Mpls virtual leased line (vll) overview, Mpls virtual leased line (vll) overview 5 – Brocade Network Advisor SAN + IP User Manual v12.1.0 User Manual
Page 1394
Brocade Network Advisor SAN + IP User Manual
1345
53-1002949-01
MPLS Virtual Leased Line (VLL) overview
37
•
Select Drill-down to LSP Hops Topology to display LSPs and hops as a line from the
ingress router with an arrow to indicate direction. Operationally enabled LSPs are
shown with a solid line. Operationally disabled LSPs are shown with a dotted line.
•
Select LSP Ping to launch the LSP Ping dialog box.
•
Select LSP Traceroute to launch the LSP Trace Route dialog box.
MPLS Virtual Leased Line (VLL) overview
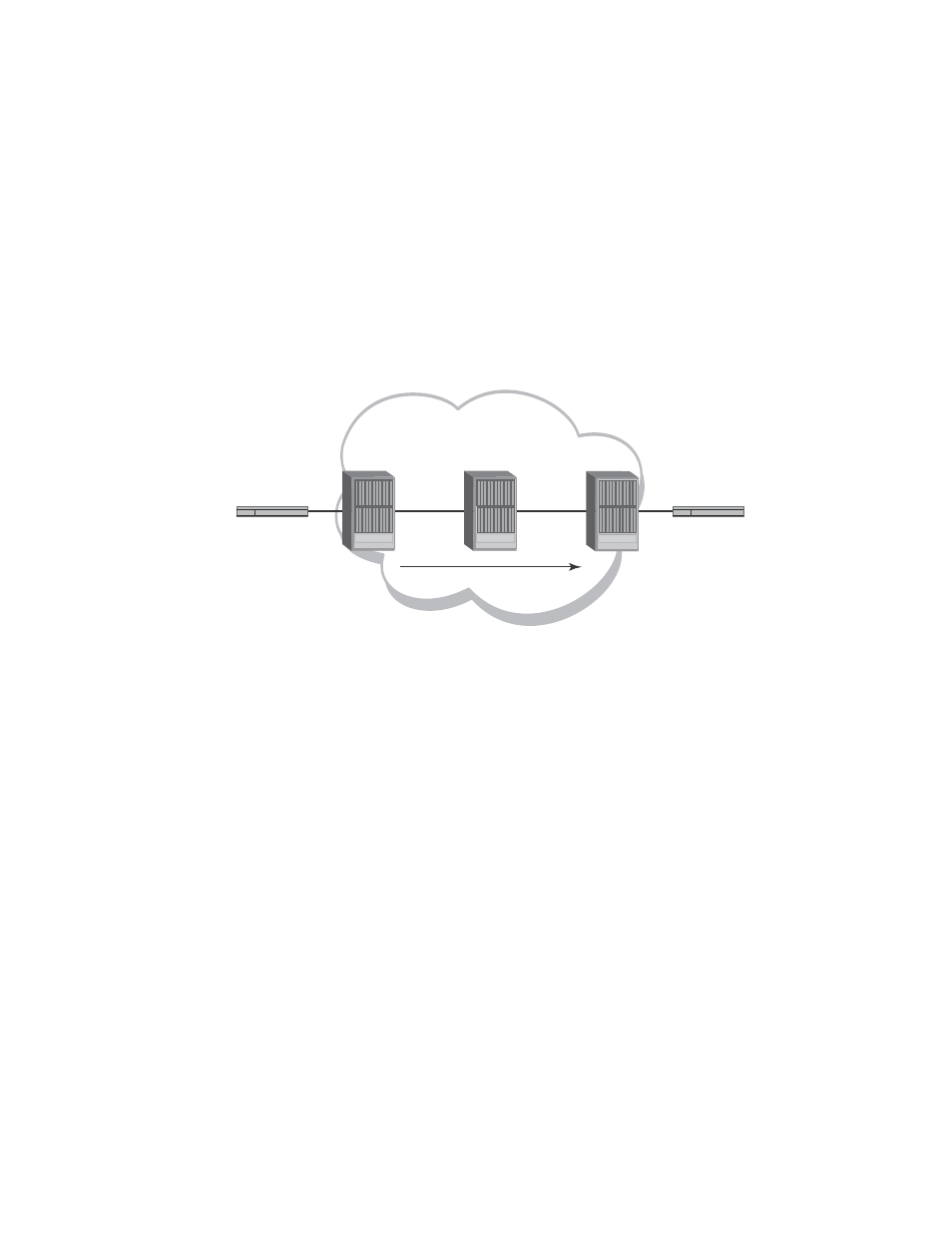
MPLS VLL provides point-to-point Ethernet or VLAN connectivity over an MPLS domain. VLL is also
known as Pseudo-Wire emulation.
illustrates a basic VLL configuration.
FIGURE 585
Basic VLL configuration
Packets are forwarded over an MPLS VLL as described below.
1. A Customer Edge (CE) product forwards a packet to an LER serving as a Provider Edge (PE)
router at the edge of the MPLS domain.
2. The PE router assigns the packet to an RSVP-signalled LSP whose destination is an LER (also
serving as a PE router) that is connected to a CE product at the far end of the MPLS domain.
The PE router at the other end of the MPLS domain is known as this PE router’s VLL peer. The
RSVP-signalled LSP used to reach the VLL peer is known as the tunnel LSP. Alternatively, an
LDP-signalled, tunneled LSP can be used.
If a Class of Service (COS) value is set for the VLL, the product selects a tunnel LSP that also
has this COS value, if one is available. If no tunnel LSP with this COS value is available, the
product selects a tunnel LSP with the highest configured COS value (although never higher
than the COS setting for the VLL).
If there are multiple tunnel LSPs that can be used to reach the VLL peer, the PE router selects
one of the tunnel LSPs by using a round-robin method.
MPLS Domain
CE Device
CE Device
Ingress
PE Router
PE Router
Penultimate
Egress
Tunnel LSP
