Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 206
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
6-16
Freescale Semiconductor
unordered condition is present when the conditional test is attempted (IEEE nonaware tests). The other 16
do not cause an exception (IEEE-aware tests). The set of IEEE nonaware tests is best used in one of the
following cases:
•
When porting a program from a system that does not support the IEEE standard to a conforming
system
•
When generating high-level language code that does not support IEEE floating-point concepts (that
is, the unordered condition).
An unordered condition occurs when one or both of the operands in a floating-point compare operation is
a NAN. The inclusion of the unordered condition in floating-point branches destroys the familiar
trichotomy relationship (greater than, equal, less than) that exists for integers. For example, the opposite
of floating-point branch greater than (FBGT) is not floating-point branch less than or equal (FBLE).
Rather, the opposite condition is floating-point branch not greater than (FBNGT). If the result of the
previous instruction was unordered, FBNGT is true, whereas both FBGT and FBLE would be false because
unordered fails both of these tests (and sets BSUN). Compiler code generators should be particularly
careful of the lack of trichotomy in the floating-point branches, because it is common for compilers to
invert the sense of conditions.
When using the IEEE nonaware tests, the user receives a BSUN exception if a branch is attempted and
FPCC[NAN] is set, unless the branch is an FBEQ or an FBNE. If the BSUN exception is enabled in FPCR,
the exception takes a BSUN trap. Therefore, the IEEE nonaware program is interrupted if an unexpected
condition occurs. Users knowledgeable of the IEEE-754 standard should use IEEE-aware tests in
programs that contain ordered and unordered conditions. Because the ordered or unordered attribute is
explicitly included in the conditional test, EXC[BSUN] is not set when the unordered condition occurs.
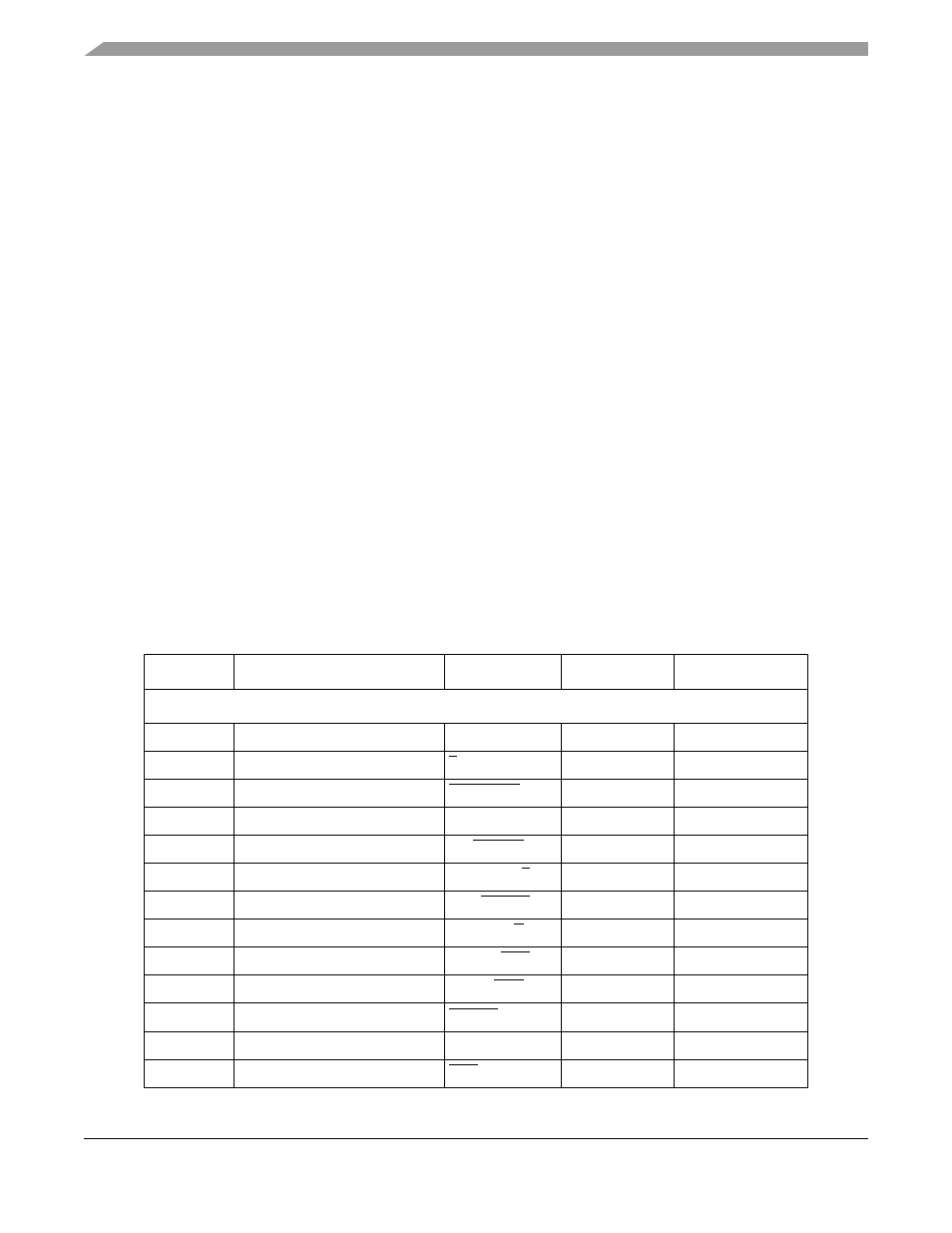
summarizes conditional mnemonics, definitions, equations, predicates, and whether
EXC[BSUN] is set for the 32 floating-point conditional tests. The equation column lists FPCC bit
combinations for each test in the form of an equation. Condition codes with an overbar indicate cleared
bits; all other bits are set.
Table 6-9. Floating-Point Conditional Tests
Mnemonic
Definition
Equation
Predicate
1
EXC[BSUN] Set
IEEE Nonaware Tests
EQ
Equal
Z
000001
No
NE
Not equal
Z
001110
No
GT
Greater than
NAN | Z | N
010010
Yes
NGT
Not greater than
NAN | Z | N
011101
Yes
GE
Greater than or equal
Z | (NAN | N)
010011
Yes
NGE
Not greater than or equal
NAN | (N & Z)
011100
Yes
LT
Less than
N & (NAN | Z)
010100
Yes
NLT
Not less than
NAN | (Z | N)
011011
Yes
LE
Less than or equal
Z | (N & NAN)
010101
Yes
NLE
Not less than or equal
NAN | (N | Z)
011010
Yes
GL
Greater or less than
NAN | Z
010110
Yes
NGL
Not greater or less than
NAN | Z
011001
Yes
GLE
Greater, less or equal
NAN
010111
Yes
