Figure 14-5. risc time-stamp register (rtsr), 10 risc microcode revision number, Table 14-5. risc microcode revision number – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 560: 4 command set, Risc microcode revision number -12, Command set -12, Risc time-stamp register (rtsr) -12, Figure 14-5
Communications Processor Module Overview
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
14-12
Freescale Semiconductor
After reset, setting RTSCR[RTE] causes the time stamp to start counting microseconds from zero.
14.3.10 RISC Microcode Revision Number
Associated with each version of CPM microcode, is a number (REV_NUM) that uniquely identifies that
specific microcode. This number is hard-coded into the microcode which is stored in the CPM's internal
ROM. At power-up, the Communication Processor (CP) reads this number, and proceeds to store it into
the miscellaneous parameter RAM portion of the CPM's internal dual-port Ram (DPR). The user can then
access this location in DPR to determine which version of CPM microcode is contained in that device.
describes which microcode version numbers are associated with each silicon revision.
14.4
Command Set
The core issues commands to the CP by writing to the CP command register (CPCR). The CPCR rarely
needs to be accessed. For example, to terminate the transmission of an SCC’s frame without waiting until
the end, a
STOP
TX
command must be issued through the CP command register (CPCR).
0
15
Field
Time Stamp
Reset
—
R/W
R
Addr
16
31
Field
Time Stamp
Reset
—
R/W
R
Addr
0X119E2
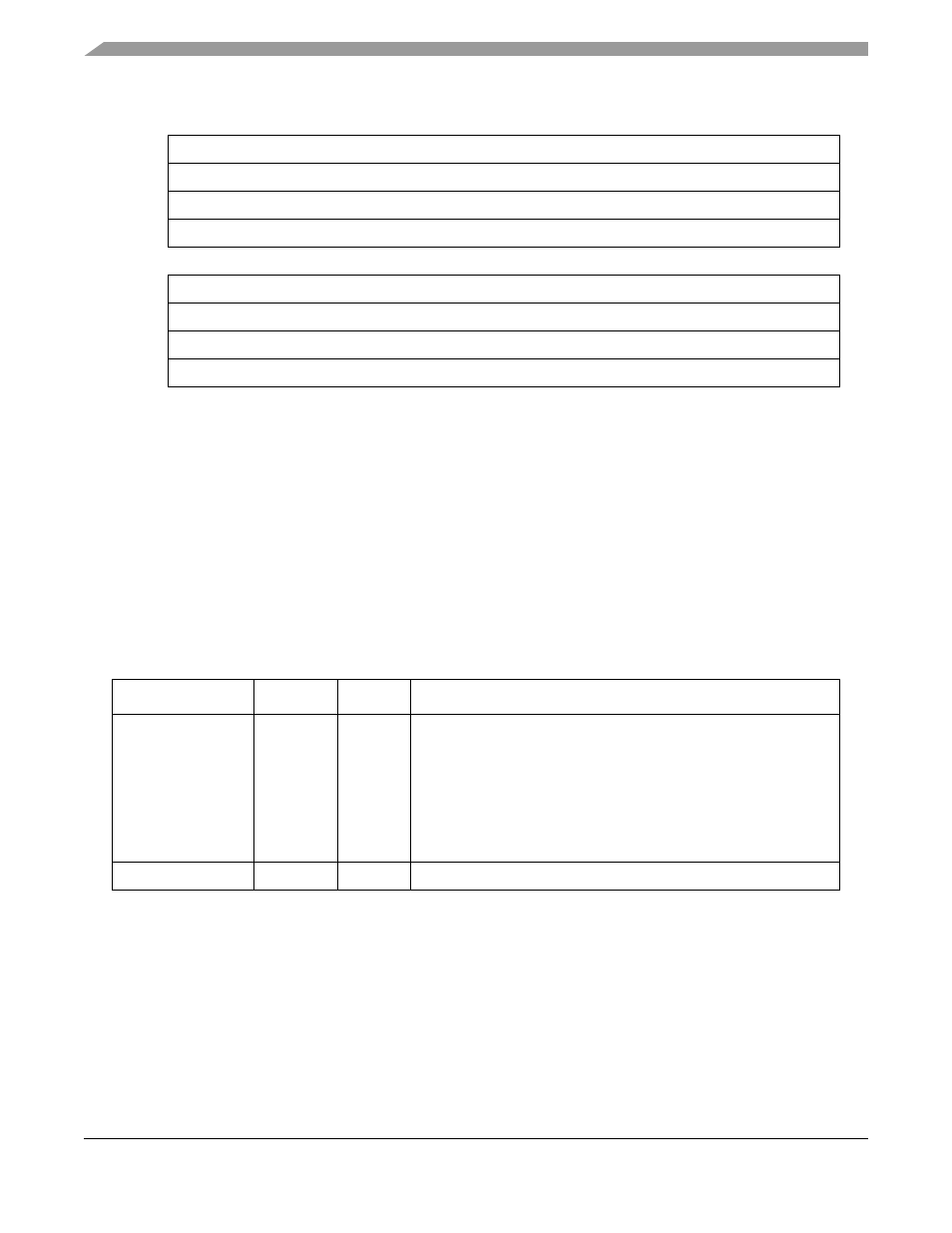
Figure 14-5. RISC Time-Stamp Register (RTSR)
Table 14-5. RISC Microcode Revision Number
Address
Name
Width
Description
RAM Base + 0x8AF0
REV_NUM Hword
Microcode revision number. If working with newer silicon than what is
shown below, consult the product page on the web.
For .29
µm (HiP3) devices:
Rev A.1—0x0001
Rev
B.2—0x003B
Rev C.2—0x007B
For .25
µm (HiP4) devices: Rev A.0—0x000D
Rev
B.1—0x002D
Rev
C.0—0x002D
RAM Base + 0x8AF2
—
Hword
Reserved
