Audio regions and waveforms – M-AUDIO Pro Tools Recording Studio User Manual
Page 447
Chapter 22: Editing Basics
429
Auto-Created Regions
These regions are auto-
matically created in the course of editing, and,
in some instances, when punch recording over
existing regions. Since these regions can accu-
mulate rapidly in a session, you can hide them
in the Region List. Auto-created regions can be
turned into user-defined regions by renaming
them.
Offline Regions
Regions are offline when their
parent files cannot be located, or are not avail-
able, when opening a session or importing a
track. Offline regions appear in the Region List
as italicized and dimmed; they appear in playl-
ists as light blue regions with italicized names.
Offline regions can be edited like other regions,
but they cannot be processed with AudioSuite
plug-ins.
Multichannel Regions
These regions, which are
displayed as a single region in the Region List,
reference multiple regions and audio files for
stereo and surround tracks. Multichannel re-
gions can be expanded (by clicking the triangle
next to their name) to see the individual chan-
nels, which can be dragged independently to
tracks.
Region Groups
A region group is a collection of
any combination of audio and MIDI regions
that looks and acts like a single region. Region
groups are essentially containers holding one or
more regions. Region groups can be created on a
single track or on multiple adjacent audio,
MIDI, and Instrument tracks. Region groups let
you “nest” multiple regions into “macro” re-
gions for groove and tempo manipulation, edit-
ing, and arranging.
Warped Regions
Regions on Real-Time Elastic
Audio-enabled tracks can be warped. Warped re-
gions are identified with a Warp Indicator icon
in the upper-right corner of regions on tracks
and to the left of region names in the Region
List. Warped regions result from the application
of Elastic Audio processing. Elastic Audio pro-
cessing can be applied manually in Warp view
or using the TCE Trimmer in Waveform view, or
automatically using tempo conform, quantiza-
tion, or transposition.
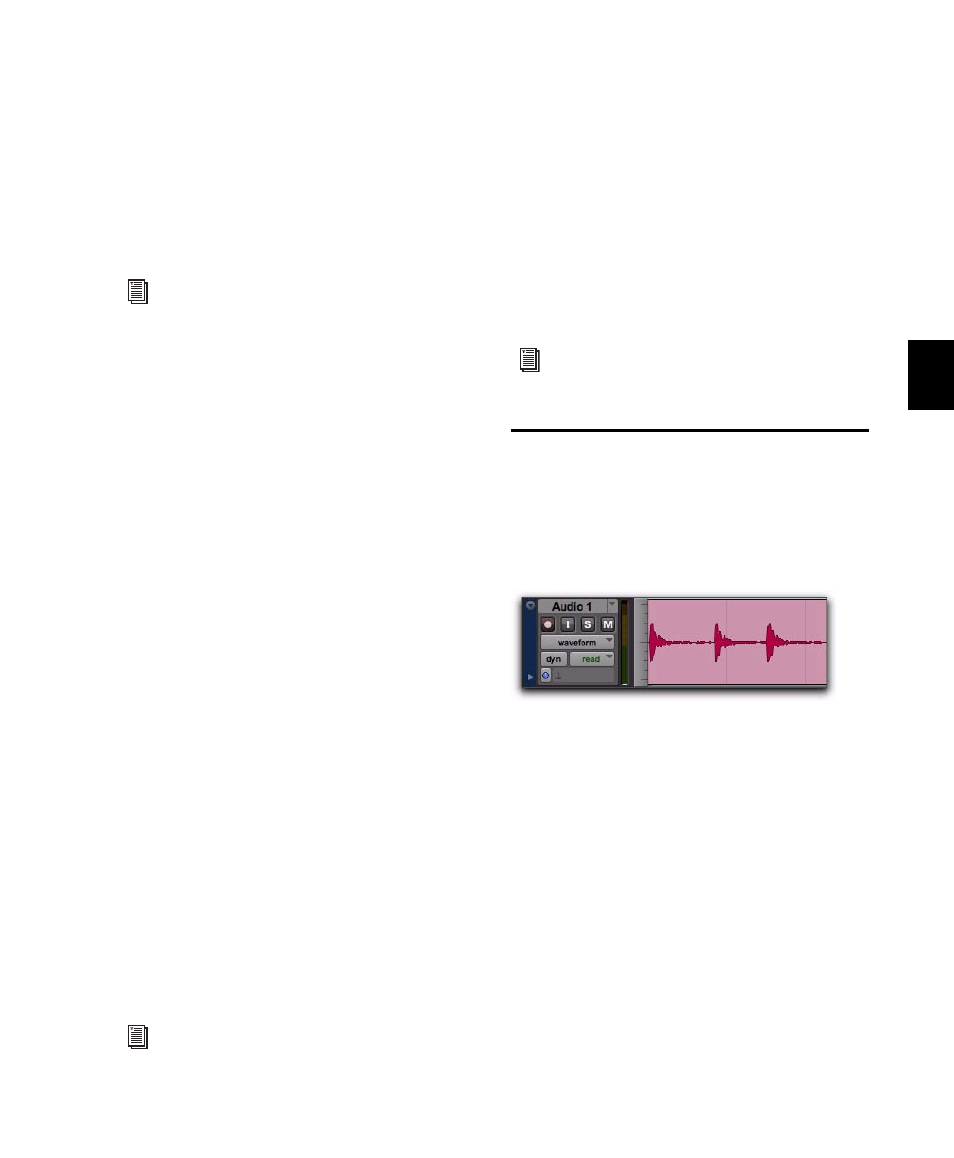
Audio Regions and Waveforms
When the Track View for audio tracks is set to
Waveform
, Pro Tools draws a waveform diagram
of the audio. Audio waveforms tell you several
things about the recorded sound.
In Figure 21, the “peaks” represent places in the
recording where the attack of the sound causes
the volume to increase momentarily. These are
followed by “valleys,” where the volume de-
creases.
Different types of sounds produce different
types of waveforms. Drums, for example, gener-
ally produce waveforms with sharp transients
(peaks of short duration) that are clearly de-
fined. A drum hit has a loud, sharp attack and a
rapid decay.
For more information, see “Naming and
Displaying Regions in the Region List” on
page 219.
For more information on region groups, see
“Region Groups” on page 743.
For more information, see “Warped Re-
gions” on page 784.
Figure 21. Audio waveform of a drum track
