Apple Final Cut Pro 7 User Manual
Page 1326
How Digital Video Signals Are Measured in Final Cut Pro
The Final Cut Pro Waveform Monitor displays Y
′
C
B
C
R
values as percentages instead of bit
values because digital video can use 8 or 10 bits per luma sample. Using 8 bits provides
up to 256 tones from black to white, although the actual range used in Y
′
C
B
C
R
video is
16 (black) to 235 (white). The remaining values, 236 through 254, provide additional
headroom used to record super-white levels such as specular highlights on shiny objects.
Values for 10-bit Y
′
C
B
C
R
Values for 8-bit Y
′
C
B
C
R
Percentage in Final Cut Pro
Waveform Monitor
n/a
n/a
-10%
64
16
0% (black)
940
235
100% (white)
1019
254
109% (super-white)
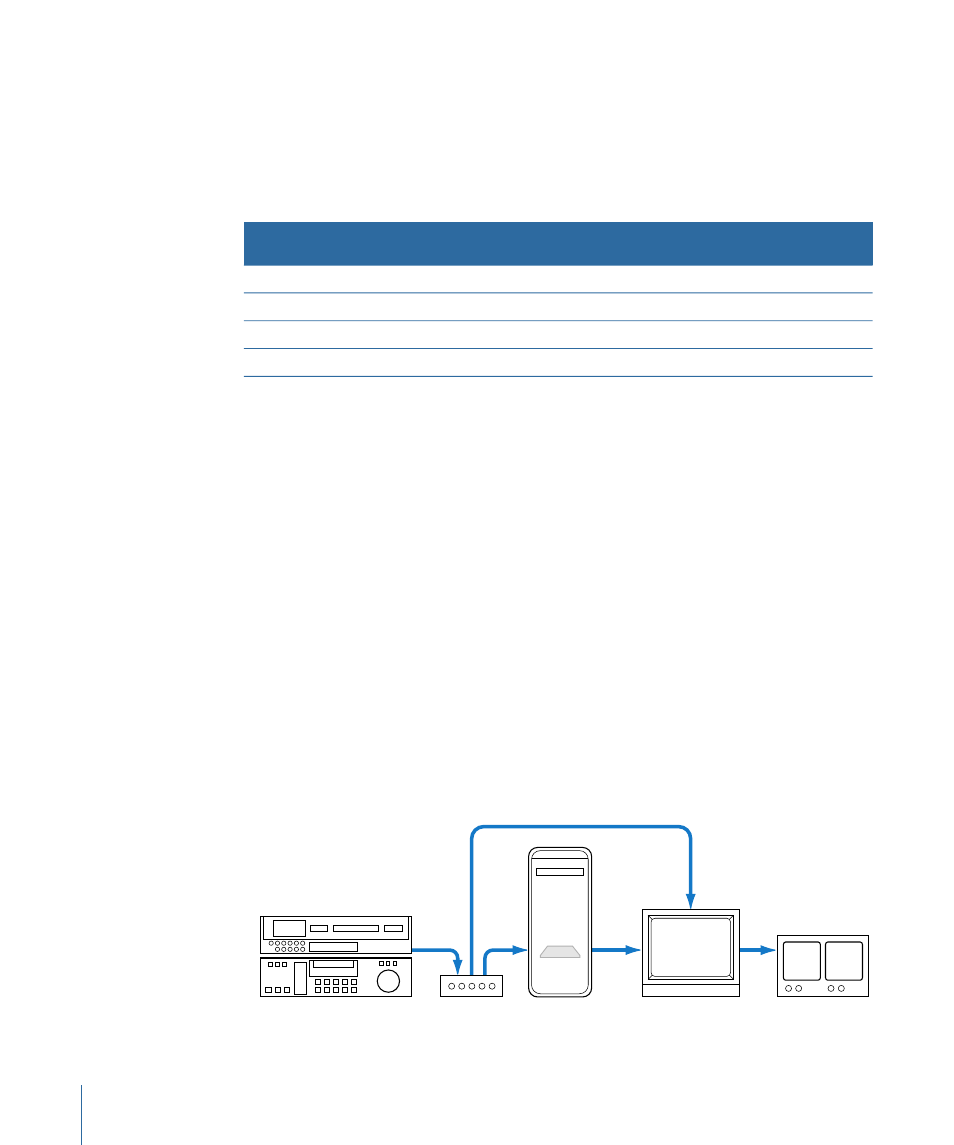
Using an External Waveform Monitor and Vectorscope to Calibrate
Analog Video Levels
The scopes in Final Cut Pro display the digital values of your video as it exists in its captured
state, but the software scopes can’t measure input and output analog signal levels from
and to your FireWire device or third-party video interface. If you like, you can set up your
Final Cut Pro workstation with a dedicated waveform monitor and vectorscope for
measuring and adjusting video input and output more accurately.
This involves using two pieces of external video hardware:
• Processing amplifier (or “proc amp”): A proc amp provides hardware control of luma, or
video gain (brightness), chroma gain (saturation), hue, and setup (black level). By
connecting a proc amp between your analog VTR and your video interface, you can
precisely control the incoming Y
′
C
B
C
R
video signal.
Note: Some VTRs have a built-in proc amp.
• Hardware waveform monitor or vectorscope: Having a dedicated hardware waveform
monitor or vectorscope enables you to measure the actual analog Y
′
C
B
C
R
output from
your video interface.
Standard definition
monitor
Waveform monitor/
vectorscope
Analog or digital VTR
Proc amp
Computer
PCI card
Input A
Input B
1326
Chapter 78
Measuring and Setting Video Levels
