Mstr block peer cop health operation, Mstr block peer cop health operation -204, 5 mstr block peer cop health operation – Delta RMC101 User Manual
Page 454
RMC100 and RMCWin User Manual
5-204
6th-9th
Routing 2-5
: Unused. Set to zeros.
Example
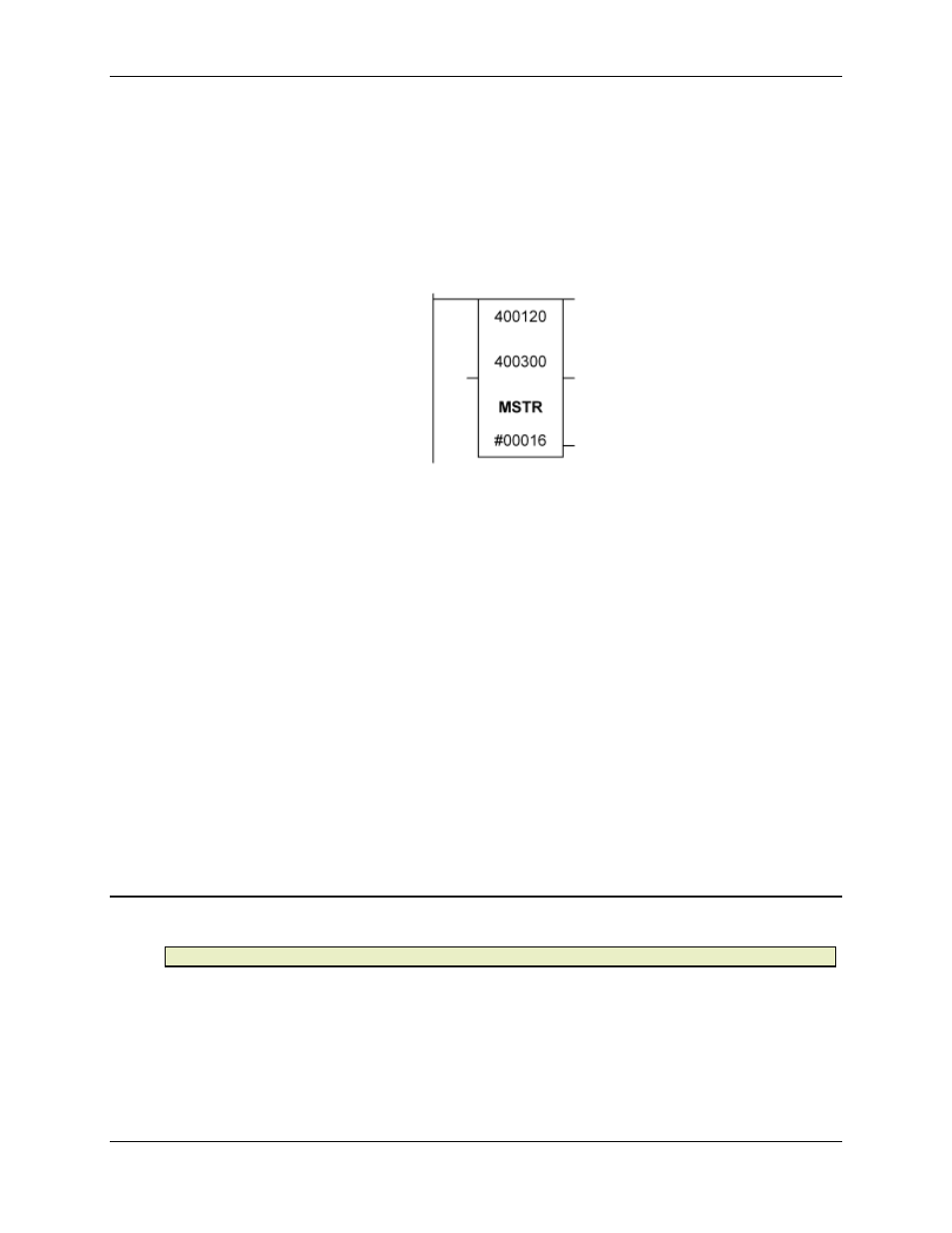
Suppose that you wish to read four global data registers from each of the first four axes of the
RMC located at node address 3. The commands to write are located in holding register 400400
through 400423. You must first choose a location for the 9-register control block. In this example,
400120 to 400128 is the location. The following MSTR block would be used:
As you can see, this function block indicates it will do an operation using the control block
beginning at 400120, using up to 32 registers beginning at 400300. The next step is to set up the
control block:
Register
Content
400120
6 (decimal): Operation type: Read global data
400121
0000 (hex): Error status: filled in by function
400122
16 (decimal): Length: we want the first 16
registers
400123
0 (decimal): Available Registers: filled in by
function
400124
3 (decimal): Routing 1 (Node address)
400125-8
0 (decimal): Unused
5.3.7.5 MSTR Block Peer Cop Health Operation
For general information on the MSTR Block, see Using the MSTR Modicon Ladder Logic Block.
Note:
This operation is only available for Modbus Plus and not Modbus/TCP.
This operation reads a portion of a 12-register Peer Cop Health table. For a description of Peer
Cop, see Using Modicon’s Peer Cop to Read Global Data. This table consists of a collection of
one bit per node address for each of three types of Peer Cop transfer. For the RMC, only the
Global Input portion is useful since Specific Inputs and Outputs are not used. Each bit that is set
indicates that the device with that address is connected using Peer Cop:
