Applying masks to replicators – Apple Motion 4 User Manual
Page 725
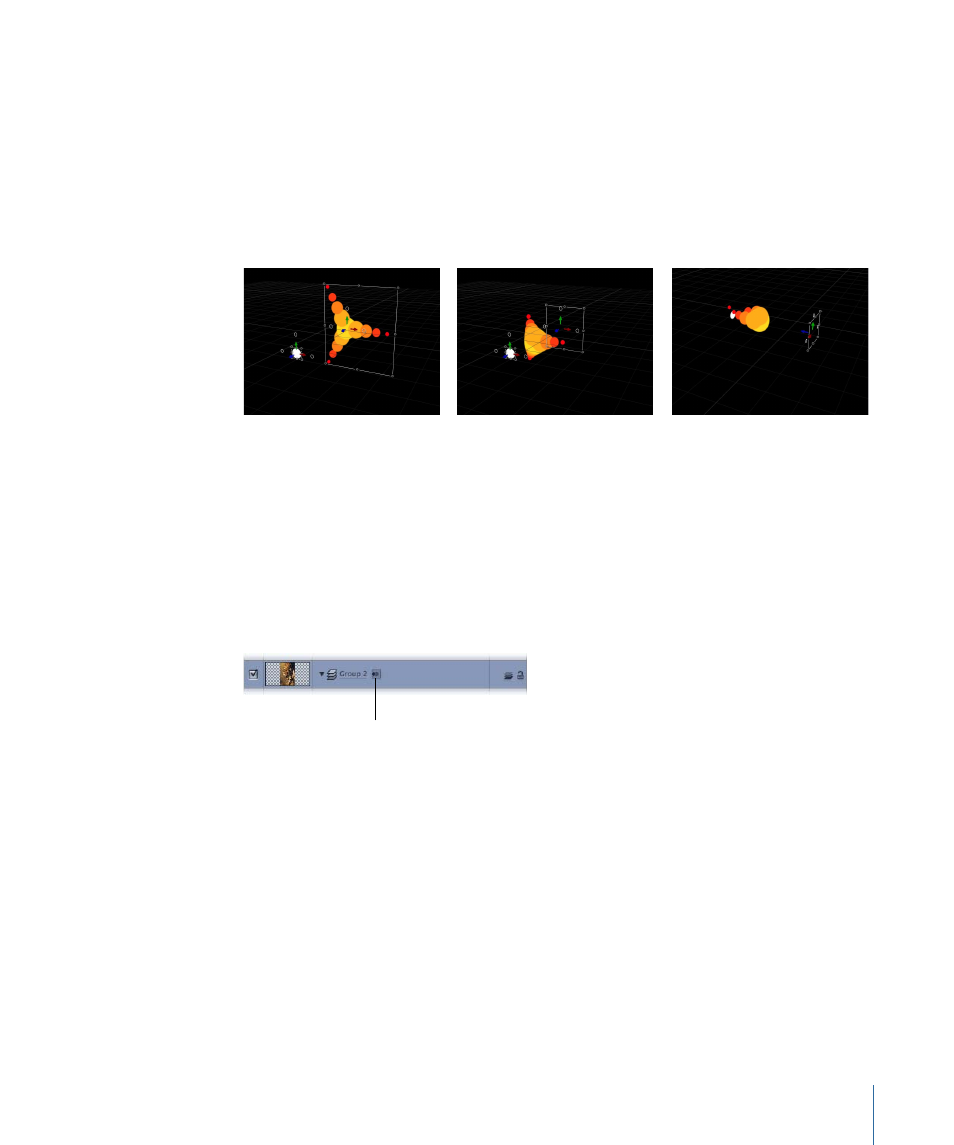
The following illustrations demonstrate replicator pattern elements pulled into Z space.
In the illustration on the left, the Burst replicator’s Z position is set to 0 and the white
circle’s Z position is set to 225. An “Attracted To” Simulation behavior is applied to the
replicator, with the white circle set as the target object. As the project plays, as shown in
the center illustration, the replicator elements move forward in Z space toward the
attractor. In the right illustration, the camera is rotated to look behind the replicator.
Under the behavior’s influence, the replicator elements move past their attractor element,
and return to their original position.
Certain operations, as well as the application of certain filters or a mask, will rasterize a
3D group. For more information on rasterization, see
Tip: When working with elements in 3D, you can quickly snap an object back to its original
orientation by using the Isolate command.
To isolate a group or layer
Do one of the following:
µ
In the Layers tab (or Timeline layers list), click the Isolate button.
Inactive Isolate button
µ
Control-click the layer or group, then choose Isolate from the shortcut menu.
µ
Choose Object > Isolate.
Click the Isolate button again to return to your previous view.
Note: Clicking a camera’s Isolate button activates that camera’s view.
Applying Masks to Replicators
Masks can be applied to a replicator’s source layer (the original layer that is replicated to
create the repeating onscreen elements), or to the replicator itself.
725
Chapter 12
Using the Replicator
