1 exception stack frame definition, Exception stack frame definition -38 – Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 142
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
3-38
Freescale Semiconductor
ColdFire processors inhibit sampling for interrupts during the first instruction of all exception handlers.
This allows any handler to effectively disable interrupts, if necessary, by raising the interrupt mask level
in the SR.
3.8.1
Exception Stack Frame Definition
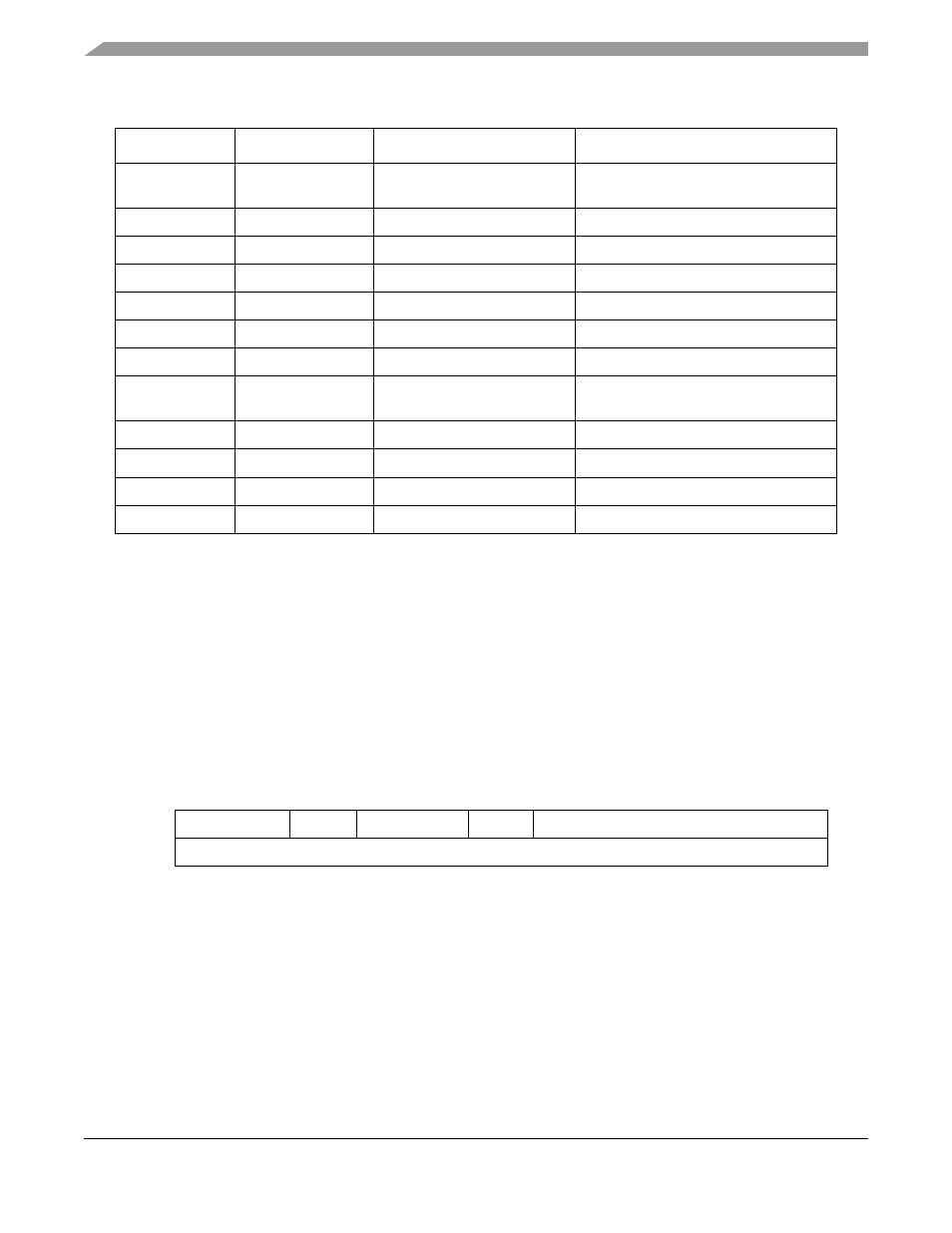
The first longword of the exception stack frame,
, holds the 16-bit format/vector word (F/V)
and 16-bit status register. The second holds the 32-bit program counter address of the faulted or interrupted
instruction.
Figure 3-15. Exception Stack Frame
describes F/V fields. FS encodings added to support the CF4e MMU are noted.
48
0C0
Fault
Floating-point branch on unordered
condition
49
0C4
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point inexact result
50
0C8
NextFP
Floating-point divide-by-zero
51
0CC
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point underflow
52
0D0
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point operand error
53
0D4
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point overflow
54
0D8
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point input not-a-number (NAN)
55
0DC
NextFP or Fault
Floating-point input denormalized
number
56–60
0E0–0F0
—
Reserved
61
0F4
Fault
Unsupported instruction
62–63
0F8–0FC
—
Reserved
64–255
100–3FC
Next
User-defined interrupts
1
‘Fault’ refers to the PC of the faulting instruction. ‘Next’ refers to the PC of the instruction immediately after the
faulting instruction. NextFP’ refers to the PC of the next floating-point instruction.
31
28
27
26
25
18
17
16
15
0
A7
→
FORMAT
FS[3–2]
VEC
FS[1–0] STATUS
REGISTER
+ 0x04
PROGRAM COUNTER [31:0]
Table 3-21. Exception Vector Assignments (Continued)
Vector Numbers Vector Offset (Hex)
Stacked Program Counter
1
Assignment
