Chapter 14 edge port module (eport), 1 introduction, 2 interrupt/general-purpose i/o pin descriptions – Freescale Semiconductor MCF5480 User Manual
Page 367: Chapter 14, Edge port module (eport), Introduction -1, Interrupt/general-purpose i/o pin descriptions -1, Chapter 14, “edge port module (eport)
MCF548x Reference Manual, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor
14-1
Chapter 14
Edge Port Module (EPORT)
14.1
Introduction
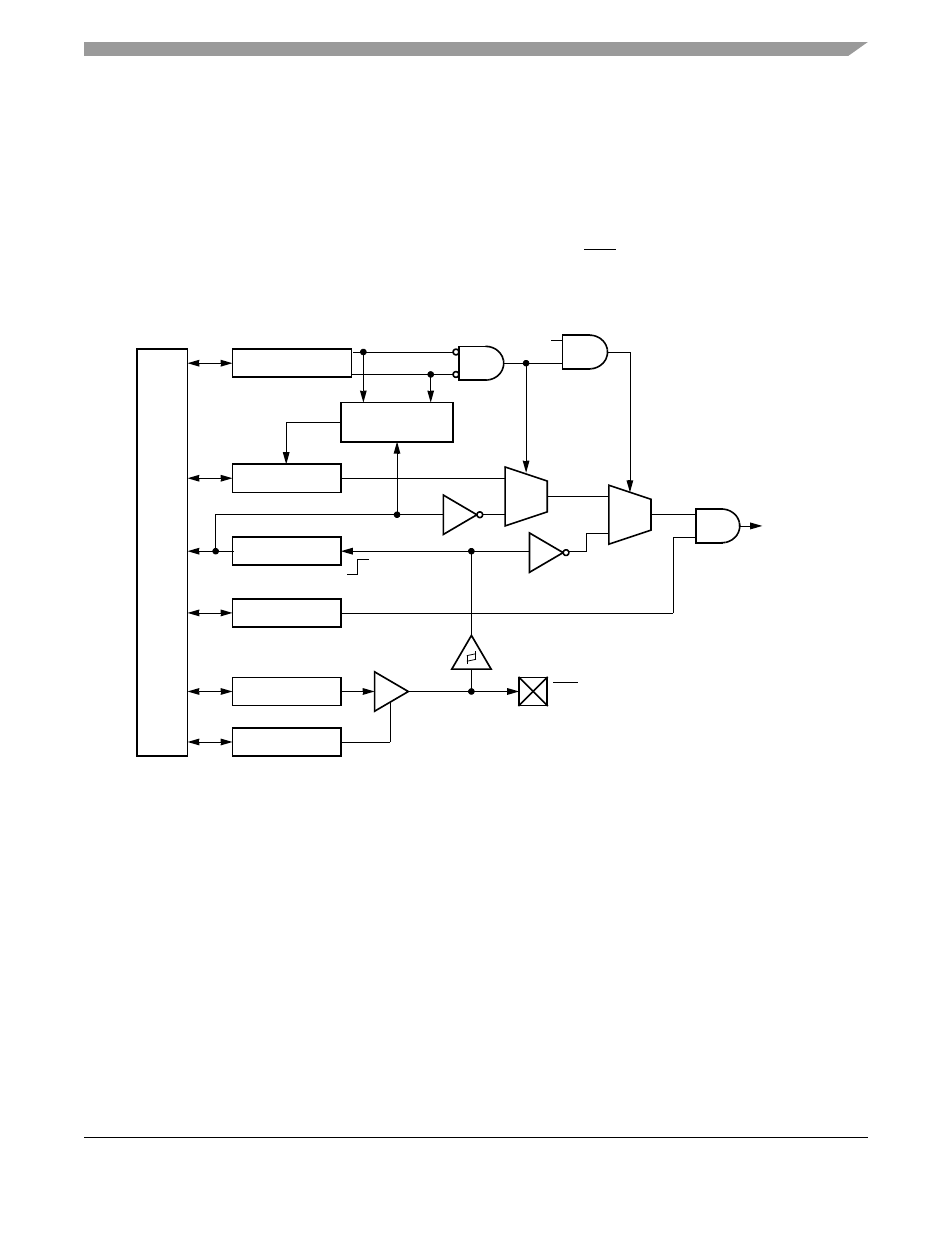
The edge port module (EPORT) has seven external interrupt pins, IRQ[7:1].
Each pin can be configured
individually as a level-sensitive interrupt pin, an edge-detecting interrupt pin (rising edge, falling edge, or
both), or a general-purpose input/output (I/O) pin. See
.
Figure 14-1. EPORT Block Diagram
14.2
Interrupt/General-Purpose I/O Pin Descriptions
All interrupt pins default to general-purpose input pins at reset. The pin value is synchronized to the rising
edge of the internal clock when read from the EPORT pin data register (EPPDR). The values used in the
edge/level detect logic are also synchronized to the rising edge of the internal clock. These pins use
Schmitt-triggered input buffers which have built-in hysteresis that decrease the probability of generating
false edge-triggered interrupts for slow rising and falling input signals.
When a pin is configured as an output, it is driven to a state whose level is determined by the corresponding
bit in the EPORT data register (EPDR). All bits in the EPDR are high at reset.
Inter
nal Bus
Synchronizer
EPDRn
EPFRn
EPPAR[2n, 2n + 1]
EPIERn
Edge Detect
D0
Stop
Logic
EPPDRn
D1
Q
D0
D1
Q
Mode
EPDDRn
To Interrupt
Controller
IRQn PIN
Rising Edge
of System Clock
