7 memory map/register definition, Memory map/register definition -16 – Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 464
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
18-16
Freescale Semiconductor
The SDRAM controller supports all possible XLB transfer sizes. SDRAMs are “burst only” devices;
unnecessary beats on the memory bus are masked (write) or discarded (read).
The SDRAMC will perform line bursts (32 byte) for all SDRAM access. This requires two beats of 16
bytes on the XLB, or eight beats of 4 bytes (one longword) on the memory bus. The SDRAM controller
transfers the critical longword first, followed by the next three sequential longwords.
The burst size and transfer order must be programmed in the SDRAM mode registers during initialization
(SDMR); the burst size also must be programmed in the memory controller (SDCFG2).
In a write operation, the data masks, SDDM[3:0], are used to inhibit writing unused bytes of each beat. In
a read operation, the excess read data is discarded.
18.7
Memory Map/Register Definition
The SDRAM controller contains four programming registers.
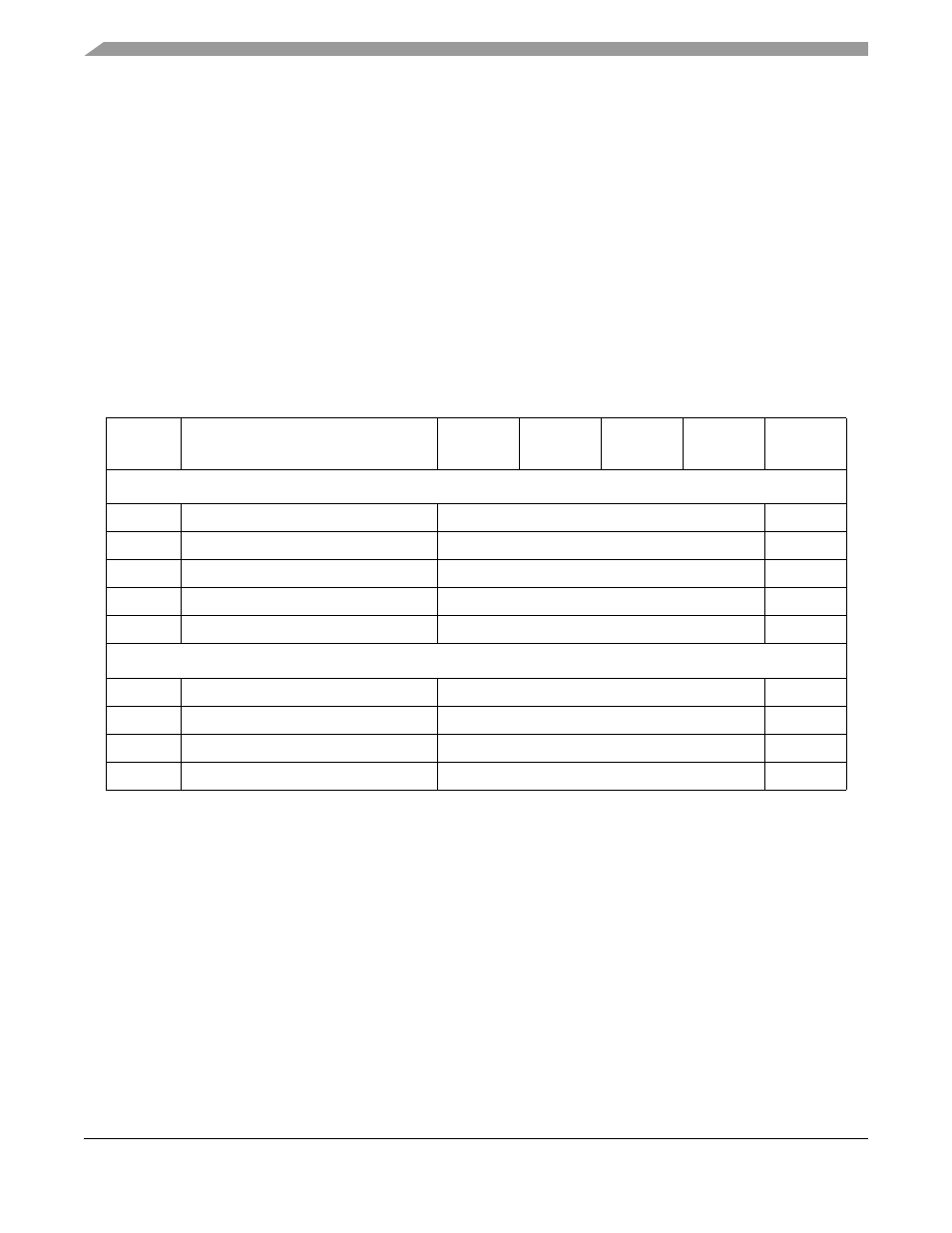
Table 18-6. SDRAMC Memory Map
Address
(MBAR +)
Name
Byte0
Byte1
Byte2
Byte3
Access
SDRAM Chip Select and Drive Strength Registers
0x04
SDRAM Drive Strength Register
SDRAMDS
R/W
0x20
SDRAM Chip Select 0 Configuration
CS0CFG
R/W
0x24
SDRAM Chip Select 1 Configuration
CS1CFG
R/W
0x28
SDRAM Chip Select 2 Configuration
CS2CFG
R/W
0x2C
SDRAM Chip Select 3 Configuration
CS3CFG
R/W
SDRAMC Configuration Registers
0x0100
SDRAM Mode/Extended Mode Register
SDMR
R/W
0x0104
SDRAM Control Register
SDCR
R/W
0x0108
SDRAM Configuration Register 1
SDCFG1
R/W
0x010C
SDRAM Configuration Register 2
SDCFG2
R/W
