1 cp command register (cpcr), Figure 14-6. cp command register (cpcr), Cp command register (cpcr) -13 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 561: Cp command register field descriptions -13
Communications Processor Module Overview
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
14-13
14.4.1
CP Command Register (CPCR)
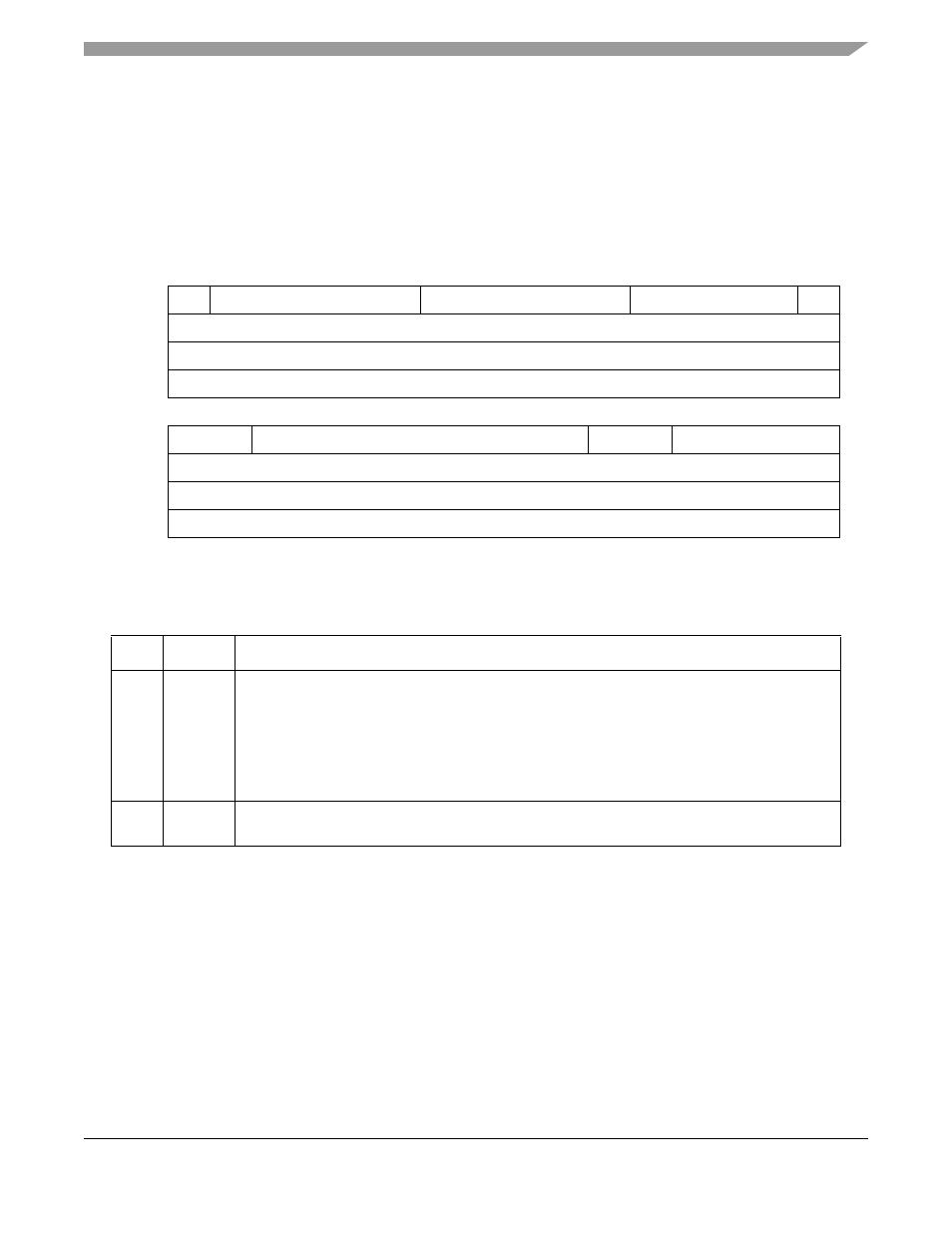
The core should set CPCR[FLG], shown in
, when it issues a command and the CP clears FLG
after completing the command, thus indicating to the core that it is ready for the next command.
Subsequent commands to the CPCR can be given only after FLG is clear. However, the software reset
command issued by setting RST does not depend on the state of FLG, but the core should still set FLG
when setting RST.
describes CPCR fields.
0
1
5
6
10
11
15
Field RST
PAGE
Sub-block code (SBC)
—
FLG
Reset
0000_0000_0000_0000
R/W
R/W
Addr
16
17
18
25
26
27
28
31
Field
—
MCC channel number (MCN)
—
OPCODE
Reset
0000_0000_0000_0000
R/W
R/W
Addr
0x119C2
Figure 14-6. CP Command Register (CPCR)
Table 14-6. CP Command Register Field Descriptions
Bit
Name
Description
0
RST
Software reset command. Set by the core and cleared by the CP. When this command is executed,
RST and FLG bit are cleared within two general system clocks. The CPM reset routine is
approximately 60 clocks long, but the user can begin initialization of the CPM immediately after
this command is issued.
RST is useful when the core wants to reset the registers and parameters for all the channels
(FCCs, SCCs, SMCs, SPI, I
2
C, MCC) as well as the CP and RISC timer tables. However, this
command does not affect the serial interface (SI
x
) or parallel I/O registers.
1–5
PAGE
Indicates the parameter RAM page number associated with the sub-block being served. See the
SBC description for page numbers.
