2 powerquicc ii-specific registers, Table 2-1. hid0 field descriptions (continued), Powerquicc ii-specific registers -11 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 129: Hardware implementation register 0 (hid0) -11, Hid0 field descriptions -11
G2 Core
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
2-11
2.3.1.2
PowerQUICC II-Specific Registers
The set of registers specific to the MPC603e are also shown in
. Most of these are described in
the G2 Core Reference Manual and are implemented in the PowerQUICC II as follows:
•
MMU software table search registers: DMISS, DCMP, HASH1, HASH2, IMISS, ICMP, and RPA.
These registers facilitate the software required to search the page tables in memory.
•
IABR. This register facilitates the setting of instruction breakpoints.
The hardware implementation-dependent registers (HIDx) are implemented differently in the
PowerQUICC II, and they are described in the following subsections.
2.3.1.2.1
Hardware Implementation-Dependent Register 0 (HID0)
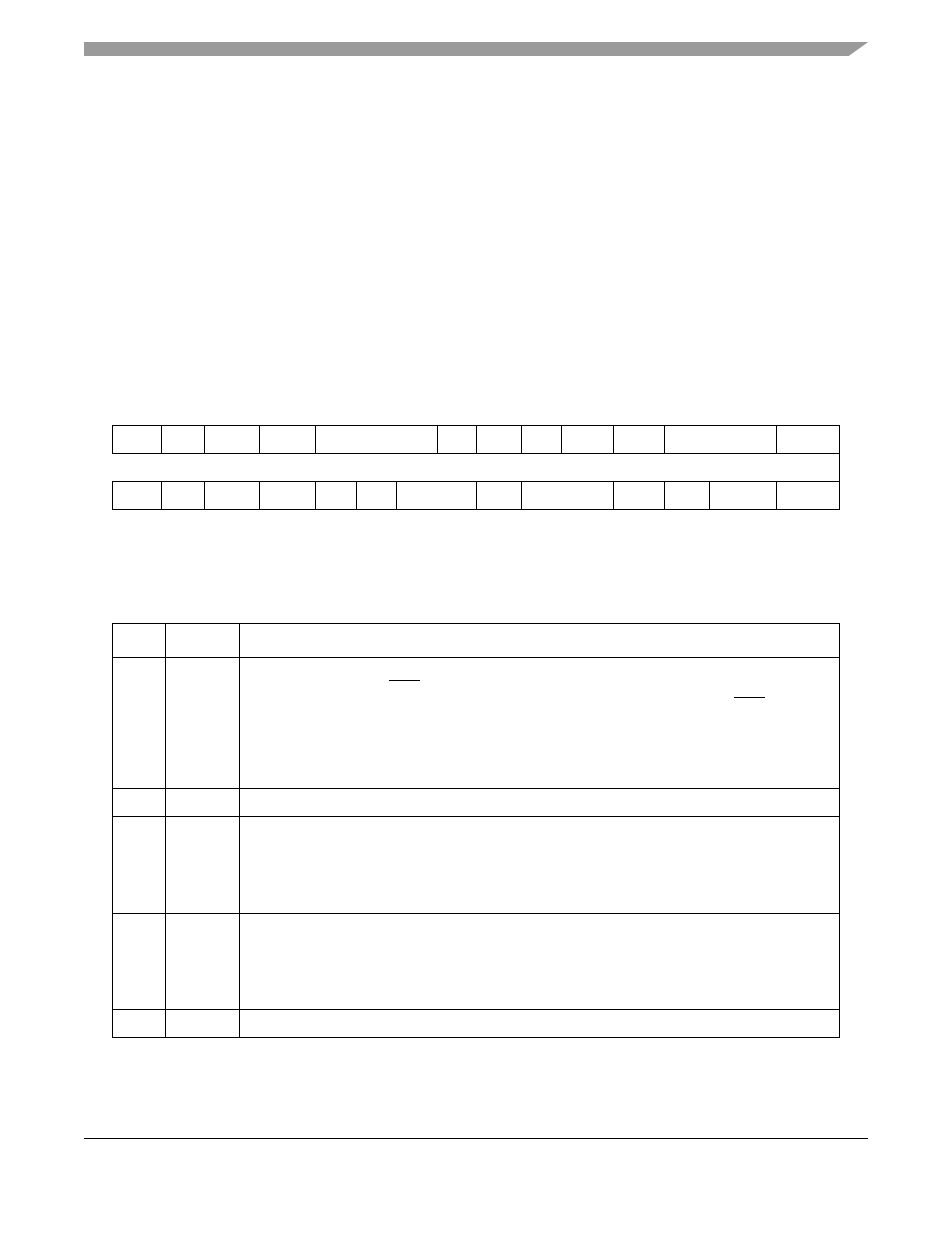
shows the PowerQUICC II implementation of HID0.
shows the bit definitions for HID0.
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
14
15
EMCP
–
EBA
EBD
–
PAR DOZE
–
SLEEP
DPM
–
NHR
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
ICE
DCE
ILOCK DLOCK ICFI DCFI
–
IFEM
–
FBIOB
ABE
–
NOOPTI
Figure 2-3. Hardware Implementation Register 0 (HID0)
Table 2-1. HID0 Field Descriptions
Bits
Name
Description
0
EMCP
Enable machine check input pin
0 The assertion of the MCP does not cause a machine check exception.
1 Enables the entry into a machine check exception based on assertion of the MCP input,
detection of a Cache Parity Error, detection of an address parity error, or detection of a data
parity error.
Note that the machine check exception is further affected by MSR[ME], which specifies whether
the processor checkstops or continues processing.
1
—
Reserved
2
EBA
Enable/disable 60x bus address parity checking
0 Prevents address parity checking.
1 Allows a address parity error to cause a checkstop if MSR[ME] = 0 or a machine check
exception if MSR[ME] = 1.
EBA and EBD let the processor operate with memory subsystems that do not generate parity.
3
EBD
Enable 60x bus data parity checking
0 Parity checking is disabled.
1 Allows a data parity error to cause a checkstop if MSR[ME] = 0 or a machine check exception
if MSR[ME] = 1.
EBA and EBD let the processor operate with memory subsystems that do not generate parity.
4–6
—
Reserved
