Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 451
Modbus Plus 5.3
Communications
5-201
MSTR block, do not add 40000 or 400000 to
indicate holding registers. MSTR blocks expect
the addresses to start at 1, rather than 40001 or
400001.
5th-9th Routing 1-5: The uses of these fields depend on whether
Modbus Plus or Modbus/TCP is being used:
Modbus Plus
: For local addresses, Routing 1 gives
the node address, and Routing 2 gives the data path
(1-8) to use in the node. Routing 3 through 5 are
zeros. For more complicated routing methods, refer
to the section on routing path structure in Modbus
Plus Network Planning and Installation Guide.
Modbus/TCP
: Routing 1 is broken into two bytes: the
MSB holds the Quantum backplane Slot ID of the
NOE module, and the LSB holds the Map Index,
which should be zero for the RMC. Routing 2
through 5 holds the four dot-separated values of the
RMC IP address (e.g. 192.168.0.5).
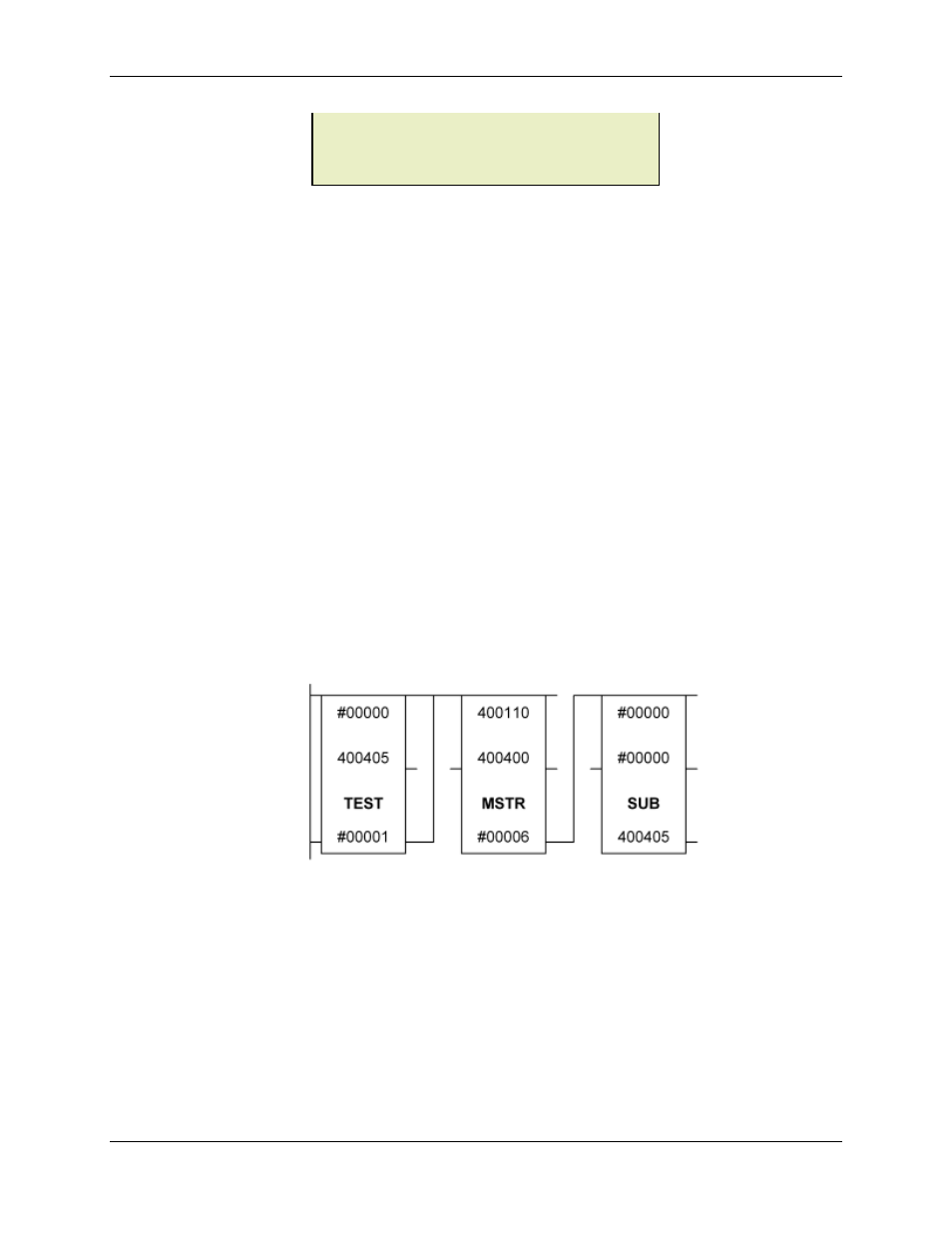
Example (Modbus Plus):
Suppose that you wish to write the six command registers to the first axis of the RMC located at
node address 3 whenever the command is non-zero. The command registers to write are located
in holding registers 400400 through 400005. You must first choose a location for the 9-register
control block. In this example, 400110 to 400118 will be the location. The following network would
be used:
This network waits until the command word at 400405 is non-zero and then triggers the MSTR
block using the control block below. When the MSTR write operation completes, the command
word in 400405 is cleared. Notice that the MSTR enable input is powered for the duration of the
operation.
Register
Content
400110
1 (decimal): Operation type: Write data
400111
0000 (hex): Error status: will be filled in by function
400112
6 (decimal): Length: there are 6 command
