Difference matte effect – Adobe After Effects User Manual
Page 484
Note:
2. Choose Lab, YUV, or RGB from the Color Space menu. If you have trouble isolating the subject using one color space, try using a different
one.
3. Select the Key Color eyedropper, and then click in the matte thumbnail to select the area that corresponds to a color in the Composition
panel you want to make transparent. Typically, this first color is the one that covers the largest area of the image.
To use the eyedroppers in the Layer panel, choose Color Range from the View menu in the Layer panel.
4. Select the plus eyedropper, and then click other areas in the matte thumbnail to add other colors or shades to the range of colors keyed out
for transparency.
5. Select the minus eyedropper, and then click areas in the matte thumbnail to subtract other colors or shades from the range of colors keyed
out.
6. Drag the Fuzziness slider to soften the edges between transparent and opaque regions.
7. Use the sliders in the Min and Max controls to fine-tune the color range you selected with the plus and minus eyedroppers. The L, Y, R
sliders control the first component of the specified color space; the a, U, G sliders control the second component; and the b, V, B sliders
control the third component. Drag the Min sliders to fine-tune the beginning of the color range. Drag the Max sliders to fine-tune the end of
the color range.
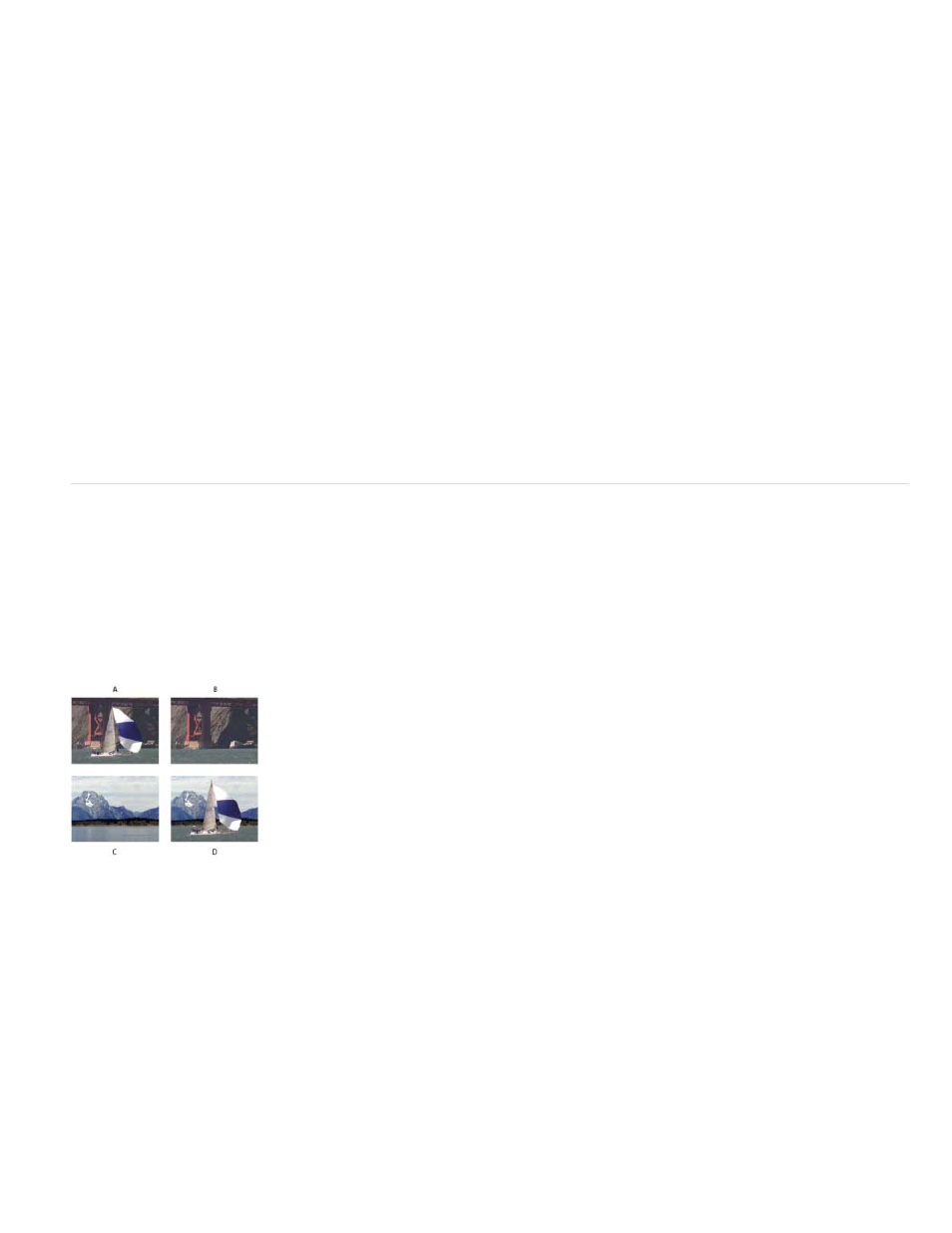
Difference Matte effect
The Difference Matte effect creates transparency by comparing a source layer with a difference layer, and then keying out pixels in the source
layer that match both the position and color in the difference layer. Typically, it’s used to key out a static background behind a moving object,
which is then placed on a different background. Often the difference layer is simply a frame of background footage (before the moving object has
entered the scene). For this reason, the Difference Matte effect is best used for scenes that have been shot with a stationary camera and an
unmoving background.
This effect works with 8-bpc and 16-bpc color.
Difference Matte Key effect
A. Original image B. Background image C. New background image D. Final composite image
Use the Difference Matte effect
1. Select a motion footage layer as the source layer.
2. In the source layer, find a frame that consists only of background, and save the background frame as an image file. (See Render and export
a single frame of a composition.)
3. Import the image file into After Effects, and add it to the composition.
480
