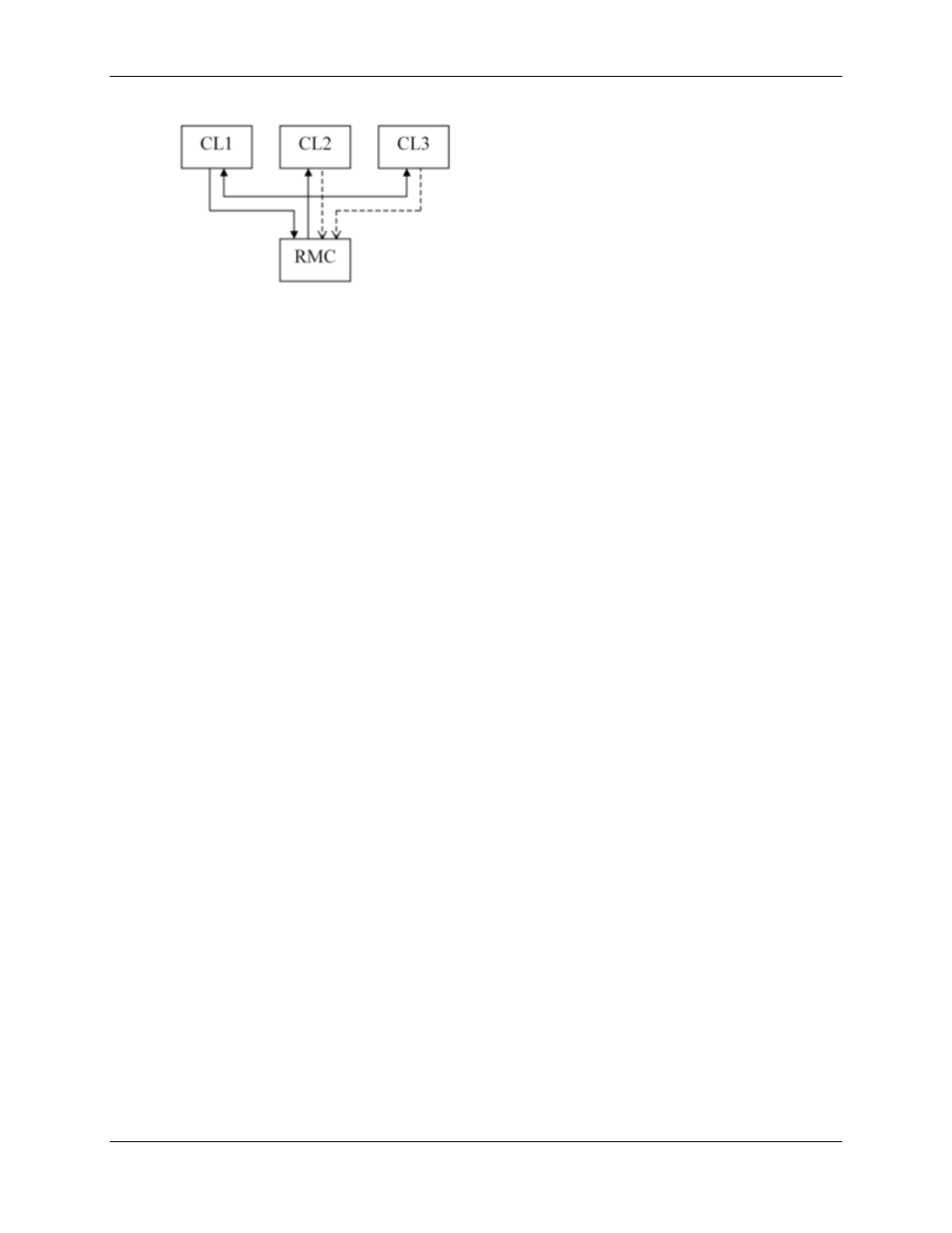
Notice how the RMC produces one data frame that is consumed by all three clients using what is
called a multicast. All three clients produce data frames consumed by the RMC, but only one has
data for the RMC (CL1 in this example). The other two are heartbeat frames to time out old
connections. These heartbeat connections are shown as dotted lines in the above diagram.
Therefore, excluding the heartbeat frames, the RMC only receives one set of data and generates
one set of data each RPI, regardless of how many I/O connections it is handling. So, what data is
included in these frames?
Output Data (from Client):
Offsets and sizes are in 16-bit words (INT on the ControlLogix).
Offset
Size
Description
0
1
Sync Out Register.
See Using the Sync Registers
below for details. This register must be used to issue
commands to the RMC.
1
6
Axis 0 Command.
These six registers correspond to the
Mode, Acceleration, Deceleration, Speed, Command
Value, and Command registers for axis 0. See Using the
Sync Registers below for details on issuing commands.
7
6
Axis 1 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
13
6
Axis 2 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
19
6
Axis 3 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
25
6
Axis 4 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
31
6
Axis 5 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
37
6
Axis 6 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
43
6
Axis 7 Command.
Same as for axis 0.
In addition to the above Output Data, the controlling client also sends a four-byte prefix, which
indicates whether the client is in Run or Program mode. This is used as described in Handling Broken
I/O Connections.
Input Data (to Client):
Offsets and sizes are in 16-bit words (INT on the ControlLogix).
Offset
Size
Description
0
1
Sync In Register.
See Using the Sync Registers below
