Figure 6-12, Shows the algorithm for rounding – Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 203
Floating-Point Computational Accuracy
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor
6-13
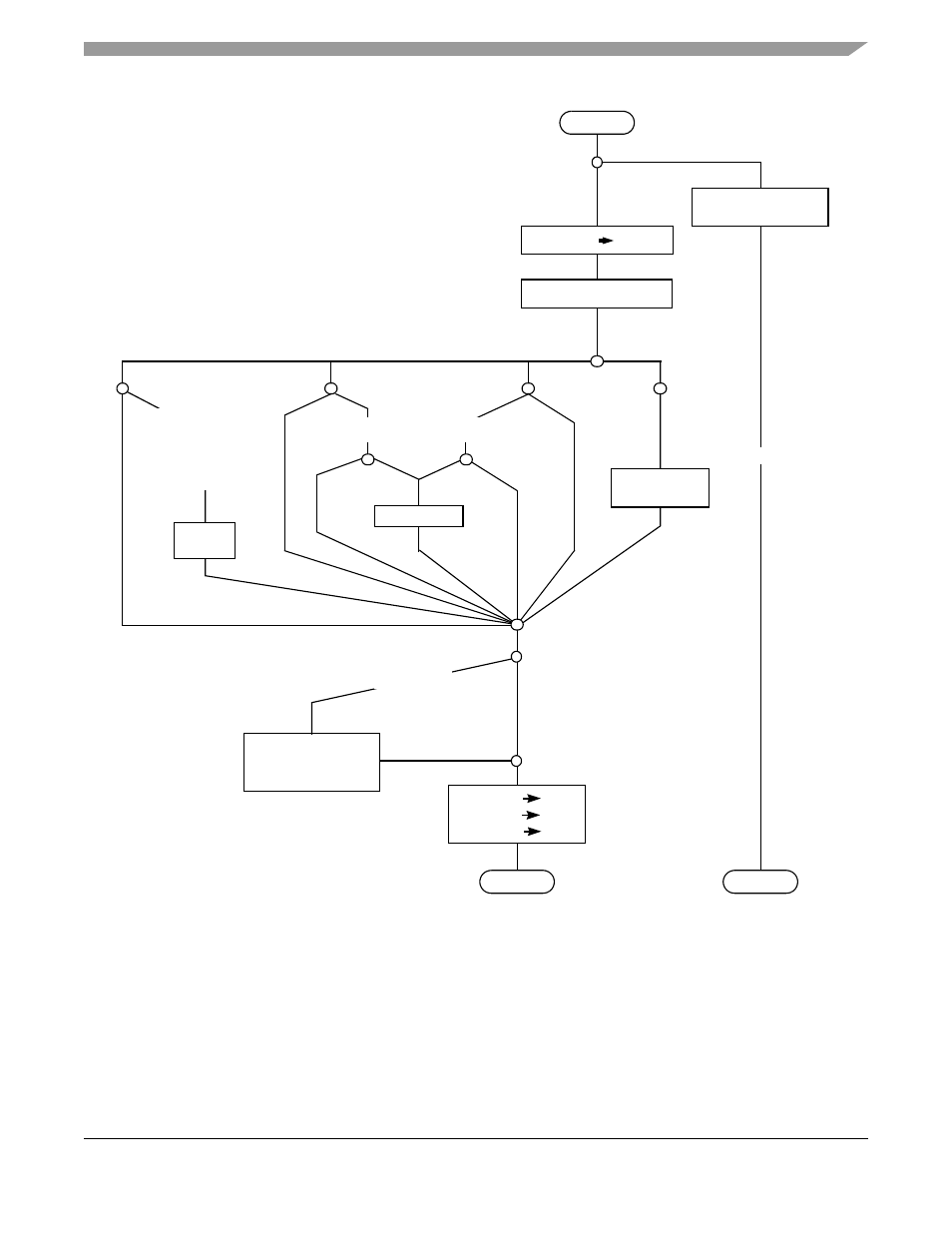
Figure 6-12. Rounding Algorithm Flowchart
The 3 additional bits beyond the double-precision format, the difference between the intermediate result’s
56-bit mantissa and the storing result’s 53-bit mantissa, allow the FPU to perform all calculations as
though it were performing calculations using a compute engine with infinite bit precision. The result is
always correct for the specified destination’s data format before rounding (unless an overflow or
underflow error occurs). The specified rounding produces a number as close as possible to the infinitely
precise intermediate value and still representable in the selected precision. The tie case in
shows
how the 56-bit mantissa allows the FPU to meet the error bound of the IEEE specification.
INEX
1
Select Rounding Mode
Guard, Round
and Sticky Bits = 0
Exact Result
G,R, and S
are chopped
RZ
Check Intermediate Result
RP
RM
RN
Neg
Pos
Neg
Pos
Add 1 to
lsb
G and lsb = 1,
R and S = 0
or
G = 1,
R or S = 1
Shift mantissa
right 1 bit,
Add 1 to exponent
Overflow = 1
Guard
0
Round
0
Sticky
0
Exit
Exit
Entry
N
Y
G, R,
or S = 1
Add 1 to lsb
G, R,
or S = 1
Y
N
