Table 23-6. bdle field descriptions, 10 handling errors in the scc bisync, Handling errors in the scc bisync -9 – Freescale Semiconductor MPC8260 User Manual
Page 759: Bdle field descriptions -9, Receiver sync pattern lengths of the dsr -9
SCC BISYNC Mode
MPC8260 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
23-9
23.9
Sending and Receiving the Synchronization Sequence
The BISYNC channel can be programmed to send and receive a synchronization pattern defined in the
DSR. GSMR_H[SYNL] defines pattern length, as shown in
. The receiver synchronizes on this
pattern. Unless SYNL is zero (external sync), the transmitter always sends the entire DSR contents, lsb
first, before each frame—the chosen 4- or 8-bit pattern can be repeated in the lower-order bits.
23.10 Handling Errors in the SCC BISYNC
The controller reports message transmit and receive errors using the channel BDs, error counters, and the
SCCE. Modem lines can be directly monitored via the parallel port pins.
describes transmit
errors.
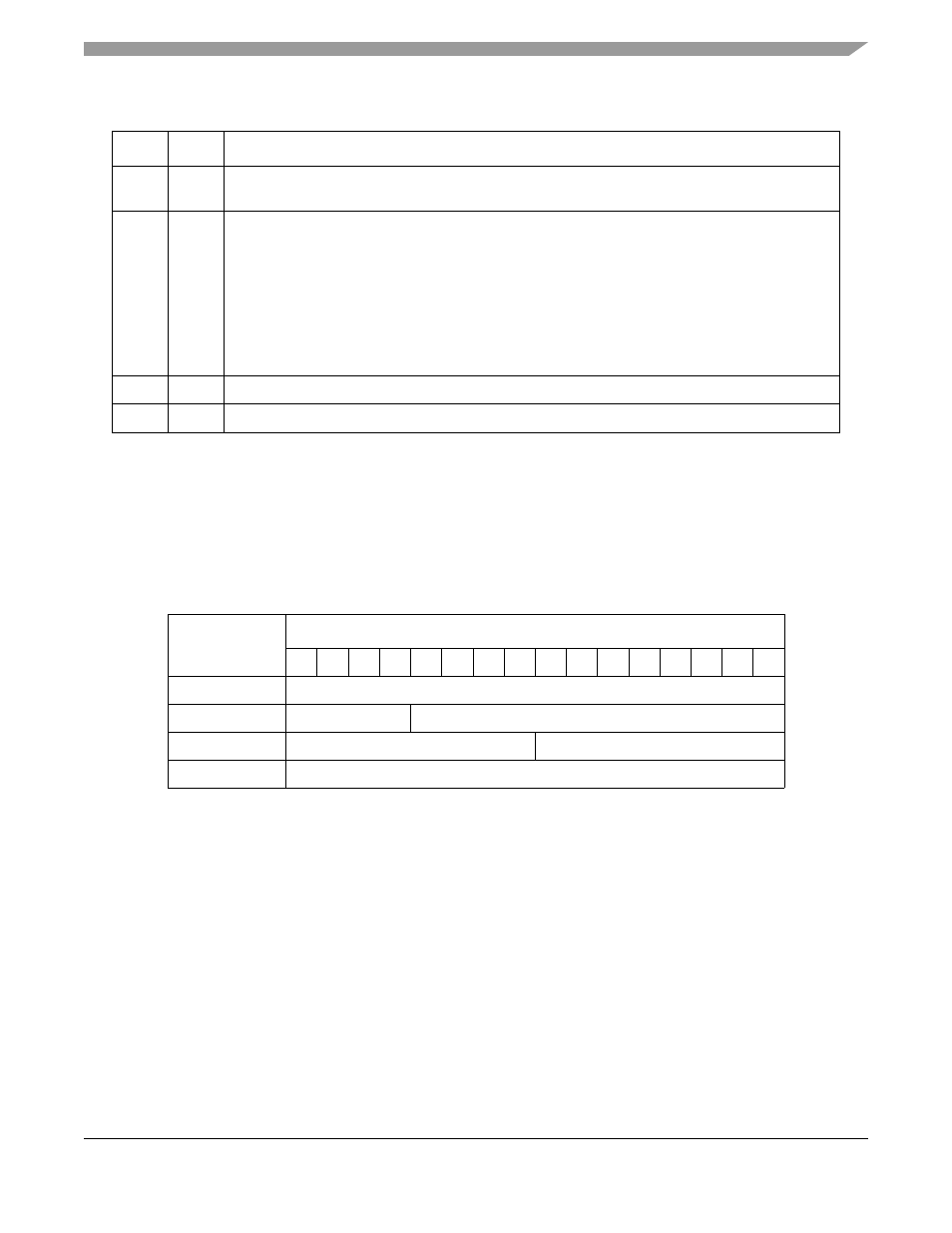
Table 23-6. BDLE Field Descriptions
Bits
Name Description
0
V
Valid. If V = 1 and the receiver is not in hunt mode when a SYNC character is received, this character
is discarded.
1
DIS
Disable DLE stripping
0 Normal mode.
1 DLE stripping disabled. When DIS is enabled in BDLE and on BSYNC the following cases occur:
DLE-DLE sequence. Both characters are written to the memory. The BCS is calculated only on
the second DLE.
DLE-SYNC sequence. Both characters are written to the memory, but neither are included in the
BCS calculation.
DLE-ETX, DLE-ITB, DLE-ETB sequence, both characters are written to memory. The BCS is
calculated only on the second character.
2–7
—
All zeros
8–15
DLE
DLE character
Table 23-7. Receiver SYNC Pattern Lengths of the DSR
GSMR_H[SYNL]
Setting
Bit Assignments
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
00
An external SYNC signal is used instead of the SYNC pattern in the DSR.
01
4-Bit
10
8-Bit
11
16-Bit
