Figure 30-7. vp pointer address compression, 2 vc-level address compression tables (vclts), Vc-level address compression tables (vclts) -17 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 937: Vp pointer address compression -17
ATM Controller and AAL0, AAL1, and AAL5
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
30-17
The PowerQUICC II can check that all unallocated bits of the PHY + VPI are 0 by setting
GMODE[CUAB] (check unallocated bits) in the parameter RAM. If they are not, the cell is considered a
misinserted cell.
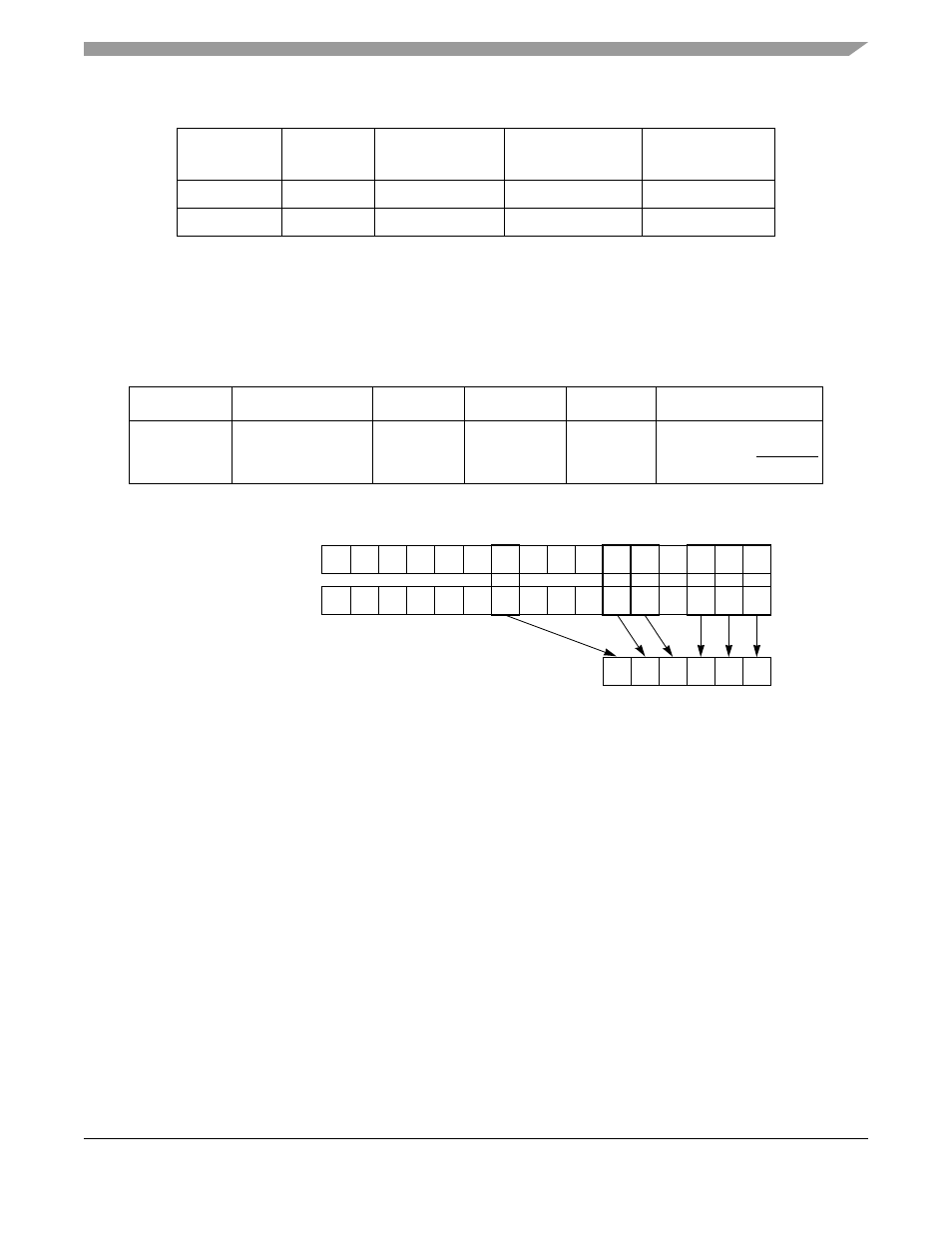
gives an example of VP-level table entry address calculation.
shows the VP pointer address compression from
Figure 30-7. VP Pointer Address Compression
30.4.2.2
VC-Level Address Compression Tables (VCLTs)
Each VPLT entry points to a single VCLT. Like the VPLT, the size of each VCLT depends on VC_MASK.
Because the VCLT contains word entries, if VC_MASK = 0b11_1111_1111, the table is 4 Kbytes. The
address of an entry in this table is VCT_BASE + VCOFFSET
× 4 + VCpointer × 4.
The PowerQUICC II can check that all unallocated VCI bits are 0 by setting GMODE[CUAB] (check
unallocated bits). If they are not, the cell is considered a misinserted cell.
An example of VC-level table entry address calculation is shown in
. Note that VCOFFSET is
assumed to be 0x100 for this example.
2
0xA007
5
2
5
= 32 entries
64 + 8 = 72
3
x
x
x
72 + 32 = 104
Table 30-5. VP-Level Table Entry Address Calculation Example
VPT_BASE
VP-Level Table Size
VP_MASK
Phy+VPI
VP Pointer
VP Entry Address
0x0024_0000
64 entries
0x0237
0x0011
0x09
VP Base = 0x240000
0x09 x 4 = 0x000024
0x240024
Table 30-4. VCOFFSET Calculation Examples for Contiguous VCLTs
VP-Level
Table Entry
VC_MASK
Number of Ones
in VC_MASK
VC-Level
Table Size
VCOFFSET
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
PHY+VPI
VP_MASK
VP Pointer
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
