2 receive buffer operation, Receive buffer operation -37, Transmit buffers and bd table example -37 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 1053
ATM AAL1 Circuit Emulation Service
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
31-37
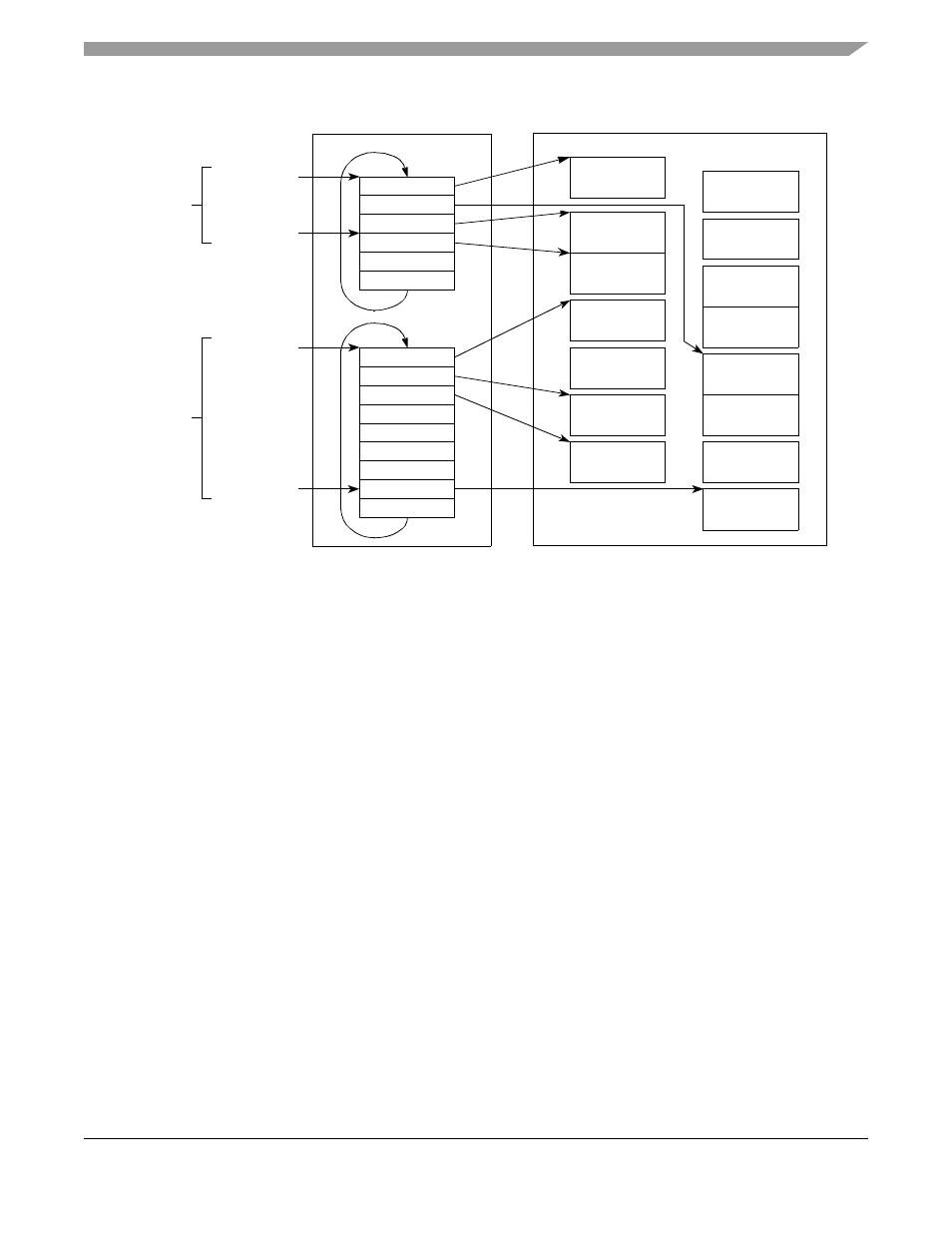
Figure 31-26. Transmit Buffers and BD Table Example
31.11.2 Receive Buffer Operation
The user prepares a table of BDs pointing to the receive buffers. The address of the first BD is put in the
channel’s RCT[RBD_BASE]. When an ATM cell arrives, the CP opens the first BD in the table and starts
filling its associated buffer with received data. When the current buffer is full, the CP increments
RBD_OFFSET, which is the offset to the current BD from RBD_BASE, and reads the next BD in the table.
If the BD is empty (RxBD[E] = 1), the CP continues receiving. If the BD is not empty, a busy condition
has occurred and the ATM receiver optionally issues an interrupt to the event queue.
Note that when the ATM receiver is in CES mode, the buffer-not-ready (busy) state is handled by an
automatic slip control mechanism; see
Section 31.5, “ATM-to-TDM Adaptive Slip Control.”
BD memory space
TBD_Base
Tx BD table
of ch 1
Tx BD table
of ch 4
TBD_Offset
TBD_Base
TBD_Offset
Pointers
TxBD 1
TxBD 2
TxBD 3
TxBD 4
TxBD 5
TxBD 6
TxBD 7
TxBD 8
TxBD 9
TxBD 1
TxBD 2
TxBD 3
TxBD 4
TxBD 5
TxBD 6
Tx buffer 3 of
channel 1
Tx buffer 4 of
channel 1
Tx buffer 1 of
channel 4
Tx buffer 2 of
channel 4
Tx buffer 3 of
channel 4
Tx buffer 2 of
channel 1
Tx buffer 8 of
channel 4
•
•
•
•
•
•
Tx buffer 1 of
channel 1
Data memory space
from ch 1
entry of
TCT
Pointers
from ch 4
entry of
TCT
