1 encoding data with a dpll, Figure 20-15. dpll encoding examples, Encoding data with a dpll -23 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 701: Dpll encoding examples -23
Serial Communications Controllers (SCCs)
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
20-23
The DPLL can also be used to invert the data stream of a transfer. This feature is available in all encodings,
including standard NRZ format. Also, when the transmitter is idling, the DPLL can either force TXD high
or continue encoding the data supplied to it.
The DPLL is used for UART encoding/decoding, which gives the option of selecting the divide ratio in
the UART decoding process (8
Ч, 16Ч, or 32×). Typically, 16× is used.
Note the 1:4 system clock/serial clock ratio does not apply when the DPLL is used to recover the clock in
the 8
Ч, 16Ч, or 32× modes. Synchronization occurs internally after the DPLL generates the Rx clock.
Therefore, even the fastest DPLL clock generation (the 8
× option) easily meets the required 1:4 ratio
clocking limit.
20.3.6.1
Encoding Data with a DPLL
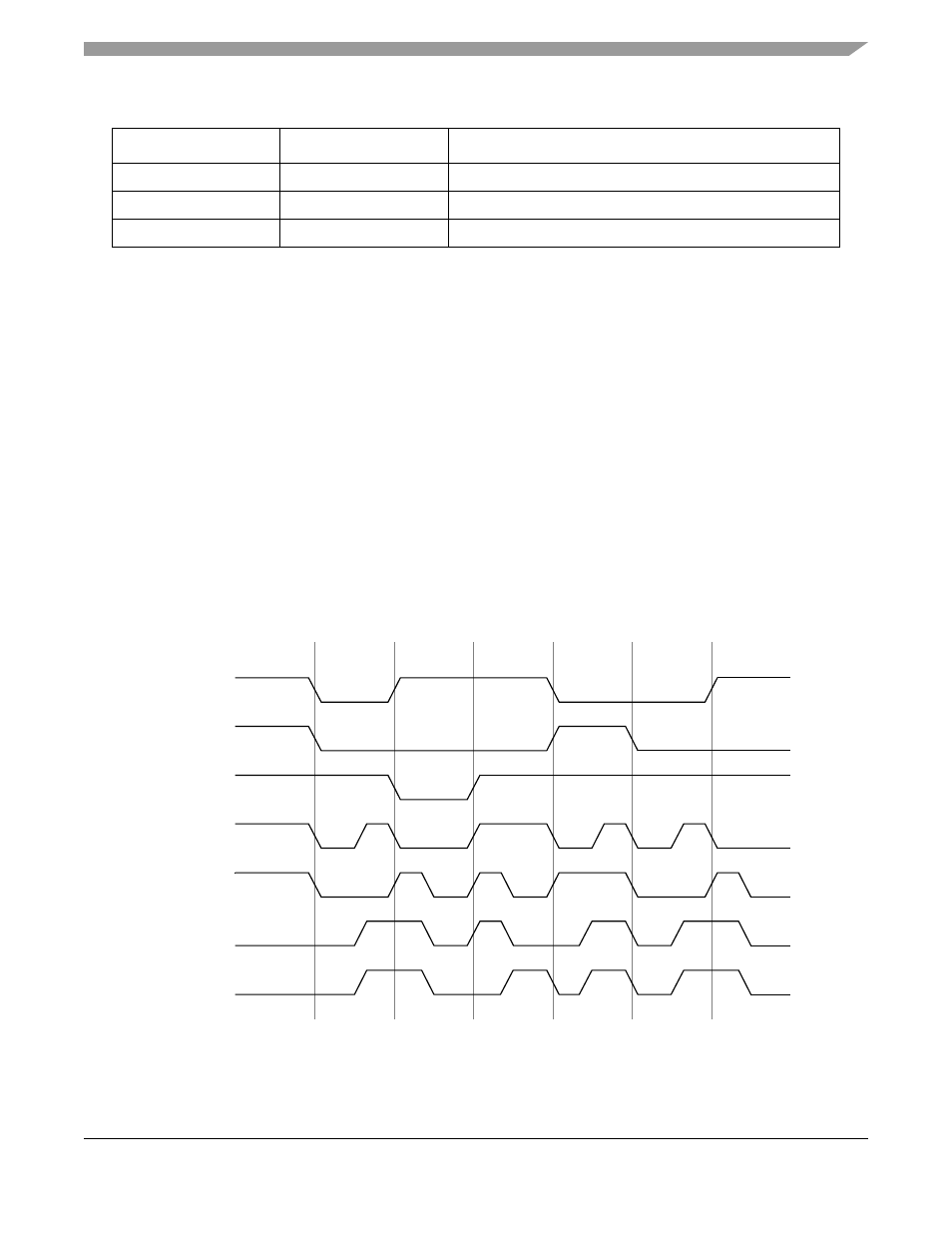
Each SCC contains a DPLL unit that can be programmed to encode and decode the SCC data as NRZ,
NRZI Mark, NRZI Space, FM0, FM1, Manchester, and Differential Manchester.
shows the
different encoding methods.
Figure 20-15. DPLL Encoding Examples
FM1
All zeros
8-bit
Manchester
101010...10
8-bit
Differential Manchester
All ones
8-bit
Table 20-8. Preamble Requirements (continued)
Decoding Method
Preamble Pattern
Minimum Preamble Length Required
Data
NRZ
NRZI Mark
NRZI Space
FM0
FM1
Manchester
Differential
Manchester
0
1
1
0
0
1
