Table 38-5. spi parameter ram memory map, Spi parameter ram memory map -11, Table 38-5 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 1257
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
38-11
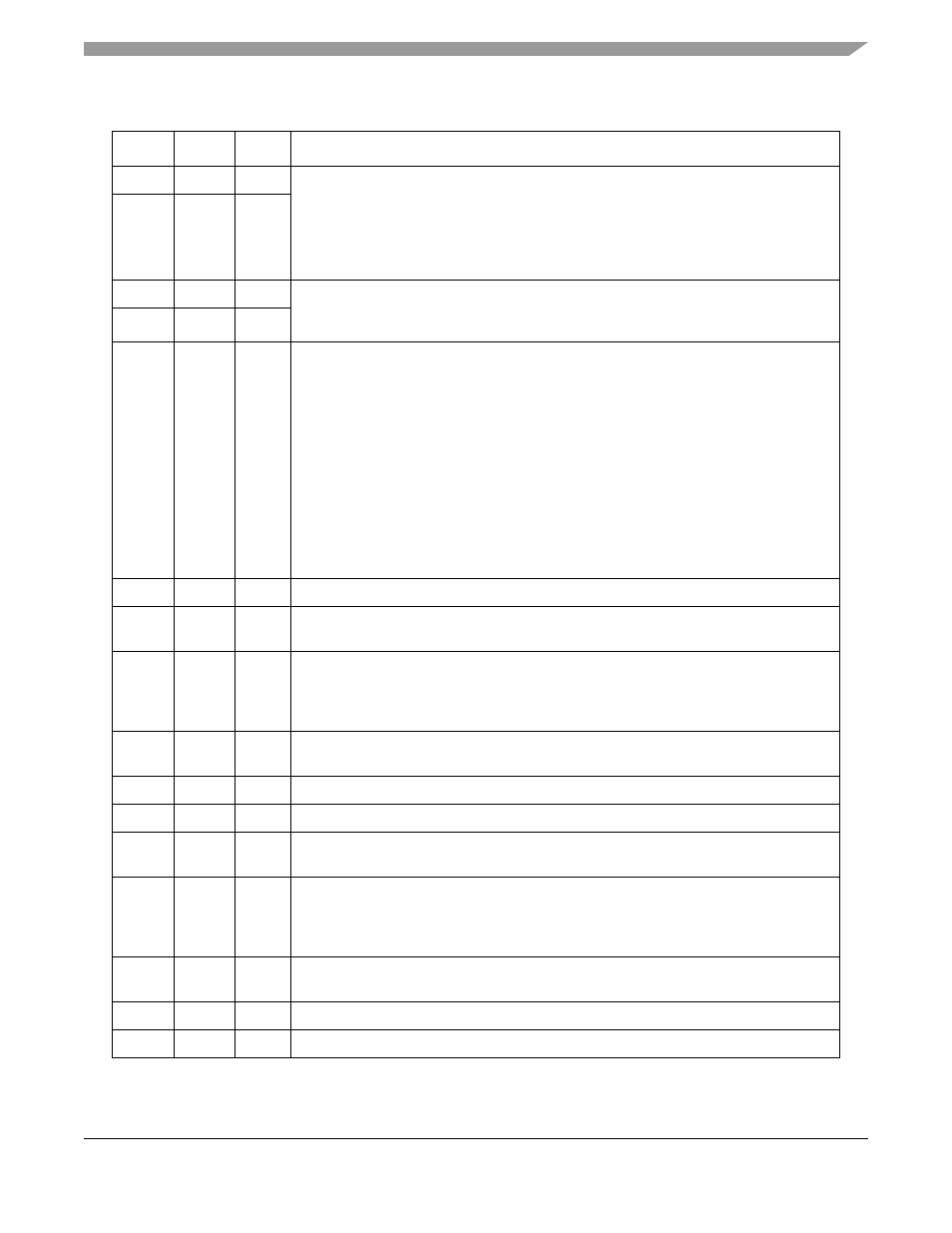
Table 38-5. SPI Parameter RAM Memory Map
Offset
1
1
From the pointer value programmed in SPI_BASE at IMMR + 0x89FC.
Name
Width
Description
0x00
RBASE
Hword Rx/Tx BD table base address. Indicate where the BD tables begin in the dual-port RAM.
Setting Rx/TxBD[W] in the last BD in each BD table determines how many BDs are
allocated for the Tx and Rx sections of the SPI. Initialize RBASE/TBASE before enabling
the SPI. Furthermore, do not configure BD tables of the SPI to overlap any other active
controller’s parameter RAM.
RBASE and TBASE should be divisible by eight.
0x02
TBASE
Hword
0x04
RFCR
Byte
Rx/Tx function code registers. The function code registers contain the transaction
specification associated with SDMA channel accesses to external memory. See
Section 38.5.1, “Receive/Transmit Function Code Registers (RFCR/TFCR)
.”
0x05
TFCR
Byte
0x06
MRBLR
Hword Maximum receive buffer length. The SPI has one MRBLR entry to define the maximum
number of bytes the PowerQUICC II writes to a Rx buffer before moving to the next buffer.
The PowerQUICC II can write fewer bytes than MRBLR if an error or end-of-frame
occurs, but never exceeds the MRBLR value. User-supplied buffers should be no smaller
than MRBLR.
Tx buffers are unaffected by MRBLR and can have varying lengths; the number of bytes
to be sent is programmed in TxBD[Data Length].
MRBLR is not intended to be changed while the SPI is operating. However it can be
changed in a single bus cycle with one 16-bit move (not two 8-bit bus cycles
back-to-back). The change takes effect when the CP moves control to the next RxBD.
To guarantee the exact RxBD on which the change occurs, change MRBLR only while
the SPI receiver is disabled. MRBLR should be greater than zero; it should be an even
number if the character length of the data exceeds 8 bits.
0x08
RSTATE
Word
Rx internal state.
2
Reserved for CP use.
0x0C
—
Word
The Rx internal data pointer
2
is updated by the SDMA channels to show the next
address in the buffer to be accessed.
0x10
RBPTR
Hword RxBD pointer. Points to the current Rx BD being processed or to the next BD to be
serviced when idle. After a reset or when the end of the BD table is reached, the CP
initializes RBPTR to the RBASE value. Most applications should not modify RBPTR, but
it can be updated when the receiver is disabled or when no Rx buffer is in use.
0x12
—
Hword The Rx internal byte count
2
is a down-count value that is initialized with the MRBLR
value and decremented with every byte the SDMA channels write.
0x14
—
Word
Rx temp.
2
Reserved for CP use.
0x18
TSTATE
Word
Tx internal state.
2
Reserved for CP use.
0x1C
—
Word
The Tx internal data pointer
2
is updated by the SDMA channels to show the next address
in the buffer to be accessed.
0x20
TBPTR
Hword TxBD pointer. Points to the current Tx BD during frame transmission or the next BD to be
processed when idle. After reset or when the end of the Tx BD table is reached, the CP
initializes TBPTR to the TBASE value. Most applications do not need to modify TBPTR,
but it can be updated when the transmitter is disabled or when no Tx buffer is in use.
0x22
—
Hword The Tx internal byte count
2
is a down-count value initialized with TxBD[Data Length] and
decremented with every byte read by the SDMA channels.
0x24
—
Word
Tx temp.
2
Reserved for CP use.
0x34
—
Word
SDMA temp.
