Chapter 17 baud-rate generators (brgs), Baud-rate generators (brgs), Chapter 17 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 631: Baud-rate generator (brg) block diagram -1, Chapter 17, “baud-rate generators (brgs)
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
17-1
Chapter 17
Baud-Rate Generators (BRGs)
The CPM contains eight independent, identical baud-rate generators (BRGs) that can be used with the
FCCs, SCCs, and SMCs. The clocks produced by the BRGs are sent to the bank-of-clocks selection logic,
where they can be routed to the controllers. In addition, the output of a BRG can be routed to a pin to be
used externally. The following is a list of BRGs’ main features:
•
Eight independent and identical BRGs
•
On-the-fly changes allowed
•
Each BRG can be routed to one or more FCCs, SCCs, or SMCs
•
A 16x divider option allows slow baud rates at high system frequencies
•
Each BRG contains an autobaud support option
•
Each BRG output can be routed to a pin (BRGOn)
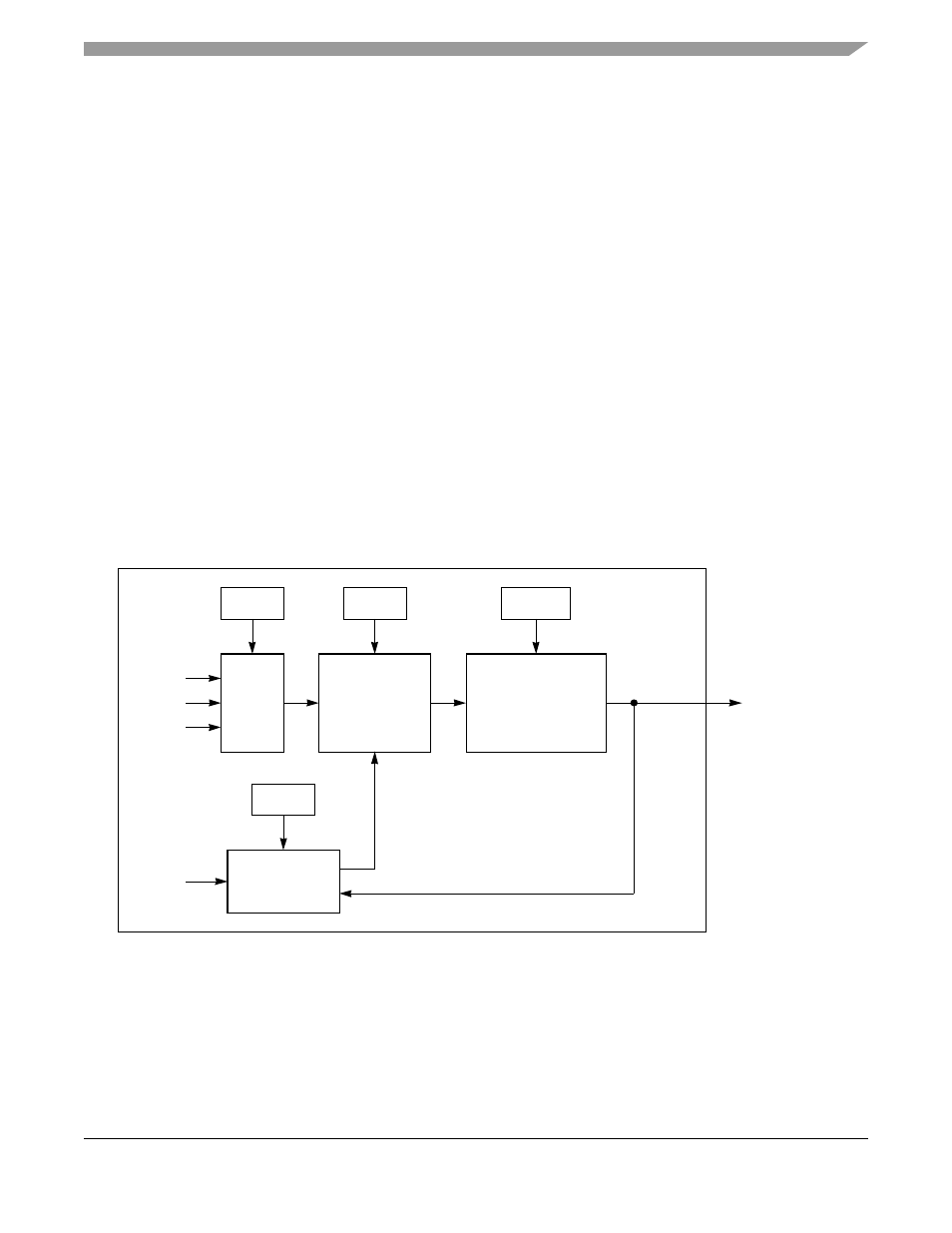
shows a BRG.
Figure 17-1. Baud-Rate Generator (BRG) Block Diagram
Each BRG clock source can be BRGCLK, or a choice of two external clocks (selected in BRGCx[EXTC]).
The BRGCLK is an internal signal generated in the PowerQUICC II clock synthesizer specifically for the
BRGs, the SPI, and the I
2
C internal BRG. Alternatively, external clock pins can be configured as clock
sources. The external source option allows flexible baud-rate frequency generation, independent of the
system frequency. Additionally, the external source option allows a single external frequency to be the
CLK Pin x
Clock
Source
MUX
Divide by
1 or 16
Prescaler
12-Bit Counter
1–4,096
DIV 16
CD[0–11]
BRGO
n
Clock
BRGCLK
EXTC
ATB
Autobaud
Control
RXD
n
To Pin and/or
Bank of Clocks
BRG
n
CLK Pin y
