3 connecting the powerquicc ii to fast ethernet, Connecting the powerquicc ii to fast ethernet -4, Connecting the powerquicc ii to ethernet -4 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 1200
Fast Ethernet Controller
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
35-4
Freescale Semiconductor
— Busy (out of buffers)
•
Error counters
— Discarded frames (out of buffers or overrun occurred)
— CRC errors
— Alignment errors
•
Internal and external loopback mode
•
Supports Fast Ethernet in duplex mode
•
Supports pause flow control frames
•
Support of out-of-sequence transmit queue (for flow-control frames)
•
External buffer descriptors (BDs)
35.3
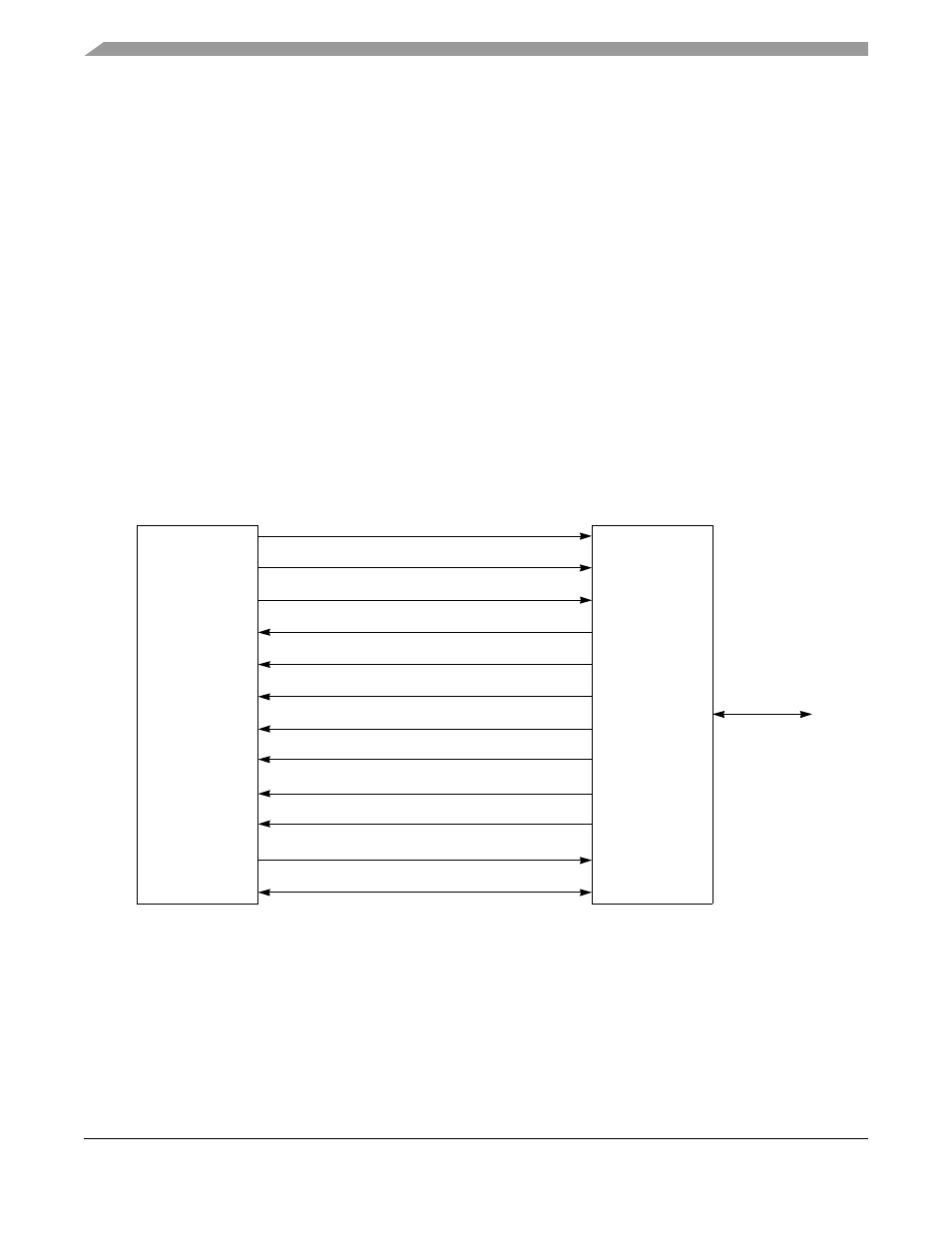
Connecting the PowerQUICC II to Fast Ethernet
shows the basic components of the media-independent interface (MII) and the signals required
to make the Fast Ethernet connection between the PowerQUICC II and a PHY.
Figure 35-3. Connecting the PowerQUICC II to Ethernet
Each FCC has 18 signals, defined by the IEEE 802.3u standard, for connecting to an Ethernet PHY. The
two management signals (MDC and MDIO) required by the MII should be implemented separately using
the parallel I/O.
Transmit Error (TX_ER)
Transmit Nibble Data 0–3 (TXD[0–3])
Transmit Enable (TX_EN)
Transmit Clock (TX_CLK)
Collision Detect (COL)
Receive Nibble Data (RXD[0–3])
Receive Error (RX_ER)
Receive Clock (RX_CLK)
Receive Data Valid (RX_DV)
Carrier Sense Output (CRS)
Management Data I/O1 (MDIO)
Management Data Clock1 (MDC)
PowerQUICC II
Fast Ethernet
PHY
Medium
Media-Independent Interface (MII)
1
The management signals (MDC and MDIO) can be common to all of the Fast Ethernet connections in
the system, assuming that each PHY has a different management address. Use parallel I/O port pins to
implement MDC and MDIO. (The I
2
C controller cannot be used for this function.)
