3 free buffer pools, Figure 30-44. free buffer pool structure, Free buffer pools -69 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 989: Receive global buffer allocation example -69, Free buffer pool structure -69
ATM Controller and AAL0, AAL1, and AAL5
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
30-69
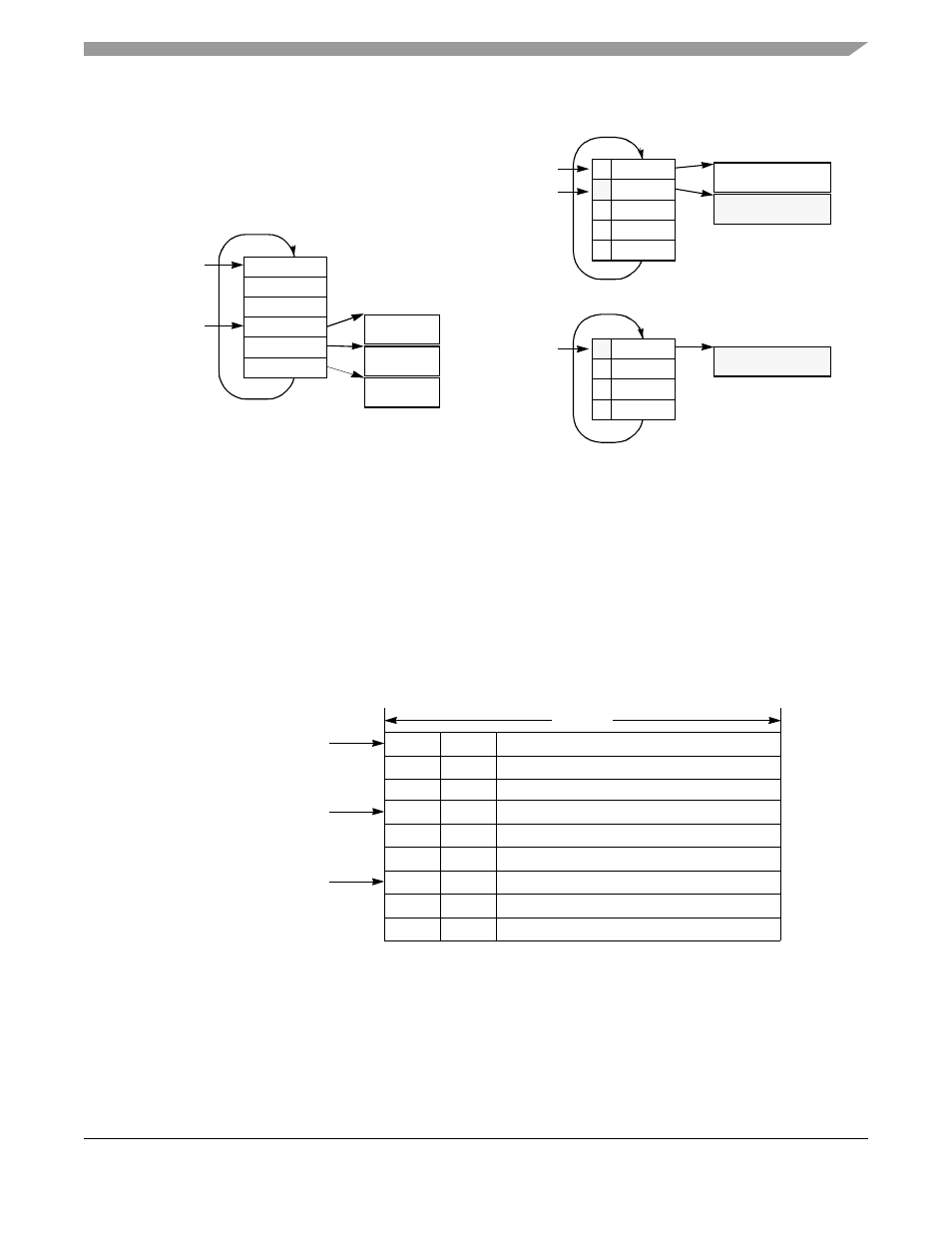
Figure 30-43. Receive Global Buffer Allocation Example
30.10.5.2.3
Free Buffer Pools
As
shows, when a buffer pointer is fetched from a pool, the CP clears the entry’s valid bit
and increments FBP#_PTR. After the CP uses an entry with the wrap bit set (W = 1), it returns to the first
entry in the pool. After a buffer pointer is returned to the pool, the user should set V to indicate that the
entry is valid. If the CP tries to read an invalid entry (V = 0), the buffer pool is out of free buffers; the
global-buffer-pool-busy event is then set in FCCE[GBPB] and a busy interrupt is sent to the interrupt
queue specifying the ATM channel code associated with the pool.
Figure 30-44. Free Buffer Pool Structure
describes the structure of a free buffer pool entry.
Buffer 1 of FBP1
Buffer 2 of FBP1
Ch1 RxBD Table
0
BD 1
1
BD 2
1
BD 3
1
BD 4
1
BD 5
RBD_BASE
RBD_Offset
Buffer 3 of FBP1
Ch4 RxBD Table
1
BD 1
1
BD 2
1
BD 3
1
BD 4
RBD_BASE,
RBD_Offset
Free Buffer Pool 1
FBP1_PTR
FBP1_BASE
Pointer 1
Pointer 2
Pointer 3
Pointer 4
Pointer 5
Pointer 6
Buffer 4
Buffer 5
Buffer 6
Notes: Buffers 2 and 3 are receiving data. After buffer 1 is processed, it can be returned to the pool.
V = 1
W = 0
Buffer Pointer
V = 1
W = 0
Buffer Pointer
V = 1
W = 0
Buffer Pointer
V = 0
W = 0
Invalid
V = 0
W = 0
Invalid
V = 0
W = 0
Invalid
V = 1
W = 0
Buffer Pointer
V = 1
W = 0
Buffer Pointer
V = 1
W = 1
Buffer Pointer
FBP#_BASE
Software (Core) Pointer
FBP#_PTR
Word
