3 remote loopback mode, 5 resets, 1 general – Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 809: 2 description of reset operation, 1 reset, 2 crsrx, 3 crstx, 4 crses, Remote loopback mode -47, Resets -47
Resets
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor
26-47
is ignored, the TxD is held marking, and the receiver is clocked by the transmitter clock. The transmitter
must be enabled, but the receiver need not be enabled.
26.4.10.3 Remote Loopback Mode
In this mode, the channel automatically transmits received data on the TxD output on a bit-by-bit basis.
The local CPU-to-transmitter link is disabled. This mode is useful in testing receiver and transmitter
operation of a remote channel. While in this mode, the receiver clock is used for the transmitter.
Because the receiver is not active, received data cannot be read by the CPU, and the error status conditions
are inactive. Received parity is not checked and is not recalculated for transmission. Stop bits are
transmitted as received. A received break is echoed as received until the next valid start bit is detected.
26.5
Resets
26.5.1
General
This section describes how to reset the device. CR refers to PSCCR.
26.5.2
Description of Reset Operation
26.5.2.1
Reset
When there is a reset, the PSC module goes to its initial state.
26.5.2.2
CRSRX
Writing the RESET RECEIVER command to the command control register PSCCR resets the receiver.
26.5.2.3
CRSTX
Writing the RESET TRANSMITTER command to the command control register PSCCR resets the
transmitter.
26.5.2.4
CRSES
Writing the RESET ERROR STATUS command to the command control register PSCCR resets the error
status held in the status register PSCSR.
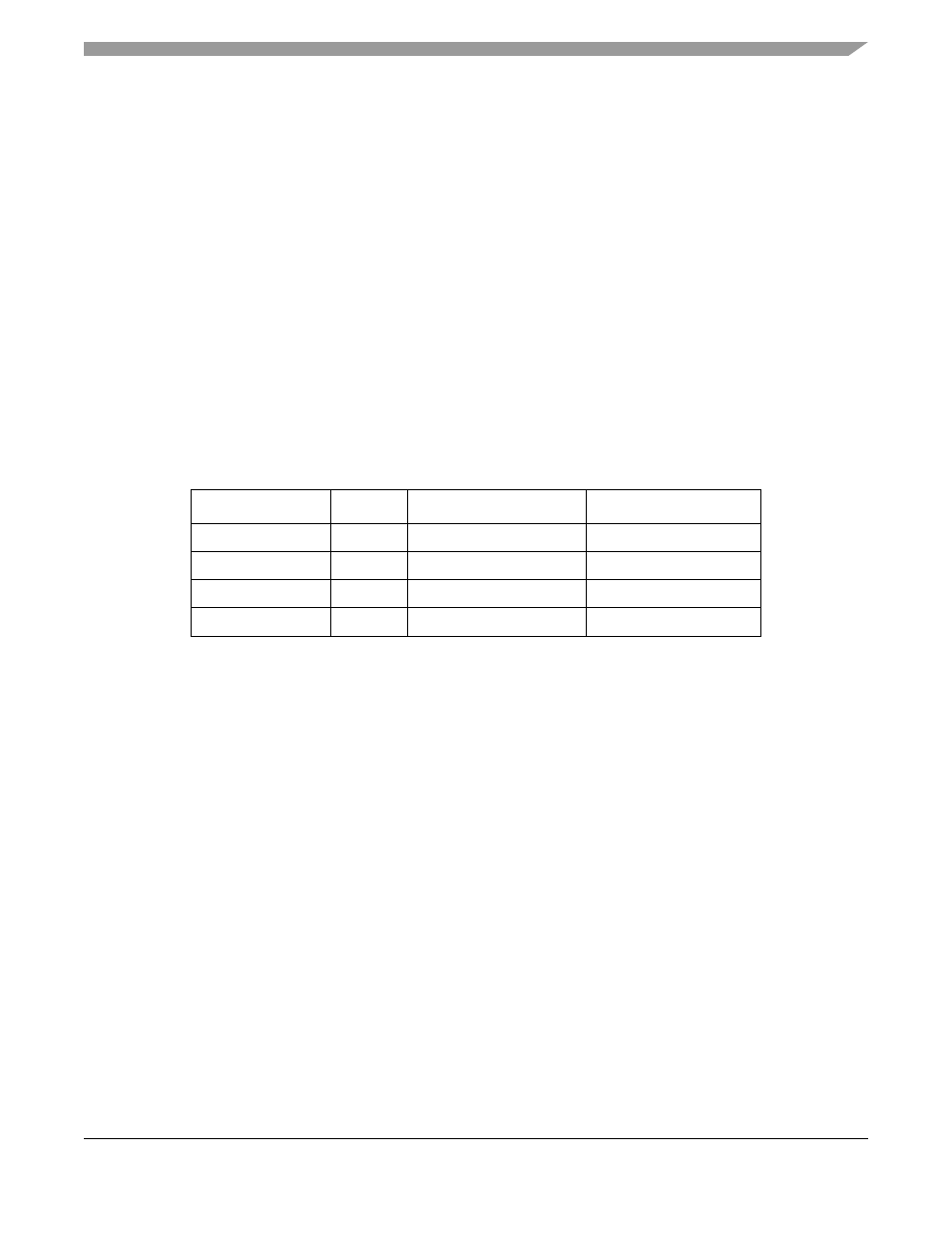
Table 26-39. Reset Summary
Reset
Priority
Source
Characteristics
Reset
High
Input port
Hardware reset
CRSRX
Low
Command to PSCCR
Reset receiver
CRSTX
Low
Command to PSCCR
Reset transmitter
CRSES
Low
Command to PSCCR
Reset error status
